通过构建天气应用程序学习 React
反应
天气应用程序
反应
在我之前的文章中,我讨论了 React 及其在 Web 应用程序开发领域的重要性。在本文中,你将学习如何通过构建 Web 应用程序来使用 React。
入门
我们已经了解了如何使用 React 启动一个新项目。那么,让我们使用以下命令开始:npx create-react-app weather-app
安装完成后,使用 进入项目目录cd weather-app。
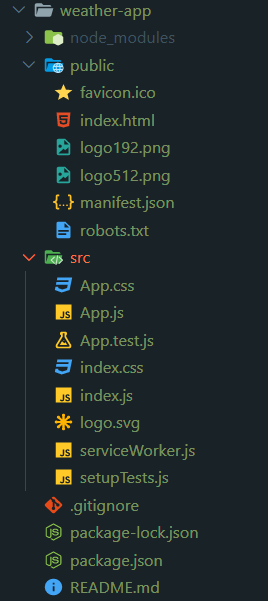
了解项目的结构
执行上述命令后,您的项目文件夹将如下所示:
我们不必担心此文件夹中的大多数文件。真正重要的是 index.html、App.js、index.css 和 index.js 文件。目前,所有我们想要渲染到屏幕上的内容都写入 App.js 文件(样式在 index.css 中),该文件会被传递给 index.js,index.js 会在 index.html 中 id 为“root”的 div 标签中渲染 App 组件,并最终将其显示在屏幕上。呼!好吧,这就是 React 的工作原理:将结构分解成组件,在需要的地方使用,最后将其传递给 html 文件。太棒了!
天气应用程序
请按照以下步骤构建一个精彩的天气应用程序:
-
在OpenWeatherMap注册并获取 API 密钥。
-
在 src 文件夹中创建一个名为“keys.js”的文件,并使用您的 api 密钥将它们放在此文件中,如下所述。
module.exports = {
API_KEY: "<your-api-key-here>",
BASE_URL: "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/",
};
- 将这段代码复制粘贴到你的 App.js 中:
import React, { useState } from "react";
import keys from "./keys";
const api = {
key: keys.API_KEY,
base: keys.BASE_URL,
};
function App() {
const dateBuild = (d) => {
let date = String(new window.Date());
date = date.slice(3, 15);
return date;
};
const [query, setQuery] = useState("");
const [weather, setWeather] = useState({});
const search = (e) => {
if (e.key === "Enter") {
fetch(`${api.base}weather?q=${query}&units=metric&APPID=${api.key}`)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((result) => {
setQuery("");
setWeather(result);
console.log(result);
});
}
};
return (
<div
className={
typeof weather.main != "undefined"
? weather.main.temp > 18
? "App hot"
: "App cold"
: "App"
}
>
<main>
<div className="search-container">
<input
type="text"
placeholder="Search..."
className="search-bar"
onChange={(e) => setQuery(e.target.value)}
value={query}
onKeyPress={search}
/>
</div>
{typeof weather.main != "undefined" ? (
<div>
<div className="location-container">
<div className="location">
{weather.name}, {weather.sys.country}
</div>
<div className="date"> {dateBuild(new Date())}</div>
</div>
<div className="weather-container">
<div className="temperature">
{Math.round(weather.main.temp)}°C
</div>
<div className="weather">{weather.weather[0].main}</div>
</div>
</div>
) : (
""
)}
</main>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
- 然后,将其复制到您的 index.css 文件中:
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: "Ubuntu", sans-serif;
}
.App {
background-image: linear-gradient(
to right,
rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.52),
rgba(0, 195, 255, 0.73)
),
url("img/app.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
transition: 0.2s ease;
}
.App.hot {
background-image: linear-gradient(
to bottom,
rgba(255, 16, 16, 0.52),
rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.73)
),
url("img/hot.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
transition: 0.2s ease;
}
main {
min-height: 100vh;
padding: 25px;
}
.App.cold {
background-image: linear-gradient(
to bottom,
rgba(0, 255, 213, 0.52),
rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.73)
),
url("img/cold.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
transition: 0.2s ease;
}
.search-container {
width: 100%;
margin: 0 0 75px;
}
.search-bar {
color: black;
font-size: 15px;
display: block;
width: 100%;
padding: 15px;
border: none;
outline: none;
appearance: none;
border-radius: 15px 15px 15px 15px;
box-shadow: 0px 5px rgba(58, 53, 53, 0.73);
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.52);
transition: 0.4s ease;
}
.search-container .search-bar:focus {
background-color: white;
}
.location-container {
color: white;
font-size: 30px;
text-align: center;
text-shadow: 3px 3px rgba(58, 53, 53, 0.73);
}
.location-container .date {
color: white;
font-size: 20px;
text-align: center;
text-shadow: 3px 3px rgba(58, 53, 53, 0.73);
}
.weather-container {
text-align: center;
}
.weather-container .temperature {
color: white;
position: relative;
display: inline-block;
margin: 30px auto;
padding: 15px 25px;
font-size: 100px;
font-weight: 700;
background-color: rgb(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
border-radius: 16px;
box-shadow: 3px 3px rgba(58, 53, 53, 0.73);
text-shadow: 3px 3px rgba(58, 53, 53, 0.73);
}
.weather-container .weather {
color: white;
font-size: 50px;
font-weight: 700;
text-shadow: 3px 3px rgba(58, 53, 53, 0.73);
}
解释
我知道你对代码感到不知所措,但是一旦我为你分解它,一切都会变得非常清晰。
HTML:仅关注 App.js 文件的 HTML 元素。这些 HTML div 包括搜索框、要显示的位置、温度和流行情况。
CSS:我们将为这些 div 元素分配一个类名,以便它们在 CSS 文件中被赋予必要的样式。
(注:先决条件是了解一点 HTML 和 CSS。)
日期函数:在处理日期的 div 类中,我们确保调用一个名为“dateBuild”的函数。JavaScript 中的这个“dateBuild”函数以字符串格式获取日期。然后,我们使用 slice() 函数提取当前的月份、日期和年份。
API 获取和 Hooks:我们利用 React 的“useState”Hook 来更改屏幕上呈现内容的状态。一个 Hook 用于搜索栏值,另一个 Hook 用于显示内容。
在处理搜索栏的 div 中,当用户按下“Enter”键时,我们会调用一个名为“search”的函数。在此函数中,我们使用凭证和查询请求 URL 来从服务器获取数据,然后更改屏幕上显示内容的状态。因此,useState Hook 在 React 的状态管理中至关重要。
动态背景:这只是一个简单的逻辑,用来展示 React 中 JSX 的强大功能。在我之前的文章中,我提到过 JSX 是 React 的一项重要特性,它结合了 JavaScript 和 HTML 的强大功能。这个动态背景功能可以让应用程序更加时尚。在渲染整个应用程序的类中,我们只需添加一个条件来检查获取的温度是否大于某个限值。如果是,则向 div 标签添加一个不同的类名,以更改屏幕的背景。同样,可以应用许多这样的条件,将各种天气场景作为背景显示。
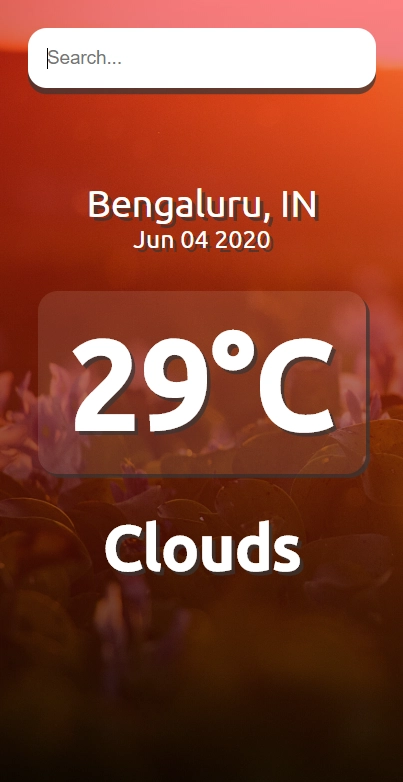
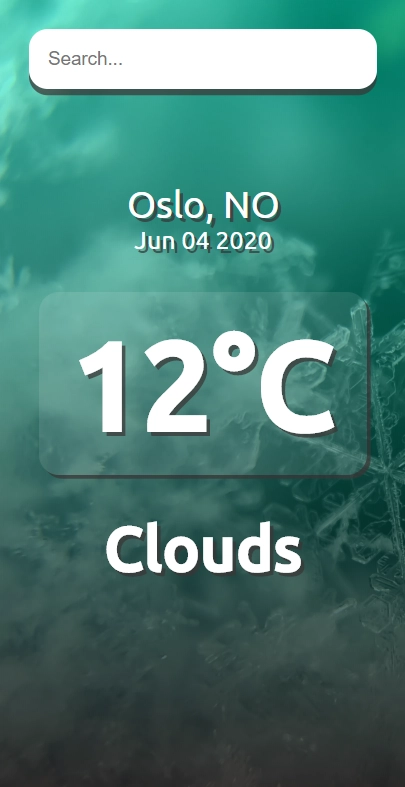
结果
如果您已经了解该应用程序的工作原理,那么请继续进入npm start您的终端以启动并运行该应用程序。
好了,您已经创建了一个令人惊叹的天气应用程序,它可以让您随时了解千里之外城市的天气状况。
感谢您阅读本文,如有任何疑问,请随时通过LinkedIn联系我。整个项目可在GitHub上获取。
文章来源:https://dev.to/kgprajwal/learn-react-by-building-a-weather-app-3229 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com