Python 从零到大师 #初学者⚡
先决条件:
1. 您的机器中装有 Python,就是这样。
如果你已经在系统中安装了python
按 Win 键并打开命令提示符
Python 中的 Hello World
评论
Python中的数据类型
获取用户的输入并将其存储在变量中
列表和索引
Python 运算符
Python 字符串操作
Python 中的集合
Python 中的类型转换
Python中的子集
列表操作
字符串操作
缩进
使用函数
Python 中的 For 循环
If 语句:
如果语句没有缩进(将引发错误)
Python 中的 While 循环
异常处理
使用模块
现在怎么样?
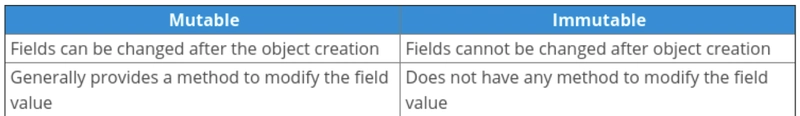
列表在 Python 中是可变的
作为一名拥有 3 年以上经验的 Python 程序员,我想分享一些 Python 基础知识,本教程适合完全的初学者以及想要在更短时间内复习 Python 的人。
本教程对 Python 编程语言进行了足够的介绍。如果您有任何疑问,请随时联系我,我会非常乐意为您提供帮助。😊😊😊😃
- Python 是一种初学者语言- Python 是一种适合初学者的优秀语言,支持开发各种应用程序,从简单的文本处理到 WWW 浏览器再到游戏。
先决条件:
1. 您的机器中装有 Python,就是这样。
(如果您的系统中没有 python)
安装 Python 的步骤:
- 前往https://www.python.org/downloads并下载。
- 在您的系统中安装 Python。非常简单!
如果你已经在系统中安装了python
按 Win 键并打开命令提示符
- 在命令提示符中输入“python”并按回车键
Python 中的 Hello World
>>> print("Hello World!")
Hello World!
评论
这是单行注释的示例,
单行注释以“#”开头
>>> print("Hello World!") #this is single line comment
Hello World!
这是多行注释(Docstrings)的示例,
多行注释以
"""This is a
multiline
Comment. It is also called docstrings"""
>>> print("Hello, World!")
Hello World!
在计算机编程中,注释是计算机程序源代码中程序员可读的解释或注解。添加注释的目的是使源代码更容易被人类理解,但通常会被编译器和解释器忽略。
Python中的数据类型
>>>x = 10
>>>print(x)
10
>>>print(type(x))
<class 'int'>
>>>y = 7.0
>>>print(y)
7.0
>>>print(type(y))
<class, 'float'>
>>>s = "Hello"
>>>print(s)
Hello
>>>print(type(s))
<class, 'str'>
获取用户的输入并将其存储在变量中
a = input('Enter Anything')
print(a)
列表和索引
>>>X=['p','r','o','b','e']
>>>print(X[1])
r
这里将打印“r”,因为“r”的索引是 1。(索引始终从 0 开始)
>>>X.append('carryminati')
>>>print(X)
['p','r','o','b','e','carryminati']
>>>print(X[-1])
carryminati
>>>x = True
>>>print(type(x))
<class 'bool'>
布尔值可以是 True 或 False
>>>S={1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,5,6}
>>>print(S)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Python 中的字典——我们稍后会学习
x = {"Name":"Dev", "Age":18, "Hobbies":["Code", "Music"]}
在编程中,变量是用来保存一个或多个值的名称。变量保存的是计算结果,而不是在代码中的多个位置重复这些值。
可变和不可变数据类型
- 不可变对象:这些是内置类型,例如 int、float、bool、string、unicode、tuple。简而言之,可变对象的值一旦创建就无法更改。
# Tuples are immutable in python
>>>tuple1 = (0, 1, 2, 3)
>>>tuple1[0] = 4
>>>print(tuple1)
TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
- 可变对象:这些类型包括列表、字典、集合。自定义类通常是可变的。简单来说,不可变对象的值即使在创建后也可以更改。
# lists are mutable in python
>>>color = ["red", "blue", "green"]
>>print(color)
["red", "blue", "green"]
>>>color[0] = "pink"
>>>color[-1] = "orange"
>>>print(color)
["red", "blue", "green", "orange" ]
Python 运算符
x = 10
# Sum of two variables
>>> print(x+2)
12
# x-2 Subtraction of two variables
>>> print(x-2)
8
# Multiplication of two variables
>>> print(x*2)
20
# Exponentiation of a variable
>>> print(x**2)
100
# Remainder of a variable
>>> print(x%2)
0
# Division of a variable
>>> print(x/float(2))
5.0
# Floor Division of a variable
>>> print(x//2)
5
Python 字符串操作
>>> x = "awesome"
>>> print("Python is " + x) # Concatenation
Python is awesome
python 无法将字符串和数字相加
>>>x=10
>>>print("Hello " + x)
File "<stdin>", line 1
print("Hello " + x)x=10
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
字符串乘法
>>> my_string = "iLovePython"
>>> print(my_string * 2)
'iLovePythoniLovePython'
转换为上部
>>> print(my_string.upper()) # Convert to upper
ILOVEPYTHON
有关字符串方法的更多信息
>>> print(my_string.lower()) # Convert to lower
ilovepython
>>> print(my_string.capitalize()) # Convert to Title Case
ILovePython
>>> 'P' in my_string # Check if a character is in string
True
>>> print(my_string.swapcase()) # Swap case of string's characters
IlOVEpTHON
>>> my_string.find('i') # Returns index of given character
0
Python 中的集合
>>>S = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
>>>print("banana" in S)
True
>>>S={1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,5,6}
>>>print(S)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Python 中的类型转换
>>> x = int(1)
>>> print(x)
1
>>> y = int(2.8)
>>> print(y)
2
>>> z = float(3)
>>> print(z)
3.0
Python中的子集
# Subset
>>>my_list=['my', 'list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> my_list[0]
'my'
>>> my_list[-3]
'list'
>>> my_list[1:3]
['list', 'is']
>>> my_list[1:]
['list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> my_list[:3]
['my', 'list', 'is']
>>> my_list[:]
['my', 'list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> my_list + my_list
>>>print(my_list)
['my', 'list', 'is', 'nice', 'my', 'list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> my_list * 2
['my', 'list', 'is', 'nice', 'my', 'list', 'is', 'nice']
>>> my_list2 > 4
True
列表操作
>>> my_list.index(a)
>>> my_list.count(a)
>>> my_list.append('!')
>>> my_list.remove('!')
>>> del(my_list[0:1])
>>> my_list.reverse()
>>> my_list.extend('!')
>>> my_list.pop(-1)
>>> my_list.insert(0,'!')
>>> my_list.sort()
字符串操作
>>> my_string[3]
>>> my_string[4:9]
>>> my_string.upper()
>>> my_string.lower()
>>> my_string.count('w')
>>> my_string.replace('e', 'i')#will replace 'e' with 'i'
>>> my_string.strip()#remove white space from whole string
缩进
Python 缩进是一种告诉 Python 解释器一系列语句属于特定代码块的方式。在 C、C++、Java 等语言中,我们使用花括号 { } 来指示代码块的开始和结束。在 Python 中,我们使用空格/制表符作为缩进,以便向编译器指示相同的内容。
使用函数
遵循此处的缩进规则(返回语句前的空格)
>>> def myfunAdd(x,y):
... return x+y
>>> myfunAdd(5,100)
105
Python 中的 For 循环
>>>fruits = ["Carry", "banana", "Minati"]
>>>for x in fruits:
... print(x)
carry
banana
Minati
If 语句:
a = 33
b = 200
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
如果语句没有缩进(将引发错误)
a = 55
b = 300
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
Python 中的 While 循环
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
i += 1
异常处理
当发生错误(或我们称之为异常)时,Python 通常会停止并生成错误消息。这些异常可以使用 try 语句来处理
try:
print(x)
except:
print("An exception occurred")
使用模块
>>>import math
>>>print(math.pi)
3.141592653589793
现在怎么样?
好吧,还有很多内容要讲,不过那是你的家庭作业了😉!
非常感谢你的阅读,祝你的 Python 之旅一切顺利!
一如既往,我欢迎你的反馈、建设性批评,以及听取你的项目建议。你可以在Linkedin上联系我,也可以在我的网站上联系我。
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com