高级开发人员的 JavaScript 基础知识
以下是我们将要深入讨论的内容
- 提升
- 暂时性死区
- 函数与函数表达式之间的差异。
- 浅拷贝与深拷贝
- 对象分配
- 切片与拼接
- forEach 与 Map 对比
- 全局执行上下文
- 填充材料
- 地图深度探索
- 类型强制
1. 提升
提升是 JavaScript 中发生在执行过程中的一种行为compilation process (during lexical analysis)。在代码执行之前,JavaScript 引擎会扫描代码,并将变量和函数声明移至其各自作用域的顶部。此过程会影响变量和函数在代码中的访问方式和时间。
- Var 被提升并用未定义初始化。
console.log(a) // undefined
var a = 10;
- Let 和 Const 被提升但未被初始化。
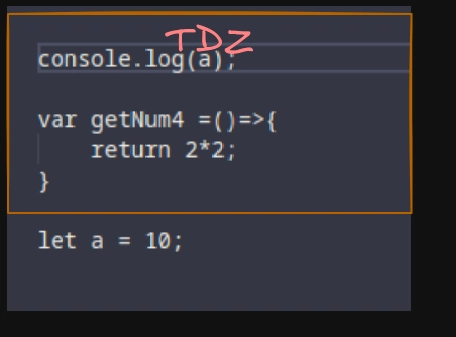
console.log(a) // Reference Error , Temporal Dead Zone.
let a = 10;
- 函数声明被提升,我们可以在代码中的任何地方访问它们。
console.log(getNum());
function getNum(){
return 2*2;
}
- 函数表达式未完全提升。
console.log(getNum()); // ReferenceError, getNum2 is not defined : Same for let , TDZ
const getNum =()=>{
return 2*2;
}
console.log(getNum4()); // TypeError: getNum4 is not a function
var getNum4 =()=>{
return 2*2;
}
上面只有变量被提升,而不是函数。
2. 暂时性盲区
它是从范围/块开始到变量被定义和初始化之间的一段时间。
什么时候发生?
- 仅存在于用 let 和 const 声明的变量中。
- 它基本上可以防止在初始化之前访问它们。
- 访问 TDZ 中的变量会导致 ReferenceError。
- TDZ 也适用于分配给 let 和 const 的函数表达式。
3. 函数 Dec 与函数表达式
函数定义:用 function 关键字定义的函数。
- 它们被吊起来了。
- 可在整个范围内访问。
函数表达式:当将函数分配给变量时。
- 未提升
- 声明后才可用
当你需要函数在作用域内的任何位置都能访问时,可以使用函数声明。
使用函数表达式可以更好地控制函数的使用时间和位置。
4.浅拷贝与深拷贝
浅拷贝:仅复制顶层属性,对于嵌套对象,传递引用。
let obj1 = { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Delhi" } };
let obj2 = {...obj1};
obj2.address.city = "Gurugram";
console.log(obj1);
console.log(obj2);
// Both prints the same output
// {
// "name": "Jayant",
// "address": {
// "city": "Gurugram"
// }
// }
进行浅拷贝的其他方法
Object.assign()Spread OperatorSlice Operator[如果存在嵌套对象,新数组将包含引用]Concat Operator
深度复制:它复制了所有属性。
let obj1 = { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Delhi" } };
// Creating a deep copy
let obj2 = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj1)); // Not Recommended
obj2.address.city = "Mumbai"; // ✅ Changes only obj2
console.log(obj1); // { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Delhi" } }
console.log(obj2); // { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Mumbai" } }
如果我们使用上述方法,我们可能会遇到这些问题
- 它无法处理未定义的函数。
- 这需要时间,因为我们正在进行序列化和反序列化。
进行深度复制的其他方法
structuredClone()- 这是一种 JS 方法,用于深度克隆。
let obj1 = { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Delhi" } };
// It addresses most of the JSON method's shortcoming.
let obj2 = structuredClone(obj1);
obj2.address.city = "Mumbai"; // Changes only obj2
console.log(obj1); // { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Delhi" } }
console.log(obj2); // { name: "Jayant", address: { city: "Mumbai" } }
Recursive based custom deep copy function
5.Object.assign()
它是一个 JS 方法,用于将属性从一个或多个对象复制到其他对象
We can do the same thing using Spread Operator。
// Syntax : Creates Shallow Copy
Object.assign(<target>,..sources)
// Example
let obj1 = {
name:"Jayant"
}
let obj2 = {
status:"single"
}
// If two objects have the same property, the last object's value will overwrite previous values.
let obj3 = Object.assign({},obj1,obj2);
6. 切片与拼接
Slice 用于提取数组的部分内容,Slice makes shallow copy
Splice 用于从数组中添加/删除元素
// Slice : arr.slice(start,end);
// end is exclusive, include nhi hoga
const arr = [1,2,3,4,45,5,6,7];
const newArray = arr.slice(1,4);
console.log(newArray); // [2,3,4 ]
console.log(arr.slice(-2)); // [6,7] , get last 2 elemnets
// Splice : arr.splice(start,deleteCount,...items);
const itemsToAdd = [2,3,4,5,6,7];
const newArr = [1,2,3,4,45,5,6,7];
console.log(newArr.splice(1,7,...itemsToAdd)); //[2,3,4,45,5,6,7]
console.log(newArr); // [1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
const newArr2 = [1,2,3,4,45,5,6,7];
console.log(newArr2.splice(-2)); // [6,7] // removed last 2 elements
console.log(newArr2); // [1,2,3,4,45,5]
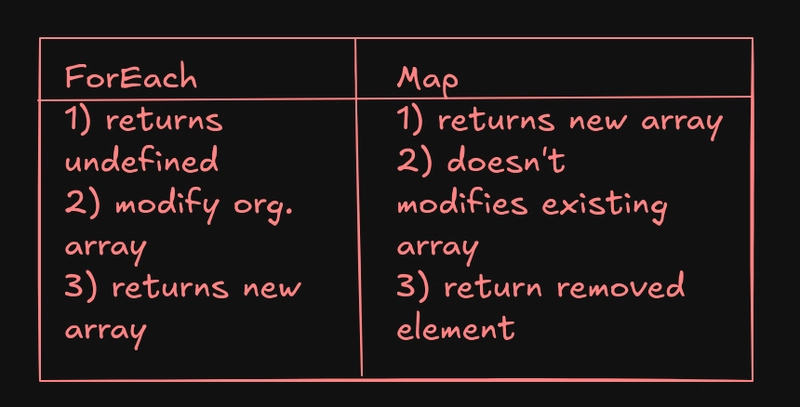
7. ForEach 与 Map
ForEach and Map doesn't support early return, if you want to return early return you can use some,every,reduce,for of loop.
[1,2,3,4,5,,6,7].forEach((el)=>{
if(!el){
break; // Gives Error, Same for Map
}
console.log(el)
})
8.执行上下文
它是代码执行的环境。
它有两种类型:
1) Global EC
2)Function EC
Global EC- 它是 JS 文件运行时第一个运行的 EC。
它包含全局变量、函数和词法环境。程序停止时,它会被移除。
9. 填充材料
这是一种编写代码的行为,使旧浏览器兼容新功能。
较旧的浏览器(例如 Internet Explorer)不支持 Array.includes()。
为了添加此功能,我们可以编写一个 polyfill。
Array.includes() 的 Polyfill
if (!Array.prototype.includes) {
Array.prototype.includes = function (element) {
return this.indexOf(element) !== -1;
};
}
10、地图深度探索
通常我们只向回调函数传递 1 个参数,
但在内部,map() 为回调函数提供了 4 个参数
// array is accessible in case of forEach also
arr.map((value,index,array,this)=>{})
const arr = [1,2,3,4,5,,65];
console.log(arr.map((val)=>{
console.log(arr[0]);
return val;
})); // arr is already available in the scope so what is the need of it?
// the third optional argument can be useful when we don't have access to it.
// For Example in a Function
function processData(arr) {
return arr.map((val, index, array) => {
console.log(array[0]); // Accessing the first element dynamically
return val * 2;
});
}
console.log(processData([10, 20, 30]));
Sparse Array - Array with missing elements
const arr = [1,2,,5,6,,7,8,9] // Sparse Array
// By default map skips this and doesn't call the callback function for them.
// the empty slots remains in the array
console.log(arr.map((val)=>{
if(!val){
return 0;
}
return val*2
})) // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, empty, 130]
如果您想在稀疏数组的情况下给出默认值而不是空值,您可以借助 forEach 或扩展运算符或使用 map 进行过滤来实现。
const arr = [1,2,,5,6,,7,8,9];
// using spread operator converts a sparse array into a dense one with explicit undefined values || use can use forEeach also || filter with map.
console.log([...arr].map((val,index,arr)=>{
if(!val){
return arr[index-1] || 0;
}
return val*2
})) // [2, 4, 2, 10, 12, 6, 14, 16, 18]
// using arr.filter(Boolean).map
// Boolean is a built in function that converts values to true or false.
// If the value is truthy, it stays in the array; if falsy, it gets removed.
arr.filter(Boolean).map((item)=>item*2);
map() Sets the Range of Elements Before Execution:表示在第一次回调执行之前确定正在由回调处理的元素。
- 执行期间添加到数组的新元素将被忽略。
- 处理之前删除的元素将被跳过。
11. 类型强制
自动从一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型。
它以三种方式发生:
隐式强制→JS 自动转换类型。
console.log(10+"2"); // [Concatation]
console.log(10-"2"); // [conversion] - To number
console.log(10*"2"); // [conversion] - To number
console.log(10/"2"); // [conversion] - To number
console.log(true+1) // true converted to number gives 1
// false -> 0
console.log(null+undefined) // NaN
// null -> 0
// undefined -> NaN
console.log(null + 10); // 10 (null → 0)
console.log(undefined + 10); // NaN (undefined → NaN)
const obj = { name: "John" };
console.log(String(obj)); // "[object Object]"
console.log(obj + ""); // "[object Object]"
// [] -> ""
console.log([] + 2); // "2" (Array → Empty String → Concatenation)
console.log([] - 2); // -2 (Array → Empty String → 0 - 2 = -2)
console.log([1] + [2]); // "12"
显式强制转换 → 我们使用函数手动转换类型。
抽象操作 → JS 中类型转换的内部规则。
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com