通过构建一个极简电商购物应用来了解 React Context API 的工作原理
所以,这是一个我考虑了一段时间的项目,但我并没有花太多心思或精力去构建它。
然后Hashnode 的 Writeathon出现了,我想,这是一个写这篇文章的绝佳机会,它既能帮助我提升 React 知识,也能帮助其他初次学习 React 或想复习 React 知识的开发者。双赢!
在本文中,您将了解 React Context API、它如何解决 prop 钻孔,以及我如何构建具有以下功能的简单购物应用程序:
- 存储当前项目
- 当用户点击“添加到购物车”按钮时更新上下文
- 在导航栏中显示购物车数量
- 在购物车中添加和删除商品
- 将购物车商品保存到本地存储
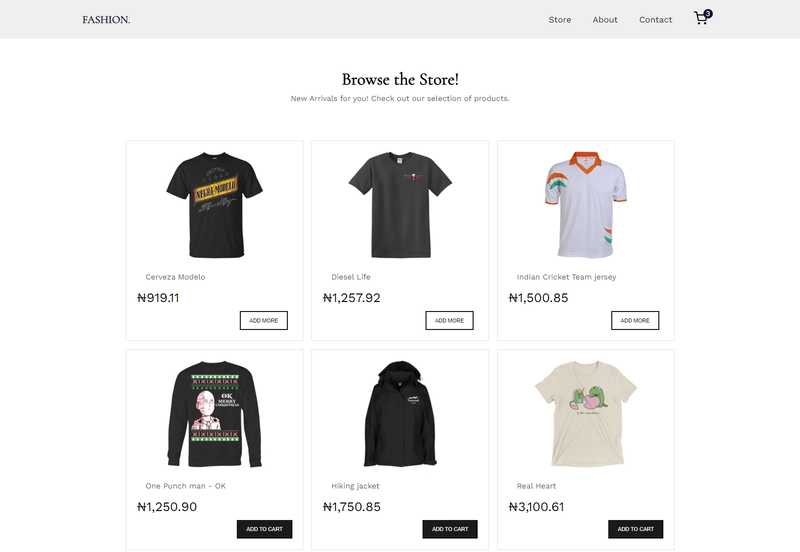
下面是我们将要构建的内容的屏幕截图:
如果看起来不错,那我们就开始吧!
先决条件
本文假设您已:
React Context 概述
什么是 React Context?
React Context 是一种将数据(和函数)从父组件传递到子组件的方法,通过将数据存储在存储中(类似于Redux),您可以从那里轻松访问数据并将其导入到您选择的任何组件中。
这是prop drilling的一个更好的替代方案,prop drilling 是一个术语,用于描述数据通过多层组件传递,即使这些组件实际上不需要这些数据。
何时使用 Context?
上下文旨在共享可视为“全局”的数据,供整个应用使用。例如,当前已验证的用户、主题或用户偏好设置(例如,语言或区域设置)。
“上下文主要用于当某些数据需要被不同嵌套级别的多个组件访问时。请谨慎使用它,因为它会使组件重用更加困难。”
来源:官方文件
构建电子商务 Web 应用程序
插图
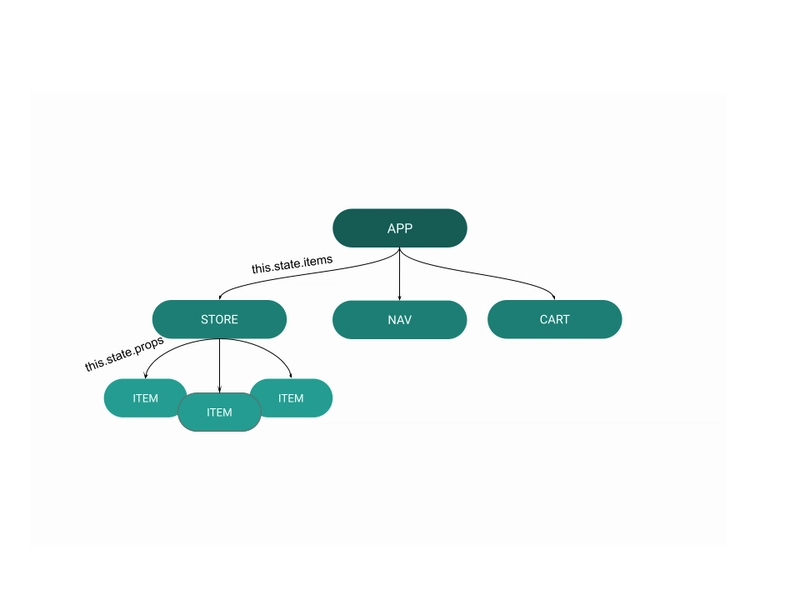
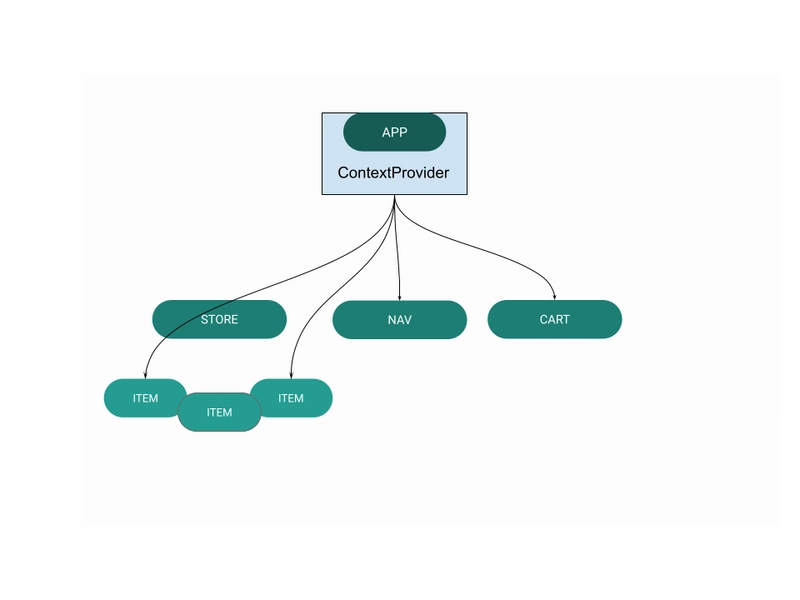
在我们进入代码之前,让我们看一下组件层次结构,以便更好地理解应用程序组件之间的关系。
下图显示了数据如何从根组件级别()传递App到渲染要显示内容的组件(items)。
然而,我们在应用中要用到的是 Context 所解决的问题:
如你所见,Context 就像你应用中的存储区。一旦设置完成,你就可以简单地将其导入到任何需要该数据的组件中。
现在我们已经了解了 React Context 的基本概述,让我们直接进入项目。
项目设置
让我们先创建一个新的 React 项目。在本教程中,我将使用 Vite。如果你还没听说过它,可以看看我之前的文章。
当然,您可以随意使用您选择的捆绑器:Vite 或 CRA。
# vite
npm init vite@latest react-shopping-cart --template react
# create react app
npx create-react-app react-shopping-cart
完成后,运行:
cd react-shopping-cart
npm install
我们将使用的依赖项:
npm install react-router-dom@6
npm install --save styled-components
注意:我们不会介绍样式以保持代码简洁;这只是为了解释应用程序的工作原理。
此外,我在代码中添加了一些注释,以便您了解它们的用途。
上下文设置
在通常需要上下文的复杂应用程序中,可以存在多个上下文,每个上下文都有其数据和功能,这些内容和功能与需要这些数据和功能的组件集有关。
例如,可以有一个ProductContext组件用于处理使用与产品相关的数据的组件,另一个组件ProfileContext用于处理与身份验证和用户数据相关的数据。
但是,为了使事情尽可能简单,我们将只使用一个上下文实例。
在该src目录中,创建三个文件夹:Context、components和pages。
在文件夹内Context创建另一个文件夹Cart。
导航到该Cart文件夹并将以下内容添加到新文件CartTypes.js。
// /src/Context/Cart/CartTypes.js`:
export const ADD_TO_CART = "ADD_TO_CART";
export const REMOVE_ITEM = "REMOVE_ITEM";
export const INCREASE = "INCREASE";
export const DECREASE = "DECREASE";
export const CHECKOUT = "CHECKOUT";
export const CLEAR = "CLEAR";
在这里,我们定义上下文应该具有的动作类型,并导出它们以在上下文中使用。
接下来,将以下内容添加到同一目录中的新文件CartContext.jsx中以创建上下文:
import { createContext } from "react";
const CartContext = createContext();
export default CartContext;
CartState.jsx接下来,在文件夹中创建一个新文件Cart。添加以下代码:
import { useReducer } from "react";
import CartContext from "./CartContext";
import CartReducer from "./CartReducer";
import { sumItems } from "./CartReducer";
const CartState = ({ children }) => {
// Initial State of the cart
const initialState = {
cartItems: [],
checkout: false,
};
//Set up the reducer
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(CartReducer, initialState);
//Function to handle when an item is added from the store into the Cart
const addToCart = (payload) => {
dispatch({ type: "ADD_TO_CART", payload });
};
//Function to handle when an item that is in the cart is added again
const increase = (payload) => {
dispatch({ type: "INCREASE", payload });
};
//Function to handle when an item is removed from the cart
const decrease = (payload) => {
dispatch({ type: "DECREASE", payload });
};
//Function to remove an item from the cart
const removeFromCart = (payload) => {
dispatch({ type: "REMOVE_ITEM", payload });
};
//Function to clear the cart
const clearCart = () => {
dispatch({ type: "CLEAR" });
};
//Function to handle when the user clicks the checkout button
const handleCheckout = () => {
dispatch({ type: "CHECKOUT" });
};
return (
//Add the functions that have been defined above into the Context provider, and pass on to the children
<CartContext.Provider
value={{
showCart: state.showCart,
cartItems: state.cartItems,
addToCart,
removeFromCart,
increase,
decrease,
handleCheckout,
clearCart,
...state,
}}
>
{children}
</CartContext.Provider>
);
};
export default CartState;
让我们将上面的代码分解成几部分。
首先,导入的useReducer(state, dispatch) => newState hook 接受一个类型为 的 reducer ,然后返回当前状态。我们还导入了上下文文件:CartContext和CartReducer。
其次,initialItems是一个定义页面加载时购物车初始状态的数组。
第三,在中CartContext.Provider,将渲染传递给它的所有道具并将其通过其传递children。
value提供程序的工作方式是,当前上下文值由near 的 prop决定<CartContext.Provider>,当它更新时,useContext钩子将触发重新渲染,并将最新的上下文值传递给CartContext提供程序。
接下来,创建一个新文件CartReducer.jsx,并添加以下代码:
// /src/Context/Cart/CartReducer.jsx
//Import the Action types
import {
REMOVE_ITEM,
ADD_TO_CART,
INCREASE,
DECREASE,
CHECKOUT,
CLEAR,
} from "./CartTypes.js";
// Export function to calculate the total price of the cart and the total quantity of the cart
export const sumItems = (cartItems) => {
Storage(cartItems);
let itemCount = cartItems.reduce(
(total, product) => total + product.quantity,
0
);
let total = cartItems
.reduce((total, product) => total + product.price * product.quantity, 0)
.toFixed(2);
return { itemCount, total };
};
// The reducer is listening for an action, which is the type that we defined in the CartTypes.js file
const CartReducer = (state, action) => {
// The switch statement is checking the type of action that is being passed in
switch (action.type) {
// If the action type is ADD_TO_CART, we want to add the item to the cartItems array
case ADD_TO_CART:
if (!state.cartItems.find((item) => item.id === action.payload.id)) {
state.cartItems.push({
...action.payload,
quantity: 1,
});
}
return {
...state,
...sumItems(state.cartItems),
cartItems: [...state.cartItems],
};
// If the action type is REMOVE_ITEM, we want to remove the item from the cartItems array
case REMOVE_ITEM:
return {
...state,
...sumItems(
state.cartItems.filter((item) => item.id !== action.payload.id)
),
cartItems: [
...state.cartItems.filter((item) => item.id !== action.payload.id),
],
};
// If the action type is INCREASE, we want to increase the quantity of the particular item in the cartItems array
case INCREASE:
state.cartItems[
state.cartItems.findIndex((item) => item.id === action.payload.id)
].quantity++;
return {
...state,
...sumItems(state.cartItems),
cartItems: [...state.cartItems],
};
// If the action type is DECREASE, we want to decrease the quantity of the particular item in the cartItems array
case DECREASE:
state.cartItems[
state.cartItems.findIndex((item) => item.id === action.payload.id)
].quantity--;
return {
...state,
...sumItems(state.cartItems),
cartItems: [...state.cartItems],
};
// If the action type is CHECKOUT, we want to clear the cartItems array and set the checkout to true
case CHECKOUT:
return {
cartItems: [],
checkout: true,
...sumItems([]),
};
//If the action type is CLEAR, we want to clear the cartItems array
case CLEAR:
return {
cartItems: [],
...sumItems([]),
};
//Return the state if the action type is not found
default:
return state;
}
};
export default CartReducer;
现在我们已经完成了上下文的设置,下一步就是将其包装在App里面Context。
为此,请导航到根目录中的main.jsx(Vite) 或index.js(CRA)。添加以下代码:
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client";
import App from "./App";
import "./index.css";
import CartState from "./Context/Cart/CartState";
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<CartState>
<App />
</CartState>
</React.StrictMode>
);
所以,现在我们的整个应用程序都可以访问 Context。
构建组件
对于App.jsx,我们将添加处理应用程序导航的代码。
import Navbar from "./components/Navbar";
import Store from "./pages/Store";
import About from "./pages/About";
import { BrowserRouter, Routes, Route } from "react-router-dom";
import Cart from "./pages/Cart";
function App() {
return (
<>
<BrowserRouter>
<Navbar />
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Store />} />
<Route exact path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route exact path="/cart" element={<Cart />} />
</Routes>
</BrowserRouter>
</>
);
}
export default App;
现在,让我们创建应用程序基本导航正常运行所需的组件。
Navbar.jsx在文件夹中创建一个新文件components,并添加以下内容:
// General
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
import { Link, NavLink } from "react-router-dom";
import CartIcon from "/assets/icons/cart.svg";
import styled from "styled-components";
import CartContext from "../Context/Cart/CartContext";
import { useContext } from "react";
const Navbar = () => {
const [toggle, setToggle] = useState(false);
const [innerWidth, setInnerWidth] = useState(window.innerWidth);
// Get Screen Size
useEffect(() => {
const changeWidth = () => {
setInnerWidth(window.innerWidth);
};
window.addEventListener("resize", changeWidth);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener("resize", changeWidth);
};
}, []);
// Extract itemscount from CartContext
const { cartItems } = useContext(CartContext);
return (
<Nav>
<NavContainer>
<Left>
<Link to={"/"}>FASHION.</Link>
</Left>
<Right>
<NavRightContainer
style={{
transform:
innerWidth <= 500
? toggle && "translateY(100vh)"
: "translateY(0%)",
}}
>
<NavList>
<NavItem>
<NavLink to="/" onClick={() => setToggle(!toggle)}>
Store
</NavLink>
</NavItem>
<NavItem>
<NavLink to="/about" onClick={() => setToggle(!toggle)}>
About
</NavLink>
</NavItem>
<NavItem>
<a href="https://twitter.com/israelmitolu" target="_blank">
Contact
</a>
</NavItem>
<NavItem>
<Link to="/cart" onClick={() => setToggle(!toggle)}>
<p>Cart</p>
<NavCartItem>
<img src={CartIcon} alt="Shopping cart" />
{/* If the number of cartItems is greater than 0, display the
number of items in the cart */}
{cartItems.length > 0 && (
<CartCircle>{cartItems.length}</CartCircle>
)}
</NavCartItem>
</Link>
</NavItem>
</NavList>
</NavRightContainer>
<MenuBtn onClick={() => setToggle(!toggle)}>
<span></span>
<span></span>
<span></span>
</MenuBtn>
</Right>
</NavContainer>
</Nav>
);
};
上面的代码设置了导航栏,它看起来如下:
pages在目录中的文件夹中src,创建Store.jsx、Cart.jsx和About.jsx。
对于Store.jsx
import { products } from "../data";
import styled from "styled-components";
import ProductCard from "../components/ProductCard";
const Store = () => {
return (
<>
<Heading>
<h1>Browse the Store!</h1>
<p>New Arrivals for you! Check out our selection of products.</p>
</Heading>
<ProductsContainer>
{products.map((product) => (
<ProductCard key={product.id} product={product} />
))}
</ProductsContainer>
</>
);
};
export default Store;
包含产品卡,这些产品卡是通过从文件导出的Store可用数组映射动态生成的:productsdata.js
export const products = [
{
id: 1,
name: "Cerveza Modelo",
price: 919.11,
image: "/assets/img/1.png",
},
{
id: 2,
name: "Diesel Life",
price: 1257.92,
image: "/assets/img/2.png",
},
{
id: 3,
name: "Indian Cricket Team jersey",
price: 1500.85,
image: "/assets/img/3.png",
},
{
id: 4,
name: "One Punch man - OK",
price: 1250.9,
image: "/assets/img/4.png",
},
{
id: 5,
name: "Hiking jacket",
price: 1750.85,
image: "/assets/img/5.png",
},
{
id: 6,
name: "Real Heart",
price: 3100.61,
image: "/assets/img/6.png",
},
{
id: 7,
name: "Fredd - Black and White",
price: 1801.1,
image: "/assets/img/7.png",
},
{
id: 8,
name: "Star Wars - The Last",
price: 1199.99,
image: "/assets/img/8.png",
},
{
id: 9,
name: "Yellow Blouse",
price: 2395.16,
image: "/assets/img/9.png",
},
{
id: 10,
name: "Rick and Morty - Supreme",
price: 1243.82,
image: "/assets/img/10.png",
},
];
该ProductCard组件显示每种产品的产品详细信息。
请注意,我们将在所有需要存储在上下文中的数据的组件中导入 useContext 和 CartContext。
onClick按钮中的事件处理我们从 CartContext 中提取的函数addToCart:increase
import styled from "styled-components";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
import { formatCurrency } from "../utils";
import CartContext from "../Context/Cart/CartContext";
import { useContext } from "react";
const ProductCard = ({ product }) => {
// Extract these functions from the CartContext
const { addToCart, increase, cartItems, sumItems, itemCount } =
useContext(CartContext);
//Check whether the product is in the cart or not
const isInCart = (product) => {
return !!cartItems.find((item) => item.id === product.id);
};
return (
<CardWrapper>
<ProductImage
src={product.image + "?v=" + product.id}
alt={product.name}
/>
<ProductName>{product.name}</ProductName>
<ProductCardPrice>{formatCurrency(product.price)}</ProductCardPrice>
<ProductCardButtons>
{isInCart(product) && (
<ButtonAddMore
onClick={() => {
increase(product);
}}
className="btn"
>
Add More
</ButtonAddMore>
)}
{!isInCart(product) && (
<Button onClick={() => addToCart(product)}>Add to Cart</Button>
)}
</ProductCardButtons>
</CardWrapper>
);
};
对于下面的代码,我们将提取组件所需的状态和函数Cart,它们是:cartItems,checkout和clearCart。
然后,如果数组中有任何项目cartItems,则将这些项目作为CartItem组件呈现到页面:
import CartItem from "../components/CartItem";
import { useContext } from "react";
import CartContext from "../Context/Cart/CartContext";
import styled from "styled-components";
import Checkout from "../components/Checkout";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
const Cart = () => {
// Extract the functions from the Context
const { cartItems, checkout, clearCart } = useContext(CartContext);
return (
<>
<Heading>
<h1>
Shopping Cart
<span>({cartItems.length})</span>
</h1>
</Heading>
{/* Show the checkout message when the Checkout Button has been clicked */}
{checkout && (
<CheckoutMsg>
<h4>Thank you for your purchase!</h4>
<p>
Your order has been placed and will be delivered to you within 24
hours.
</p>
<Link to="/">
<ShopBtn onClick={clearCart}>Continue Shopping</ShopBtn>
</Link>
</CheckoutMsg>
)}
<Layout>
<div>
{
<CartItemWrapper>
{/* If cart is empty, display message, and if not, display each cart
Item in cart: {cartItems.length} */}
{cartItems.length === 0 ? (
<h4 style={{}}>Cart is empty</h4>
) : (
<ul>
{cartItems.map((product) => (
<CartItem key={product.id} product={product} />
))}
</ul>
)}
</CartItemWrapper>
}
</div>
<div>
{/* Checkout component */}
{cartItems.length > 0 && <Checkout />}
</div>
</Layout>
</>
);
};
该CartItem组件包含当前状态下存在的项目。并且,我们将从中提取一些函数,CartContext即:removeFromCart和:increasedecrease
import { useContext } from "react";
import CartContext from "../Context/Cart/CartContext";
import styled from "styled-components";
import { formatCurrency } from "../utils";
import TrashIcon from "/assets/icons/trash-outline.svg";
import Plus from "/assets/icons/add-circle-outline.svg";
import Minus from "/assets/icons/remove-circle-outline.svg";
const CartItem = ({ product }) => {
const { removeFromCart, increase, decrease } = useContext(CartContext);
return (
<SingleCartItem>
<CartImage src={product.image} alt={product.name} />
<div>
<h5>{product.name}</h5>
<p>{formatCurrency(product.price)}</p>
</div>
{/* Buttons */}
<BtnContainer>
<button
onClick={() => increase(product)}
className="btn btn-primary btn-sm mr-2 mb-1"
>
<Icon src={Plus} alt="" />
</button>
<div>
<p>Qty: {product.quantity}</p>
</div>
{/* Display a minus icon or trash/delete icon based on the quantity of a particular product is in the cart */}
{product.quantity > 1 && (
<button onClick={() => decrease(product)} className="btn">
<Icon src={Minus} alt="" />
</button>
)}
{product.quantity === 1 && (
<button onClick={() => removeFromCart(product)} className="btn">
<Icon src={TrashIcon} alt="" />
</button>
)}
</BtnContainer>
</SingleCartItem>
);
};
添加购物车管理
现在我们可以添加、删除和显示产品了,最后要做的就是实现购物车管理。我们已经在 中将购物车初始化为一个空数组CartState.jsx,这意味着一旦我们重新启动应用程序,它将恢复为空。
现在,我们要做的是确保在组件加载时从本地存储加载现有的购物车。
更新initialState方法CartState.jsx如下:
const initialState = {
cartItems: storage,
...sumItems(storage),
checkout: false,
};
接下来,我们需要定义storage,同样在CartContext.jsx:
//Local Storage
const storage = localStorage.getItem("cartItems")
? JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("cartItems"))
: [];
最后,在中CartReducer.jsx,我们将定义Storage:
const Storage = (cartItems) => {
localStorage.setItem(
"cartItems",
JSON.stringify(cartItems.length > 0 ? cartItems : [])
);
};
并导出计算购物车总价和购物车总数量的函数
export const sumItems = (cartItems) => {
Storage(cartItems);
let itemCount = cartItems.reduce(
(total, product) => total + product.quantity,
0
);
let total = cartItems
.reduce((total, product) => total + product.price * product.quantity, 0)
.toFixed(2);
return { itemCount, total };
};
至此,我们成功完成了购物应用程序的实施。
结论
完成了!
在本文中,我们讨论了 Context 及其用法,并使用 React 搭建了一个极简购物应用的界面。我们还使用 context 在多个组件之间移动数据和方法,并使用useReducer和添加了它的功能dispatch。
如果您觉得这篇文章有用(我相信您确实觉得有用),请与您的朋友和同事分享,并关注我以获取更多内容。如果您有任何疑问或发现任何错误或拼写错误,请在评论区留下您的反馈。
感谢您的阅读,祝您编码愉快!
文章来源:https://dev.to/israelmitolu/learn-how-react-context-api-works-by-building-a-minimal-ecommerce-shopping-app-2479 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com