10 个 React Hooks 详解✨
本博客最初发表于:我的博客
在 React Hooks 出现之前(React < 16.8),开发者需要编写class组件才能使用某些 React 功能。但现在,我们React Hooks提供了一种更符合人体工程学的组件构建方式,因为我们可以在不改变组件层次结构的情况下使用状态逻辑。
总共有 10 个 Hooks🔥
🚀 useState :
这是最重要且最常用的钩子。此钩子的目的是处理响应式数据,应用程序中任何发生变化的数据都称为状态,当任何数据发生变化时,React 都会重新渲染 UI。
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
🚀 useEffect :
它允许我们从单个函数 API 中实现所有生命周期挂钩。
// this will run when the component mounts and anytime the stateful data changes
React.useEffect(() => {
alert('Hey, Nads here!');
});
// this will run, when the component is first initialized
React.useEffect(() => {
alert('Hey, Nads here!');
}, []);
// this will run only when count state changes
React.useEffect(() => {
fetch('nads').then(() => setLoaded(true));
}, [count]);
// this will run when the component is destroyed or before the component is removed from UI.
React.useEffect(() => {
alert('Hey, Nads here');
return () => alert('Goodbye Component');
});
🚀 useContext :
这个钩子允许我们使用React's Context API,它本身就是一种机制,允许我们在组件树中共享数据,而无需通过 props 传递。它基本上消除了prop-drilling
const ans = {
right: '✅',
wrong: '❌'
}
const AnsContext = createContext(ans);
function Exam(props) {
return (
// Any child component inside this component can access the value which is sent.
<AnsContext.Provider value={ans.right}>
<RightAns />
</AnsContext.Provider>
)
}
function RightAns() {
// it consumes value from the nearest parent provider.
const ans = React.useContext(AnsContext);
return <p>{ans}</p>
// previously we were required to wrap up inside the AnsContext.Consumer
// but this useContext hook, get rids that.
}
🚀 useRef :
这个钩子允许我们创建一个可变对象。当值持续变化时,它会被使用,就像 useState 钩子的情况一样,但不同之处在于,当值发生变化时,它不会触发重新渲染。
它的常见用例是从 DOM 中抓取 HTML 元素。
function App() {
const myBtn = React.useRef(null);
const handleBtn = () => myBtn.current.click();
return (
<button ref={myBtn} onChange={handleBtn} >
</button>
)
}
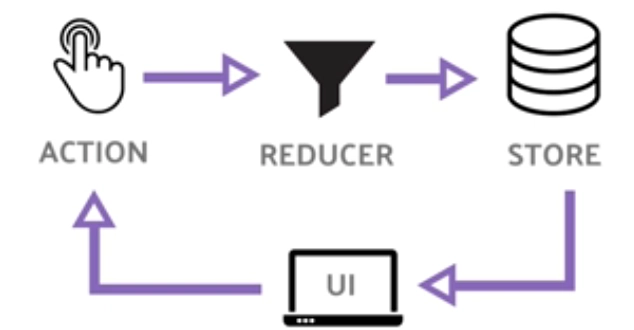
🚀 useReducer :
它和 setState 非常相似,只是用 来管理状态的方式有所不同Redux Pattern。我们不是直接更新状态,而是dispatch将操作传递给一个reducer函数,然后这个函数会计算出如何计算下一个状态。
function reducer(state, dispatch) {
switch(action.type) {
case 'increment':
return state+1;
case 'decrement':
return state-1;
default:
throw new Error();
}
}
function useReducer() {
// state is the state we want to show in the UI.
const [state, dispatch] = React.useReducer(reducer, 0);
return (
<>
Count : {state}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type:'decrement'})}>-</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type:'increment'})}>+</button>
</>
)
}
🚀 useMemo :
这个钩子可以帮助你优化计算成本或提高性能。它主要用于需要进行高开销计算的情况。
function useMemo() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(60);
const expensiveCount = useMemo(() => {
return count**2;
}, [count]) // recompute when count changes.
}
非常适合记忆返回值,但在其他情况下CSSNamespaceRule,我们想要记忆整个函数,在这种情况下,我们可以使用这个钩子 ↓
🚀 useCallback :
function useCallbackDemo() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(60);
const showCount = React.useCallback(() => {
alert(`Count ${count}`);
}, [count])
return <> <SomeChild handler = {showCount} /> </>
}
🚀 useImperativeHandle :
这个钩子用于修改暴露的引用,很少使用。
function useImperativeHandleDemo(props, ref) {
const myBtn = useRef(null);
React.useImperativeHandle(ref, () => ({
click: () => {
console.log('clicking button!');
myBtn.current.click();
}
}));
}
🚀 useLayoutEffect :
它的工作原理与 useEffect 钩子相同,但有一个区别,回调将在渲染组件之后但在实际更新绘制到屏幕之前运行。
⚠️:阻止视觉更新,直到回调完成。
function useLayoutEffectDemo() {
const myBtn = React.useRef(null);
React.useLayoutEffect(() => {
const rect = myBtn.current.getBoundingClientRect();
// scroll position before the dom is visually updated
console.log(rect.height);
})
}
🚀 useDebugValue :
这个钩子意义不大,但它允许我们在 中定义自定义标签React Dev Tools,这对于调试很有用。假设我们有n多个使用相同逻辑的组件,那么我们可以分别定义自己的函数,并将其用于其他组件,但关键在于我们可以进行调试。
function useDisplayName() {
const [displayName, setDisplayName] = React.useState();
React.useEffect(() => {
const data = fetchFromDatabase(props.userId);
setDisplayName(data.displayName);
}, []);
React.useDebugValue(displayName ?? 'loading...');
return displayName;
}
返回值可以在其他组件或应用程序中的其他地方使用,就像这样👇🏽
function App() {
const displayName = useDisplayName();
return <button>{displayName}</button>;
}
参考资料Fireship's Youtube Video——React Hooks
想要连接吗?推特
文章来源:https://dev.to/abhisheknaiidu/10-react-hooks-explained-3ino 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com