在 React 中上传文件并保持 UI 完全同步
在Medium上找到我。
构建文件上传组件是一项非常重要的技能,因为它允许用户在本地环境之外选择和发送文件。
话虽如此,本文重点介绍 JavaScript 中的原生文件API。如果您想进一步了解文件 API 的工作原理,请点击此处。
一开始,构建文件上传组件可能比较难掌握,尤其是当你想自定义它的外观和感觉的时候。(我们可以在以后的教程中讨论如何自定义文件输入组件的设计)。但一旦你很好地理解了这些概念,其实并没有那么难!
我的意思是,你可以创建一个文件输入元素,传入 onChange 事件,然后就完事了。但是,你会通过每次都向用户展示流程的当前状态来照顾用户吗?还是你只是让他们坐在那里,希望他们看到流程的结束,中间没有任何视觉更新?
如果用户的网络断线了怎么办?如果服务器没有任何响应怎么办?如果14个文件里第8个文件对他们来说太大怎么办?如果用户等待上传过程10分钟才完成,想看看进度如何?或者哪些文件已经上传完毕怎么办?
如果希望用户体验保持一致,就必须让用户持续了解后台运行情况。专业且一致的用户界面有助于从技术角度建立用户对你应用的信任。如果你计划开发一款用户注册并付费使用你提供的服务的应用,那么他们必须信任你提供的技术,并且相信你的技术比其他任何人都更优秀。你正在使用 React 进行开发,你拥有超越一切的力量!
但我该从哪里开始呢?
别担心!这篇文章将教你如何创建一个包含文件上传组件的用户界面,帮助用户选择文件并将其发送到某个位置,同时允许界面从实例化到最终状态更新。创建组件是一回事,但在整个过程中让 UI 与状态更新同步又是另一回事。
让我们开始吧!
在本教程中,我们将使用create-react-app快速生成一个 React 项目。
继续使用以下命令创建一个项目。在本教程中,我将其命名为file-upload-with-ux。
npx create-react-app file-upload-with-ux
完成后进入目录:
cd file-upload-with-ux
我们要做的第一件事是打开App.js并用我们自己的实现替换默认代码:
src/App.js
import React from 'react'
import './App.css'
const Input = (props) => (
<input type='file' name='file-input' multiple {...props} />
)
const App = () => {
const onSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
}
const onChange = (e) => {
console.log(e.target.files)
}
return (
<div className='container'>
<form className='form' onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<div>
<Input onChange={onChange} />
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
)
}
export default App
在这里,我们定义了一个表单元素并传递了一个onSubmit处理程序,以便我们可以访问用户提交后选择的所有文件。
在表单内部,我们定义了文件输入组件,允许用户选择任意文件。输入组件接收一个onChange处理函数,因此我们也将其传入。onChange 处理函数可以通过访问第一个参数中的e.target.files来接收文件。
我在里面应用了一些基本样式App.css。您可以选择使用它们,也可以跳过此步骤:
应用程序.css
.container {
padding: 8px;
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
.form {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.form input,
button {
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.form button {
padding: 8px 17px;
border: 0;
color: #fff;
background: #265265;
cursor: pointer;
}
.form button:hover {
background: #1e3d4b;
}
至此,我们已经设置好了基本组件,并设置好了相应的处理程序。现在,我们将创建一个自定义的 React Hook,以便将所有繁琐的状态逻辑都放在里面,远离 UI 组件。
我要这样称呼它useFileHandlers.js:
src/useFileHandlers.js
import React from 'react'
const initialState = {
files: [],
pending: [],
next: null,
uploading: false,
uploaded: {},
status: 'idle',
}
const useFileHandlers = () => {
return {}
}
export default useFileHandlers
整篇文章最重要的部分可能是上面显示的initialState。它使得 UI 能够捕捉文件上传过程的每个时刻。
files是用户最初通过从文件输入中选择文件来加载文件数组的地方。
pending将用于让 UI 知道当前正在处理哪个文件以及还剩下多少个文件。
当代码检测到已准备好执行此操作时,next将被分配待处理数组中的下一个项目。
上传将用于让代码知道文件仍在上传。
uploaded将是文件上传完成后我们插入到的对象。
最后,提供状态作为额外的便利,主要是为了用户界面充分利用其优势。
我们将使用来自 react 的useReducer hook api,因为它非常适合我们的用途。
但首先,让我们在useFileHandlers钩子上方定义一些常量,以确保稍后应用状态更新时不会输入错误:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const LOADED = 'LOADED'
const INIT = 'INIT'
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FILES_UPLOADED = 'FILES_UPLOADED'
const UPLOAD_ERROR = 'UPLOAD_ERROR'
这些将进入作为useReducer第一个参数传入的reducer。
现在定义减速器:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
default:
return state
}
}
我们现在可能不应该忘记从 react导入useReducer ,是吗?
src/useFileHandlers.js
import { useReducer } from 'react'
现在将 state/dispatch api 定义到钩子中:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const useFileHandlers = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState)
return {}
}
export default useFileHandlers
现在我们将回到之前设置的onChange实现并进一步增强它。
在执行此操作之前,让我们在 Reducer 中添加一个新的 Switch Case:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
default:
return state
}
}
这将允许 onChange 处理程序在调用时立即将文件传递到状态中:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const onChange = (e) => {
if (e.target.files.length) {
const arrFiles = Array.from(e.target.files)
const files = arrFiles.map((file, index) => {
const src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file)
return { file, id: index, src }
})
dispatch({ type: 'load', files })
}
}
这里要注意的是,当我们从事件对象中检索e.target.files时,它不是一个数组——它是一个FileList。
我们将其转换为数组的原因是,UI 组件可以映射它们并显示文件大小和文件类型等有用信息。否则,组件在尝试映射 *FileList* 时会导致应用崩溃。
到目前为止,这是我们自定义钩子的完整实现:
src/useFileHandlers.js
import { useReducer } from 'react'
// Constants
const LOADED = 'LOADED'
const INIT = 'INIT'
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FILES_UPLOADED = 'FILES_UPLOADED'
const UPLOAD_ERROR = 'UPLOAD_ERROR'
const initialState = {
files: [],
pending: [],
next: null,
uploading: false,
uploaded: {},
status: 'idle',
}
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
default:
return state
}
}
const useFileHandlers = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState)
const onChange = (e) => {
if (e.target.files.length) {
const arrFiles = Array.from(e.target.files)
const files = arrFiles.map((file, index) => {
const src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file)
return { file, id: index, src }
})
dispatch({ type: 'load', files })
}
}
return {}
}
export default useFileHandlers
现在我们将重点介绍另一个处理程序—— onSubmit。它在用户提交表单时调用(这是显而易见的)。在onSubmit处理程序内部,我们用useCallback将其包装起来,以便它始终获取最新的状态值。
src/useFileHandlers.js
import { useCallback, useReducer } from 'react'
src/useFileHandlers.js
const onSubmit = useCallback(
(e) => {
e.preventDefault()
if (state.files.length) {
dispatch({ type: 'submit' })
} else {
window.alert("You don't have any files loaded.")
}
},
[state.files.length],
)
此 onSubmit 处理程序在 onChange之后调用,因此它可以从刚刚由onChange设置的state.files中提取文件,以实例化上传过程。
为了实例化上传过程,我们需要另一个 switch case:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
case 'submit':
return { ...state, uploading: true, pending: state.files, status: INIT }
default:
return state
}
}
好的,现在发生的情况如下:
-
它将state.uploading改为true。当你将 state.uploading 改为true时,你就可以开始对 UI 组件进行破坏,并向用户显示任何你想要的内容,只要他们明白你试图向他们传达文件正在上传的信息。
-
它使用用户选择的所有文件来初始化state.pending。你也可以用它来对 UI 组件进行一些改动。状态的这一部分有很多使用方法。不过现在我先跳过这部分,因为我想先和你一起完成整个教程 :)
-
它将状态的便捷部分status设置为"INIT"。您也可以在钩子或 UI 中的某个地方使用它来触发某些 " onStart " 逻辑,或者任何您想要的操作——因为在新的上传过程开始之前,它永远不会回到这个值。
现在我们将返回状态以及 onSubmit 和 onChange 处理程序,以便 UI 可以顺利访问它们:
src/useFileHandlers.js
return {
...state,
onSubmit,
onChange,
}
src/useFileHandlers.js
接下来我们要处理的是useEffect部分。我们需要useEffect 来实现“运行到完成”的功能。
这些 useEffects 是本教程中非常重要的实现,因为它们在 UI 和自定义钩子之间创建了完美、一致的同步流——正如您稍后将看到的,它们无处不在。
src/useFileHandlers.js
import { useCallback, useEffect, useReducer } from 'react'
我们将定义我们的第一个 useEffect,它将负责在检测到准备好时立即促进下一个文件的上传(只要state.pending中仍有项目):
src/useFileHandlers.js
// Sets the next file when it detects that state.next can be set again
useEffect(() => {
if (state.pending.length && state.next == null) {
const next = state.pending[0]
dispatch({ type: 'next', next })
}
}, [state.next, state.pending])
它抓取state.pending数组中的下一个可用文件,并使用dispatch创建信号,将该文件作为下一个state.next对象发送:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
case 'submit':
return { ...state, uploading: true, pending: state.files, status: INIT }
case 'next':
return {
...state,
next: action.next,
status: PENDING,
}
default:
return state
}
}
为了方便起见,我们在此处添加了“待处理”状态。如何处理此上传过程完全由您自行决定!
下一个代码片段将显示我提供的实用函数,该函数仅用于帮助记录到控制台供您查看,仅供本教程使用。
src/useFileHandlers.js
const logUploadedFile = (num, color = 'green') => {
const msg = `%cUploaded ${num} files.`
const style = `color:${color};font-weight:bold;`
console.log(msg, style)
}
我们接下来要应用的第二个 useEffect将负责上传刚刚在状态中设置的下一个文件:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const countRef = useRef(0)
// Processes the next pending thumbnail when ready
useEffect(() => {
if (state.pending.length && state.next) {
const { next } = state
api
.uploadFile(next)
.then(() => {
const prev = next
logUploadedFile(++countRef.current)
const pending = state.pending.slice(1)
dispatch({ type: 'file-uploaded', prev, pending })
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
dispatch({ type: 'set-upload-error', error })
})
}
}, [state])
在.then()处理程序中,我创建了一个新的变量prev ,并将下一个已完成上传的对象赋值给它。这只是为了提高可读性,因为我们不想在 switch case 中混淆,稍后我们会看到。
你可能注意到了,里面有一个useRef函数。是的,我承认,我这么做了。但我这么做的原因是,我们要在我提供的logUploadedFile工具函数中使用它并进行修改。
src/useFileHandlers.js
import { useCallback, useEffect, useReducer, useRef } from 'react'
哦,如果您需要一些模拟函数来模拟代码片段中看到的“上传”承诺处理程序,您可以使用这个:
const api = {
uploadFile({ timeout = 550 ) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
}, timeout)
})
},
}
现在继续通过应用“file-uploaded”和“set-upload-error”开关情况来更新您的reducer:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
case 'submit':
return { ...state, uploading: true, pending: state.files, status: INIT }
case 'next':
return {
...state,
next: action.next,
status: PENDING,
}
case 'file-uploaded':
return {
...state,
next: null,
pending: action.pending,
uploaded: {
...state.uploaded,
[action.prev.id]: action.prev.file,
},
}
case 'set-upload-error':
return { ...state, uploadError: action.error, status: UPLOAD_ERROR }
default:
return state
}
}
对于文件上传的情况,我们将next重置为null ,以便第一个 useEffect可以再次响应它。当它响应时,它会拉取state.pending队列中的下一个文件,并将其赋值给下一个state.next值。你已经可以看到它是如何成为一个自运行的进程——一个运行到完成的实现!
无论如何,我们将刚刚上传的文件应用到state.uploaded对象,以便 UI 也能利用它。这在本教程中也是一个非常有用的功能,因为如果你正在渲染一堆缩略图,你可以在它们上传后动态地为每一行添加阴影!:) 截图在本文末尾。
第三个useEffect将负责通过向reducer发送文件上传信号来关闭上传过程:
src/useFileHandlers.js
// Ends the upload process
useEffect(() => {
if (!state.pending.length && state.uploading) {
dispatch({ type: 'files-uploaded' })
}
}, [state.pending.length, state.uploading])
将其添加到减速器中看起来是这样的:
src/useFileHandlers.js
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
case 'submit':
return { ...state, uploading: true, pending: state.files, status: INIT }
case 'next':
return {
...state,
next: action.next,
status: PENDING,
}
case 'file-uploaded':
return {
...state,
next: null,
pending: action.pending,
uploaded: {
...state.uploaded,
[action.prev.id]: action.prev.file,
},
}
case 'files-uploaded':
return { ...state, uploading: false, status: FILES_UPLOADED }
case 'set-upload-error':
return { ...state, uploadError: action.error, status: UPLOAD_ERROR }
default:
return state
}
}
自定义钩子终于完成了!太棒了!
以下是自定义钩子的最终代码:
src/useFileHandlers.js
import { useCallback, useEffect, useReducer, useRef } from 'react'
const api = {
uploadFile({ timeout = 550 }) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
}, timeout)
})
},
}
const logUploadedFile = (num, color = 'green') => {
const msg = `%cUploaded ${num} files.`
const style = `color:${color};font-weight:bold;`
console.log(msg, style)
}
// Constants
const LOADED = 'LOADED'
const INIT = 'INIT'
const PENDING = 'PENDING'
const FILES_UPLOADED = 'FILES_UPLOADED'
const UPLOAD_ERROR = 'UPLOAD_ERROR'
const initialState = {
files: [],
pending: [],
next: null,
uploading: false,
uploaded: {},
status: 'idle',
}
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'load':
return { ...state, files: action.files, status: LOADED }
case 'submit':
return { ...state, uploading: true, pending: state.files, status: INIT }
case 'next':
return {
...state,
next: action.next,
status: PENDING,
}
case 'file-uploaded':
return {
...state,
next: null,
pending: action.pending,
uploaded: {
...state.uploaded,
[action.prev.id]: action.prev.file,
},
}
case 'files-uploaded':
return { ...state, uploading: false, status: FILES_UPLOADED }
case 'set-upload-error':
return { ...state, uploadError: action.error, status: UPLOAD_ERROR }
default:
return state
}
}
const useFileHandlers = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState)
const onSubmit = useCallback(
(e) => {
e.preventDefault()
if (state.files.length) {
dispatch({ type: 'submit' })
} else {
window.alert("You don't have any files loaded.")
}
},
[state.files.length],
)
const onChange = (e) => {
if (e.target.files.length) {
const arrFiles = Array.from(e.target.files)
const files = arrFiles.map((file, index) => {
const src = window.URL.createObjectURL(file)
return { file, id: index, src }
})
dispatch({ type: 'load', files })
}
}
// Sets the next file when it detects that its ready to go
useEffect(() => {
if (state.pending.length && state.next == null) {
const next = state.pending[0]
dispatch({ type: 'next', next })
}
}, [state.next, state.pending])
const countRef = useRef(0)
// Processes the next pending thumbnail when ready
useEffect(() => {
if (state.pending.length && state.next) {
const { next } = state
api
.uploadFile(next)
.then(() => {
const prev = next
logUploadedFile(++countRef.current)
const pending = state.pending.slice(1)
dispatch({ type: 'file-uploaded', prev, pending })
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
dispatch({ type: 'set-upload-error', error })
})
}
}, [state])
// Ends the upload process
useEffect(() => {
if (!state.pending.length && state.uploading) {
dispatch({ type: 'files-uploaded' })
}
}, [state.pending.length, state.uploading])
return {
...state,
onSubmit,
onChange,
}
}
export default useFileHandlers
可是等等,还没完呢。我们还需要把这个逻辑应用到用户界面上。哎呀!
我们将导入useFileHandlers钩子并在组件中使用它。我们还将为每个文件创建 UI 映射,并将它们渲染为缩略图:
src/App.js
import React from 'react'
import useFileHandlers from './useFileHandlers'
import './App.css'
const Input = (props) => (
<input
type='file'
accept='image/*'
name='img-loader-input'
multiple
{...props}
/>
)
const App = () => {
const {
files,
pending,
next,
uploading,
uploaded,
status,
onSubmit,
onChange,
} = useFileHandlers()
return (
<div className='container'>
<form className='form' onSubmit={onSubmit}>
<div>
<Input onChange={onChange} />
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
</div>
<div>
{files.map(({ file, src, id }, index) => (
<div key={`thumb${index}`} className='thumbnail-wrapper'>
<img className='thumbnail' src={src} alt='' />
<div className='thumbnail-caption'>{file.name}</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
</form>
</div>
)
}
export default App
这个基础组件在加载时只会渲染一些缩略图。样式方面我没有太过复杂,因为一切都留给大家自己去发挥吧 :)
但是如果你想使用这里的基本样式,它们是:
src/App.css
.thumbnail-wrapper {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 6px 4px;
}
.thumbnail {
flex-basis: 100px;
height: 100%;
max-width: 50px;
max-height: 50px;
object-fit: cover;
}
.thumbnail-caption {
flex-grow: 1;
font-size: 14px;
color: #2b8fba;
margin-bottom: 5px;
padding: 0 12px;
}
所有文件上传完成后会发生什么?嗯,实际上还没有。但我们至少可以向用户显示一些内容,让他们知道上传完成了:
src/App.js
{
status === 'FILES_UPLOADED' && (
<div className='success-container'>
<div>
<h2>Congratulations!</h2>
<small>You uploaded your files. Get some rest.</small>
</div>
</div>
)
}
src/App.css
.success-container {
position: absolute;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.success-container h2,
small {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
这次用到了status 。瞧,它很实用,不是吗?你也可以用其他status值,结合state.pending和其他一些属性,制作出一些非常精美复杂的 UI。如果你用本教程做出了一些很棒的作品,请给我发邮件,并附上几张截图!
最终输出:
src/App.js
import React from 'react'
import useFileHandlers from './useFileHandlers'
import './App.css'
const Input = (props) => (
<input
type='file'
accept='image/*'
name='img-loader-input'
multiple
{...props}
/>
)
const App = () => {
const {
files,
pending,
next,
uploading,
uploaded,
status,
onSubmit,
onChange,
} = useFileHandlers()
return (
<div className='container'>
<form className='form' onSubmit={onSubmit}>
{status === 'FILES_UPLOADED' && (
<div className='success-container'>
<div>
<h2>Congratulations!</h2>
<small>You uploaded your files. Get some rest.</small>
</div>
</div>
)}
<div>
<Input onChange={onChange} />
<button type='submit'>Submit</button>
</div>
<div>
{files.map(({ file, src, id }, index) => (
<div
style={{
opacity: uploaded[id] ? 0.2 : 1,
}}
key={`thumb${index}`}
className='thumbnail-wrapper'
>
<img className='thumbnail' src={src} alt='' />
<div className='thumbnail-caption'>{file.name}</div>
</div>
))}
</div>
</form>
</div>
)
}
export default App
src/App.css
(包括移动设备的媒体查询)
.container {
padding: 8px;
width: 100%;
box-sizing: border-box;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
.form {
position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.form input,
button {
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.form button {
padding: 8px 17px;
border: 0;
color: #fff;
background: #265265;
cursor: pointer;
}
.form button:hover {
background: #1e3d4b;
}
.thumbnail-wrapper {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 6px 4px;
}
.thumbnail {
flex-basis: 100px;
height: 100%;
max-width: 50px;
max-height: 50px;
object-fit: cover;
}
.thumbnail-caption {
flex-grow: 1;
font-size: 14px;
color: #2b8fba;
margin-bottom: 5px;
padding: 0 12px;
}
.success-container {
position: absolute;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.success-container h2,
small {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 472px) {
.container {
padding: 6px;
}
.thumbnail-wrapper {
padding: 6px 2px;
}
.thumbnail {
flex-basis: 40px;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
max-height: 40px;
max-width: 40px;
}
.thumbnail-caption {
font-size: 12px;
}
}
截图
我提供了使用本教程中的代码实现的基本UX的一些屏幕截图:
onChange
记录上传文件()
状态待定
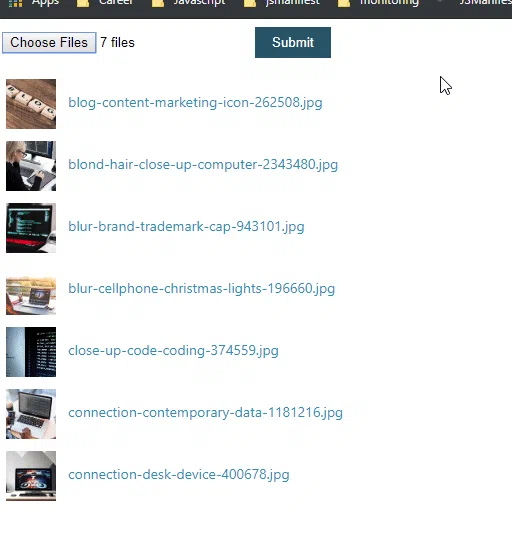
结论
这篇文章到此结束。希望你喜欢,并敬请期待更多精彩文章!:)
文章来源:https://dev.to/jsmanifest/keeping-ui-completely-synchronized-when-uploading-files-in-react-dj3 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com