使用 TypeScript、Node、Express 和 Vue 构建 Instagram - 第一部分
这是 5 部分教程中的第 1 部分,但每个教程都可以单独阅读,以了解 Node+Express+TypeScript+Vue API/Vue Web 应用程序设置的各个方面。
在本教程的 5 个部分结束时,您将学会构建如下应用程序:
想学习移动/桌面应用?这里的技能和概念是基础,并且可复用到移动应用(NativeScript)或桌面应用(Electron)。我可能会在后续课程中介绍它们。
导航至其他部分(您位于第 1 部分)
- 使用 TypeScript 设置 Node 和 Express API
- 使用 TypeScript 设置 VueJs
- 使用 Sequelize ORM 设置 Postgres
- 基本 Vue 模板和与 API 的交互
- 高级 Vue 模板和图像上传到 Express
介绍
所有优秀的应用都应该从坚实的基础开始,本教程正是为此而生。我们将通过构建一个非常简单的照片分享应用来进行说明,而不是像 Todo 那样(其实没什么用)。通过这些教程,你将学习 TypeScript、Node、Express 和 VueJS,并使用本文撰写时尽可能前沿的版本(一些可行的预发布版本)。
*遗憾的是,Deno曾被考虑过,但目前还为时过早,无法使用。不过,如果能够遵循本教程中的最佳实践,到时候您很可能能够切换到 Deno 并重用大部分 API 代码库。由于视图代码与 API 不耦合,因此您可以重用所有视图代码。
说实话,Instagram 不可能只靠一个教程就能搭建出来,所以这篇文章的标题确实有点夸张。我们把这个项目命名为“Basicgram”。
获取你的 repo
您可以通过克隆并检出 tutorial-part1 分支来开始构建:
git clone https://github.com/calvintwr/basicgram.git
git checkout tutorial-part1
文件夹结构
文件夹将分为“api”,它将运行 Node+Express 设置,以及“view”,它将运行 Vue+Webpack 设置。
入门 - 安装 Express(API 引擎)
npx express-generator --view=hbs
我选择 Handlebars (hbs) 作为视图引擎,因为它看起来像 HTML,所以你不需要学习新的模板语法。由于我们只使用 Express 提供 API 服务,所以你几乎不会用到它——但当你需要它的时候,它就在那里。
我们将使用最新的 Express 5.0(预发布版)并更新所有模块版本,因此编辑该package.json文件:
{
"name": "api",
"version": "0.0.1",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"start": "node ./bin/www"
},
"dependencies": {
"cookie-parser": "~1.4.5",
"debug": "~4.1.1",
"express": "~5.0.0-alpha.8",
"hbs": "~4.1.1",
"http-errors": "~1.7.3",
"morgan": "~1.10.0"
}
}
启动它并查看是否一切正常
npm install
npm start
快速路线
你想获得的 Express 功能之一就是express-routemagic,它会自动引用所有路由,而无需逐个文件地声明它们(你会看到巨大的 Express 应用及其层层堆叠的路由代码,这毫无意义)。所以,只需获取routemagic,问题就解决了。
npm install express-routemagic --save
我们将替换路由要求:
var indexRouter = require('./routes/index')
var usersRouter = require('./routes/users')
app.use('/', indexRouter)
app.use('/users', usersRouter)
和:
const Magic = require('express-routemagic')
Magic.use(app, { invokerPath: __dirname }) // need `invokerPath` because we shifting Express into a `src` folder.
就这样,你再也不用担心路线问题了。我们继续吧。
转换为 TypeScript
TypeScript 提供了许多实用的功能来构建更优秀的代码。你可以谷歌一下它的优点。但它也有缺点,尤其是比较繁琐,而且需要处理非 TypeScript 的包(有很多实用且久经考验的包,但我并不觉得有必要移植到 TypeScript 语法中)。在本教程中,弄清楚如何将某些 JS 语法转换为 TypeScript 语法要么很痛苦,要么几乎不可能。不过,我们还是坚持下去。
由于现在我们需要将 TS 编译为 Node 运行时所需的 JS,因此我们需要几个步骤才能实现。
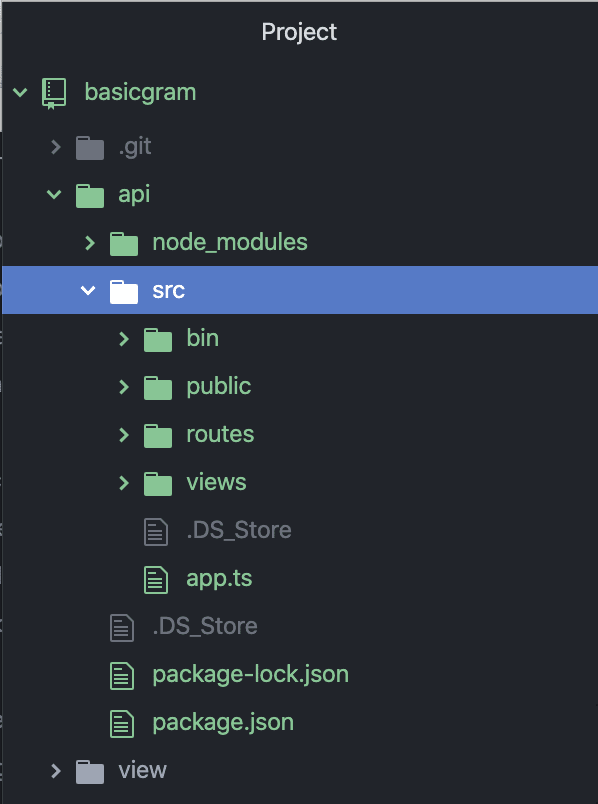
1. 将 Express 打包到“src”文件夹中,如下所示:
还要注意的是,“app.js” 被重命名为“app.ts”。我们就从这里开始,其他的暂时不用管。慢慢来。
提示:我认为混合代码库是可以接受的。并非所有代码都需要用 TypeScript 编写,而且你会错过很多非常好的 JS 模块。但我确信这种说法会在 TypeScript 用户中引起争议。好吧,请在下方提出你的观点。
2.安装 TypeScript 包并设置配置
安装 TypeScript(注意:所有 npm 命令都要在文件夹中运行basicgram/api。从技术上讲,api它们view是两个不同的应用程序。如果在中运行 npm basicgram,则会混淆它们的 node_modules 和其他配置。)
设置 TypeScript 编译器
npm install typescript --save-dev
设置tsc命令package.json:
"script": {
"start": "node ./bin/www", // this came default with express, but we will change it later.
"tsc": "tsc"
}
并初始化 tsc,它将生成一个配置文件:
npx tsc --init
tsconfig.json现在将出现在 中basicgram/api。这控制编译器的行为。我们通常想要更改两种默认行为:
-
TSC 默认输出 ES5,这对于作为服务器端运行时的 Node 来说确实没有必要(如果阻止您升级 Node 的是您的旧应用程序,请参阅Node 版本管理器)。
-
它将搜索并编译
.ts其中的所有文件basicgram/api,并.js随之生成,但这实际上不是我们想要的。
因此我们做出以下更改:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES6", // you can go for higher or lower ECMA versions depending on the node version you intend to target.
"outDir": "./dist" // to output the compiled files.
}, "include": [
"src" // this tells tsc where to read the source files to compile.
]
}
现在让我们尝试一下我们的命令:
npm run tsc
您将看到类似以下错误:
src/app.ts:21:19 - error TS7006: Parameter 'req' implicitly has an 'any' type.
21 app.use(function (req, res, next) {
这意味着 TypeScript 可以正常工作,它会告诉你app.ts——它仍然是 JavaScript——存在类型安全违规,这是理所当然的。于是我们开始转换。
3. 代码转换和类型声明
首先,我们需要为所有模块安装类型声明。先跟着我一起看,稍后我会解释这一切。它们被命名为“@types/[modulename]”。它们是否可用取决于包所有者是否创建了它。很多人其实并没有这样做。无论如何,我们只以node和express为例进行此操作,同时跳过对使用 的其他模块进行类型检查// @ts-ignore。
npm install @types/node
npm install @types/express
并将其转换app.ts为:
(注意:不建议使用@ts-ignore,仅用于本演示的目的。)
// @ts-ignore
import createError = require('http-errors') // change all `var` to import
import express = require('express')
import { join } from 'path' // this is a Node native module. only using #join from `path`
// @ts-ignore
import cookieParser = require('cookie-parser')
// @ts-ignore
import logger = require ('morgan')
// @ts-ignore
import Magic = require('express-routemagic')
const app: express.Application = express() // the correct type declaration style.
// view engine setup
app.set('views', join(__dirname, 'views'))
app.set('view engine', 'hbs')
app.use(logger('dev'))
app.use(express.json())
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
app.use(cookieParser())
app.use(express.static(join(__dirname, 'public')))
Magic.use(app, { invokerPath: __dirname }) // // need to use `invokerPath` because we are not in api's root dir.
// catch 404 and forward to error handler
app.use((req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) => { // type declaration, and changed to use arrow function
next(createError(404))
})
// error handler
app.use((err: any, req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) => {
// set locals, only providing error in development
res.locals.message = err.message
res.locals.error = req.app.get('env') === 'development' ? err : {}
// render the error page
res.status(err.status || 500)
res.render('error')
})
module.exports = app
什么是
app.use?它是 Express 使用“中间件”(将运行并接收 HTTP 请求以“读取”并执行某些操作的函数)的方式。它是顺序执行的,一种方式是想象一个 HTTP 请求“流经”你的中间件:在这种情况下,它会首先经过logger('dev'),它会将请求记录到你的终端上,然后express.json()它会将请求解析为 json……依此类推,按顺序执行。
TypeScript 基础知识讲解
您安装的模块@types/express是 Express 对象的 TypeScript 声明。声明就像一本字典——它解释了某个东西是什么,不是什么。
如果您参考下面的内容app.ts,代码块// error handler显示了如何将此“字典”应用于函数参数:
(err: Error, req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) => { ... }
它的意思是,这些req参数与 Express 的对象/原型“属于同一类型,并且——由于缺乏更好的词汇——形式” Request(我拒绝使用“类”这个词,因为Javascript 无可辩驳地是无类的)。
因此,在函数内,如果您尝试使用Request不存在的类型,或者尝试调用Request不存在的方法,TypeScript 就会对此发出警告。
(req: express.Request) => {
req.aMethodThatDoesNotExist() // red curlies underlines, and will not compile.
if (req === 'someString') {} // TypeScript will tell you this is always false.
})
所有这些本质上是对 TypeScript 如何对代码进行类型检查的一个非常基本的解释。
现在如果您npm run tsc再次运行,就不会再出现任何错误。
4.将所有文件复制到“./dist”
TSC 只会编译.ts文件,这是理所当然的。但你需要复制其余文件,包括那些.js你不打算转换或稍后会转换的文件(这就是它的妙处,你不需要总是把所有东西都强制转换成 TypeScript——并非所有代码都值得你花时间)。tsc这似乎没有提供一个好的方法(请参阅此处的问题),所以我们将使用cpy-cli和del-cli模块:
npm install cpy-cli del-cli --save-dev
在 中设置 npm 脚本package.json。
prebuild使用delshell 命令(来自del-cli模块)删除旧“./dist”文件夹的脚本:
"prebuild": "del './dist'"
postbuild使用cpyshell 命令(来自cpy-cli模块)复制剩余文件的脚本:
"postbuild": "cpy --cwd=src '**/*' '!**/*.ts' './../dist' --parents"
// --cwd=src means the Current Working Directory is set to "./src"
// '**/*' means all files and folder in the cwd.
// '!**/*.ts' means excluding all typescript files.
// './../dist' means "basicgram/api/dist", and is relative to "src" folder
// --parents will retain the folder structure in "src"
您的脚本package.json将是:
{
"scripts": {
"start": "node ./dist/bin/www",
"build": "npm run tsc",
"prebuild": "del './dist'",
"postbuild": "cpy '**/*' '!**/*.ts' './../dist' --cwd=src --parents",
"tsc": "tsc"
}
}
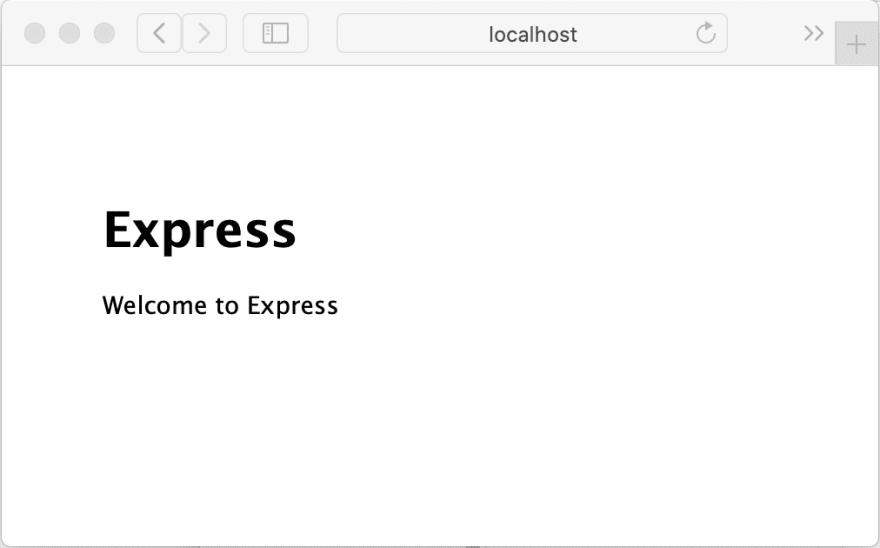
现在,只需检查一切是否正常,请转到“src/routes/index.js”并将其更改title为:ExpressExpress in TypeScript
res.render('index', { title: 'Express with TypeScript' })
构建并运行它:
npm build
npm start
5. 设置自动重新编译
npm build对于开发来说,持续运行和效率很低npm start。因此,我们将使用nodemon在文件更改时自动重启服务器,并将ts-nodeTypeScript 文件像 Javascript 一样执行(注意:这适用于开发环境,不会输出到./dist):
npm install nodemon ts-node --save-dev
添加以下内容package.json:
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon --ext js,ts,json --watch src --exec 'ts-node' ./src/bin/www"
}
解释:
--exec:我们使用--exec标志是因为nodemon不会使用,而是在入口文件不是“.ts”时ts-node使用。在本例中不是 。:当使用 时,我们还需要使用来手动指定要监视更改的文件。:这定义了 nodemon 将监视哪个文件夹的更改以执行重启。 (此视频 版权所有)nodewww--ext--exec--ext--watch
运行你的开发服务器:
npm run dev
你的 API 已经启动了!做一些修改,看看 nodemon 如何自动重新编译。请参阅第二部分,了解如何在 TypeScript 中使用 VueJS 设置你的视图引擎。
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com