如何使用 React、Hardhat 和 ethers.js 制作全栈 dapp(附示例)
在本文中,我们将学习如何构建一个类似于本文封面的全栈 dapp。我们将使用 Solidity 编写一个简单的安全远程购买托管合约。然后,为其编写测试并构建前端。
如果您需要聘请全栈区块链开发人员,可以通过 Telegram 联系我。
您还可以加入我维护的 Telegram 群组,在那里您可以找到其他区块链开发人员、招聘人员、项目所有者、提出问题并建立联系。
我最近在 BSC 主网上部署了一个 BEP20token 用于学习目的。
我参考了全栈以太坊开发完整指南来在本地设置开发环境。
您可以在存储库中克隆此帖子使用的代码,并使用 $yarn 安装此处使用的依赖项。
在本教程中,我们将使用Metamask 浏览器插件。
如果您还没有安装,请先将其安装到您的浏览器中。
这里使用了红色汽车图片,使示例更加逼真。您也可以使用其他产品,并在前端代码中编辑一些描述。
您将按顺序使用这些命令来本地开发本文中使用的 dapp。如果您想创建自己的版本,请在阅读本文后使用这些命令。
# See your Solidity code for the contract
# is ok and compile without any error or warning.
compile="npx hardhat compile",
# Write tests to see the smart contract code works
# as you expect for various situations.
test="npx hardhat test",
# Run local solidity development environment.
# It will set up dummy accounts that you can use to test.
serve="npx hardhat node",
# Upload your Solidity contract code to it
# before you run the frontend code.
deploy="npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network localhost",
# Run your React frontend code.
start="react-scripts start",
如果您想保存评论,请将它们保存在package.json中并与 etc 一起使用,或者编写一个简单的 CLI。$yarn compile
在测试您的 dapp 时,您将需要一些帐户,并且加入任何社区来帮助您也会很有帮助。
如果您还没有任何加密货币钱包,您可以在币安创建一个。
如果您有兴趣学习ERC20或BEP20代币,您可以参与这个社区来学习区块链相关内容。
您还可以在Opensea购买和出售您的工艺品。
目录
- 使用 Solidity 编写智能合约
- 准备测试
- 使用 Hardhat 设置 Metamask
- 使用 React 和 ethers.js 编写前端代码
- 结论
1.用Solidity编写智能合约
如果你对 Solidity 以及其他以太坊开发相关的东西还不熟悉,可以参考其官方网站。
这里使用的代码改编自官方的安全远程购买示例。
请先仔细阅读下面的代码。我稍后会提供解释。
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity >=0.7.0 <0.9.0;
contract Escrow {
uint public price;
address payable public seller;
address payable public buyer;
// 1.
address[] previousBuyers;
// 2.
enum State { Sale, Locked, Release, Closed, Complete }
State public state;
modifier condition(bool _condition) {
require(_condition);
_;
}
modifier onlyBuyer() {
require(
msg.sender == buyer,
"Only buyer can call this."
);
_;
}
modifier onlySeller() {
require(
msg.sender == seller,
"Only seller can call this."
);
_;
}
// 3.
modifier notSeller() {
require(
msg.sender != seller,
"Seller shouldn't call this."
);
_;
}
modifier inState(State _state) {
require(
state == _state,
"Invalid state."
);
_;
}
// 4.
event Closed(
uint256 when
);
event ConfirmPurchase(
uint256 when,
address by
);
event ConfirmReceived(
uint256 when,
address by
);
event SellerRefundBuyer(
uint256 when
);
event SellerRefunded(
uint256 when
);
event Restarted(
uint256 when
);
event End(
uint256 when
);
constructor() payable {
seller = payable(msg.sender);
price = msg.value / 2;
require((2 * price) == msg.value, "Value has to be equal.");
}
// 5.
function close()
public
onlySeller
inState(State.Sale)
{
state = State.Closed;
seller.transfer(address(this).balance);
emit Closed(
block.timestamp
);
}
function confirmPurchase()
public
notSeller
inState(State.Sale)
condition(msg.value == (2 * price))
payable
{
buyer = payable(msg.sender);
state = State.Locked;
emit ConfirmPurchase(
block.timestamp,
buyer
);
}
function confirmReceived()
public
onlyBuyer
inState(State.Locked)
{
state = State.Release;
buyer.transfer(price); // Buyer receive 1 x value here
emit ConfirmReceived(
block.timestamp,
buyer
);
}
// 6.
function refundBuyer()
public
onlySeller
inState(State.Locked)
{
// Give the option to the seller to refund buyer before sending a product(car) here.
state = State.Sale;
buyer = payable(0);
emit SellerRefundBuyer(
block.timestamp
);
}
function refundSeller()
public
onlySeller
inState(State.Release)
{
state = State.Complete;
seller.transfer(3 * price);
// 1.
previousBuyers.push(buyer);
emit SellerRefunded(
block.timestamp
);
}
// 7.
function restartContract()
public
onlySeller
// inState(State.Complete)
payable
{
if (state == State.Closed || state == State.Complete) {
require((2 * price) == msg.value, "Value has to be equal to what started the contract.");
state = State.Sale;
// Reset buyer to allow the same buyer again.
buyer = payable(0);
// This doesn't work.
// buyer = address(0);
emit Restarted(
block.timestamp
);
}
}
// 1.
function listPreviousBuyers()public view returns(address [] memory){
return previousBuyers;
}
// totalPreviousBuyers
function totalSales() public view returns(uint count) {
return previousBuyers.length;
}
function end()
public
onlySeller
{
if (state == State.Closed || state == State.Complete) {
// Should put End event before selfdestruct to update the frontend.
// 8.
emit End(
block.timestamp
);
// state = State.End;
selfdestruct(seller);
// This doesn't work.
// emit End(
// block.timestamp
// );
}
}
}
希望你已经读过这段代码了。为了帮助你理解它的作用,我们假设一个真实世界的事件。
假设你是一名汽车销售商。你想用 ETH 和这里使用的智能合约来出售你的汽车。
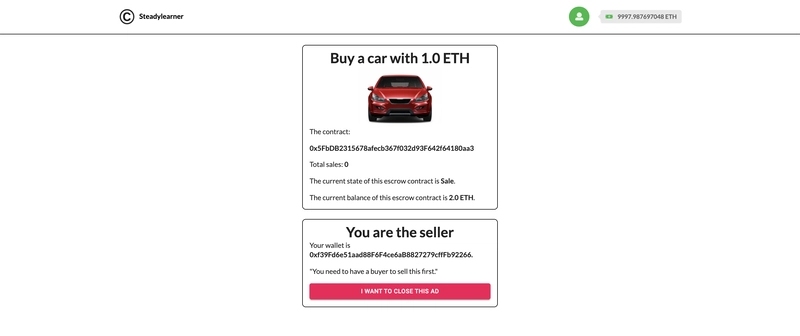
首先,您需要将其部署到以太坊网络。部署成功后,合约状态将默认为“销售”。此时不存在买家,只有卖家(合约所有者)。
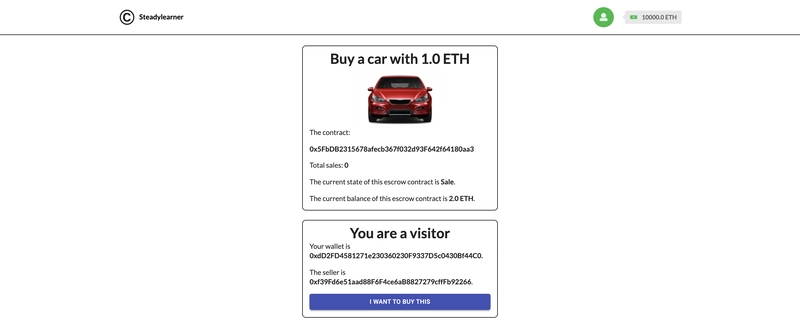
您可以等待访客付款后再成为买家,或者如果在此之前出现任何问题,则可以终止合同。
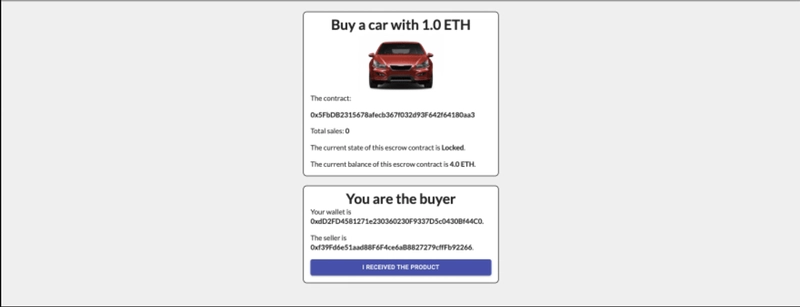
如果你找到一个买家,并在他支付了 2ETH(价格 * 2)的托管金后,合约状态将变为Locked。然后,你作为卖家就可以向用户发送一辆车,并等待他使用ConfirmReceived确认已收到车辆。
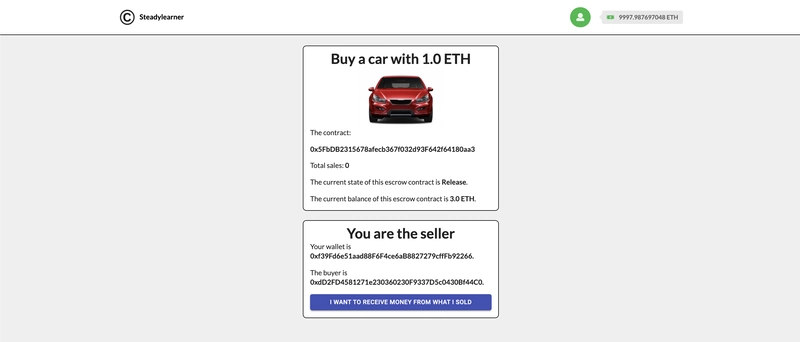
然后,一切就都好了,买家可以提取剩余的 1ETH 用于托管,卖家也可以用他的 3ETH 来做这件事,其中包括他卖掉的汽车的 1ETH。
至此,合同已经完成了所有工作,卖方可以决定是否重新开始(转售另一辆车)或终止合同。
思考一下这个合约可能发生的各种情况。这将帮助你找到代码的细节以及它们的工作原理。
1.我们会列出之前的买家名单,只有当卖家决定转售合同时才会将其纳入。其他买家(从第二个买家开始)在决定是否购买之前可以查看该名单。
2.当我们稍后使用时请求合约状态,Solidity 的 Enum 值返回 int 值(0、1、2、3、4)await Escrow.state()。
我们稍后会为其编写一个转换器(humanReadableEscrowState)。
3.我们将添加notseller修饰符,不允许卖家同时成为买家。
4.您可以在下面看到与函数名称几乎相同的事件。稍后我们将使用它来更新前端部分(无需刷新页面),并显示一些控制台消息。请在此处添加您想要从区块链中使用的变量。
5.我们在函数结束时,在状态和其他变量被修改后发出事件。函数结束是个例外,因为 afterselfdestruct(seller);事件不起作用。
6.我们添加了一个refundBuyer功能,当合约处于“锁定”状态时,卖方可以选择退款给买方。之后,合约可以重新启动或关闭。
7.如果买家决定重新开始合同,我们要求他再次存入2ETH,并将之前的买家列入之前的买家名单,以帮助其他未来的访客可以参考。
这些信息足以帮助您了解合约的功能。此处使用的代码尚未验证。因此,请仅将其用作参考和学习目的。
由于我们已经准备好了智能合约,我们将编写测试来验证它是否能按预期运行。这在您需要更新合约以及编辑前端部分之前也会有所帮助。
使用$yarn compile ($npx hardhat compile)验证您的智能合约是否编译。
2. 准备测试
在上一部分中,我们准备了 Solidity 合约代码。接下来,我们将测试其各个部分,以确保其能够按预期运行。
在继续阅读之前,您可以参考 Openzeppelin 的测试文档。
这里用到的代码片段比较长,所以我先对它们进行解释。你可以和我们稍后看到的前端代码进行比较和参考。
1.首先,准备好每个测试将要用到的内容,并在下面的每个测试用例的beforeEach处进行设置。
2.我们为每个测试用例部署一个合约beforeEach。您可以看到,我们从Hardhat提供的签名者(账户)列表中仅选择了seller、firstBuyer和secondBuyer。
3.如果将此部分与上一部分中的事件相关代码进行比较,您会发现我们在此处包含了使用它们的代码,以便在每个测试用例中使用。
4.这些将测试卖方在部署合约后可以执行的操作。您可以看到,在等待函数首先被调用之后,事件和合约状态的变化在这里进行了测试await。您还可以expectRevert从@openzeppelin/test-helpers中看到,它们用于测试发生还原时出现的错误消息。
5.这些代码将测试访客成为第一个买家后卖家和买家可以做什么。您可以查看
谁可以调用合约中的 withescrow.connect方法。
6.您可以看到,买家可以使用下面的代码将商品转售给同一个买家(第一个买家)或第二个买家。您还可以看到,应该使用to.deep.equal来比较数组。
const { expect } = require("chai");
const { expectRevert } = require('@openzeppelin/test-helpers');
const humanReadableUnixTimestamp = (timestampInt) => {
return new Date(timestampInt * 1000);
}
describe("Escrow Events and State", function() {
// 1.
let provider;
let Escrow, escrow, seller, firstBuyer, secondBuyer; // seller is owner
let closedEvent,
confirmPurchaseEvent,
sellerRefundBuyerEvent,
confirmReceivedEvent,
sellerRefundedEvent,
restartedEvent,
endEvent;
beforeEach(async () => {
provider = ethers.getDefaultProvider();
Escrow = await ethers.getContractFactory("Escrow");
escrow = await Escrow.deploy({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
// 2.
[seller, firstBuyer, secondBuyer, _] = await ethers.getSigners();
// 3.
closedEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('Closed', (when, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
confirmPurchaseEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('ConfirmPurchase', (when, by, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
by,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
sellerRefundBuyerEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('SellerRefundBuyer', (when, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
confirmReceivedEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('ConfirmReceived', (when, by, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
by,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
sellerRefundedEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('SellerRefunded', (when, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
restartedEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('Restarted', (when, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
endEvent = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
escrow.on('End', (when, event) => {
event.removeListener();
resolve({
when,
});
});
setTimeout(() => {
reject(new Error('timeout'));
}, 60000)
});
})
// 4.
it("Should set the contract state to 'Closed'.", async function () {
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.totalSales()).to.equal(0); // Should be 0
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
// 4.
await escrow.close();
let event = await closedEvent;
console.log("Closed");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(3); // Closed
});
it("Should set the contract state to 'Closed' to 'Sale' again", async function () {
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
// const beforeContractBalance = await provider.getBalance(escrow.address);
// console.log(ethers.utils.formatEther(beforeContractBalance));
// expect(ethers.utils.formatEther(beforeContractBalance)).to.equal(2);
// const beforeCloseSellerBalance = await provider.getBalance(seller.address);
// console.log(ethers.utils.formatEther(beforeCloseSellerBalance));
await escrow.close();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(3); // Closed
await escrow.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
let event = await restartedEvent;
console.log("Restarted");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
});
it("Should allow the seller to end the contract when the state is 'Closed'", async function () {
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
await escrow.close();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(3); // Closed
// Revert with the error message "Seller shouldn't call this"
// 4.
await expectRevert(escrow.connect(firstBuyer).end(), "Only seller can call this.");
await expectRevert(escrow.connect(secondBuyer).end(), "Only seller can call this.");
// Only seller can call this.
await escrow.end();
let event = await endEvent;
console.log("End");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
});
// 5.
it("Should set the contract state to 'Sale' to 'Locked' and refundSeller should fail and refundBuyer should work.", async function () {
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal("0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000"); // Not set yet, default
// Revert with the error message "Seller shouldn't call this"
await expectRevert(escrow.confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") }), "Seller shouldn't call this");
// How to set msg.sender for ether js?
// Use connect method
// 5.
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") })
let event = await confirmPurchaseEvent;
console.log("ConfirmPurchase");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
expect(event.by).to.equal(firstBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal(firstBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(1); // Locked
// When "Locked", shouldn't allow this. Revert with the error message "revert Invalid state"
await expectRevert(escrow.refundSeller(), "revert Invalid state");
await escrow.refundBuyer();
event = await sellerRefundBuyerEvent;
console.log("SellerRefundBuyer");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal("0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000");
});
it(`
Should set the contract state to 'Sale' -> 'Locked' -> 'Release' (First Buyer)
and allow refundSeller -> 'Complete' and contract should increase total sales. (Seller)
`, async function () {
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal("0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000"); // Not set yet, default
// Revert with the error message "Seller shouldn't call this"
await expectRevert(escrow.confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") }), "Seller shouldn't call this");
// How to set msg.sender for ether js?
// Use connect method
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") })
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal(firstBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(1); // Locked
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmReceived();
let event = await confirmReceivedEvent;
console.log("ConfirmReceived");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
expect(await event.by).to.equal(firstBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(2); // Released
await escrow.refundSeller();
event = await sellerRefundedEvent;
console.log("SellerRefunded");
console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(event.when.toString()));
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(4); // Complete
expect(await escrow.totalSales()).to.equal(1); // Complete
});
const firstPurchase = async () => {
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal("0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000"); // Not set yet, default
// Revert with the error message "Seller shouldn't call this"
await expectRevert(escrow.confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") }), "Seller shouldn't call this");
// How to set msg.sender for ether js?
// Use connect method
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") })
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal(firstBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(1); // Locked
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmReceived();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(2); // Released
await escrow.refundSeller();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(4); // Complete
expect(await escrow.totalSales()).to.equal(1); // Complete
}
// 6.
it(`
(First Buyer)
Should set the contract state to 'Sale' -> 'Locked' -> 'Release'
(Seller)
and allow refundSeller -> 'Complete' and contract should increase total sales.
Then, the seller can restart the contract.
`, async function () {
await firstPurchase();
await escrow.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale again
});
it(`
(First Buyer)
Should set the contract state to 'Sale' -> 'Locked' -> 'Release'
(Seller)
and allow refundSeller -> 'Complete' and contract should increase total sales.
Then, the seller can end the contract.
`, async function () {
await firstPurchase();
await escrow.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
await escrow.end();
});
it(`
(First Buyer)
Should set the contract state to 'Sale' -> 'Locked' -> 'Release'
(Seller)
and allow refundSeller -> 'Complete' and contract should increase total sales.
Then, the seller can restart the contract.
(First Buyer)
Then, first buyer can rebuy
`, async function () {
await firstPurchase();
await escrow.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
//
expect(await escrow.seller()).to.equal(seller.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal("0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000"); // Not set yet, default
// Revert with the error message "Seller shouldn't call this"
await expectRevert(escrow.confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") }), "Seller shouldn't call this");
// How to set msg.sender for ether js?
// Use connect method
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") })
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal(firstBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(1); // Locked
await escrow.connect(firstBuyer).confirmReceived();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(2); // Released
await escrow.refundSeller();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(4); // Complete
expect(await escrow.totalSales()).to.equal(2); // Complete
});
it(`
(Second Buyer)
Should set the contract state to 'Sale' -> 'Locked' -> 'Release'
(Seller)
and allow refundSeller -> 'Complete' and contract should increase total sales.
Then, the seller can restart the contract
`, async function () {
await firstPurchase();
await escrow.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
// Second Buyer
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(0); // Sale again
// Buyer should be reset;
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal("0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000");
// Repeat the almost same code for the second buyer.
// expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal(firstBuyer.address); // Yet, First Buyer
// Revert with the error message "Seller shouldn't call this"
await expectRevert(escrow.confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") }), "Seller shouldn't call this");
await escrow.connect(secondBuyer).confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") })
// New buyer
expect(await escrow.buyer()).to.equal(secondBuyer.address);
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(1); // Locked
await escrow.connect(secondBuyer).confirmReceived();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(2); // Released
await escrow.refundSeller();
expect(await escrow.state()).to.equal(4); // Complete
expect(await escrow.totalSales()).to.equal(2); // One more purchase
await escrow.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
// 6.
// Without deep, it fails here.
expect(await escrow.listPreviousBuyers()).to.deep.equal([firstBuyer.address, secondBuyer.address])
});
});
用测试代码$yarn test,你会看到与此类似的内容并通过测试。
Creating Typechain artifacts in directory typechain for target ethers-v5
Successfully generated Typechain artifacts!
我们验证了测试代码是否按我们预期的那样工作。
所以我们的 dapp 的后端部分已经基本完成了。在处理前端部分之前,我们需要先设置好 Metamask,并使用本地安全帽中的账户进行测试。
3. 使用 Hardhat 设置 Metamask
要将我们之前阅读的 Solidity 代码与前端代码一起使用,我们需要先使用$yarn serve($npx hardhat node) 命令运行本地区块链。
它将显示一些类似的免费帐户,每个帐户都有免费的 10000ETH。
$npx hardhat node
Started HTTP and WebSocket JSON-RPC server at http://127.0.0.1:8545/
Accounts
========
Account #0: 0xf39fd6e51aad88f6f4ce6ab8827279cfffb92266 (10000 ETH)
Private Key: 0xac0974bec39a17e36ba4a6b4d238ff944bacb478cbed5efcae784d7bf4f2ff80
Account #1: 0x70997970c51812dc3a010c7d01b50e0d17dc79c8 (10000 ETH)
Private Key: 0x59c6995e998f97a5a0044966f0945389dc9e86dae88c7a8412f4603b6b78690d
Account #2: 0x3c44cdddb6a900fa2b585dd299e03d12fa4293bc (10000 ETH)
Private Key: 0x5de4111afa1a4b94908f83103eb1f1706367c2e68ca870fc3fb9a804cdab365a
$yarn deploy然后,使用($npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network localhost) 命令在另一个控制台部署您的合约。
在您的浏览器上启动您的 Metamask 插件。
然后,将上述至少三个免费帐户添加到其中。
然后,将他们的名字设置为卖方、第一买家和第二买家。
更新详细信息
更新 Metamask 帐户名称
我们只是在做与上一节中用 Metamask 测试时所做的事情相同的事情,以帮助您稍后使用前端。
[seller, firstBuyer, secondBuyer, _] = await ethers.getSigners();
希望您可以毫无问题地将它们包括在内。
之后,如果您在多次使用前端测试此合约时发现 nonce 问题,您可以重新定义您的帐户并再次测试。
配置/高级/重新定义
4. 使用 React 和 ethers.js 编写前端代码
我们已准备好编写智能合约前端代码的一切。如果您已经在GitHub上阅读过,您会发现主要逻辑位于App.js文件中。
您可以看到,有些部分与我们之前读过的测试文件几乎完全相同。其他部分是 CSS 和模块,用于更好地显示此处使用的数据。
因此,我只会解释最重要的部分。
1.我们允许卖家、访客、买家根据合同状态使用我们在本文第一部分定义的功能。
2.然后,我们使用 contract.on() 及其回调函数更新其区块链事件监听器中的前端应用程序状态。
import { useEffect, useState, createRef } from 'react';
import { Contract, ethers } from 'ethers'
import moment from "moment";
import { Container, Dimmer, Loader, Grid, Sticky, Message } from 'semantic-ui-react';
import 'semantic-ui-css/semantic.min.css';
import Escrow from './artifacts/contracts/Escrow.sol/Escrow.json'
import {
humanReadableEscrowState,
humanReadableUnixTimestamp,
} from "./formatters";
import ContractDetails from "./components/ContractDetails";
import Balance from "./components/Balance";
import Seller from "./components/users/Seller";
import Visitor from "./components/users/Visitor";
import Buyer from "./components/users/Buyer";
import PreviousBuyers from "./components/PreviousBuyers";
// localhost
const escrowAddress = "0x5FbDB2315678afecb367f032d93F642f64180aa3"
// Move this to context?
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(window.ethereum);
const contract = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, provider);
// Show metamask for users to decide if they will pay or not
async function requestAccount() {
try {
await window.ethereum.request({ method: 'eth_requestAccounts' });
} catch (error) {
console.log("error");
console.error(error);
alert("Login to Metamask first");
}
}
function App() {
const [contractEnd, setContractEnd] = useState(true);
const [escrow, setEscrow] = useState({
state: null,
balance: 0,
price: 1, // 1 ETH by default
sales: 0,
previousBuyers: [],
});
// Use object instead?
const [seller, setSeller] = useState();
const [sellerBalance, setSellerBalance] = useState();
// Use object instead?
const [buyer, setBuyer] = useState();
const [buyerBalance, setBuyerBalance] = useState();
// Use object instead?
const [user, setUser] = useState();
const [userBalance, setUserBalance] = useState();
const [role, setRole] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
async function fetchData() {
try {
// 2.
// Contract event handlers
contract.on("Closed", async (when, event) => {
event.removeListener(); // Solve memory leak with this.
const contractState = await contract.state();
// const contractState = await contract.showState();
const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
const previousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
setEscrow({
...escrow,
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState), // Easier
// state: await contractState.toString(),
balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
previousBuyers,
})
const contractSeller = await contract.seller();
const contractSellerBalance = await provider.getBalance(contractSeller);
setSellerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractSellerBalance));
// console.log("when");
// console.log(when);
// console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when));
console.log("Event - Closed");
console.log(`State - ${humanReadableEscrowState(contractState)}`);
console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`)
});
contract.on("ConfirmPurchase", async (when, by, event) => {
event.removeListener(); // Solve memory leak with this.
const contractState = await contract.state();
const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
const previousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
setEscrow({
...escrow,
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState),
balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
previousBuyers,
})
setBuyer(by);
const contractBuyerBalance = await provider.getBalance(by);
setBuyerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBuyerBalance));
setRole("buyer");
console.log("This visitor became the buyer of this contract");
// console.log("when");
// console.log(when);
// console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when));
console.log("Event - ConfirmPurchase");
console.log(`By - ${by}`);
console.log(`State - ${humanReadableEscrowState(contractState)}`);
console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`)
});
contract.on("SellerRefundBuyer", async (when, event) => {
event.removeListener(); // Solve memory leak with this.
const contractState = await contract.state();
// const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
// const previousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
setEscrow({
...escrow,
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState),
// balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
// previousBuyers,
})
console.log("This seller refunded the buyer of this contract");
// console.log("when");
// console.log(when);
// console.log(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when));
console.log("Event - SellerRefundBuyer");
console.log(`State - ${humanReadableEscrowState(contractState)}`);
console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`)
});
contract.on("ConfirmReceived", async (when, by, event) => {
event.removeListener(); // Solve memory leak with this.
const contractState = await contract.state();
const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
const previousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
console.log(previousBuyers);
setEscrow({
...escrow,
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState),
balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
previousBuyers,
})
setBuyer(by);
const contractBuyerBalance = await provider.getBalance(by);
setBuyerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBuyerBalance));
console.log("Event - ConfirmReceived");
console.log(`By - ${by}`);
console.log(`State - ${humanReadableEscrowState(contractState)}`);
console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`)
});
contract.on("SellerRefunded", async (when, event) => {
event.removeListener(); // Solve memory leak with this.
const contractState = await contract.state();
const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
const previousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
console.log(previousBuyers);
setEscrow({
...escrow,
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState),
balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
previousBuyers,
})
const contractSeller = await contract.seller();
const contractSellerBalance = await provider.getBalance(contractSeller);
setSellerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractSellerBalance));
console.log("Event - SellerRefunded");
console.log(`State - ${humanReadableEscrowState(contractState)}`);
console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`)
});
contract.on("Restarted", async (when, event) => {
event.removeListener();
const contractState = await contract.state();
const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
const previousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
setEscrow({
...escrow,
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState),
balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
previousBuyers,
})
const contractSeller = await contract.seller();
const contractSellerBalance = await provider.getBalance(contractSeller);
setSellerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractSellerBalance));
setBuyer();
setBuyerBalance();
console.log("Event - Restarted");
console.log(`State - ${humanReadableEscrowState(contractState)}`);
console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`);
});
contract.on("End", async (_when, _event) => {
// This doesn't work
// event.removeListener();
// console.log("Event - End");
// console.log(`${moment(humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)).fromNow()} - ${humanReadableUnixTimestamp(when)}`)
setContractEnd(false);
});
// Contract State
const contractState = await contract.state()
const contractBalance = await provider.getBalance(contract.address);
const contractPrice = await contract.price()
// const contractSales = await contract.totalSales();
const contractPreviousBuyers = await contract.listPreviousBuyers();
// console.log(contractPreviousBuyers);
setEscrow({
state: humanReadableEscrowState(contractState),
balance: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBalance.toString()),
price: ethers.utils.formatEther(contractPrice.toString()),
// sales: contractSales.toString(),
previousBuyers: contractPreviousBuyers,
})
const contractSeller = await contract.seller();
setSeller(contractSeller);
const contractSellerBalance = await provider.getBalance(contractSeller);
setSellerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractSellerBalance));
const contractBuyer = await contract.buyer()
setBuyer(contractBuyer);
const contractBuyerBalance = await provider.getBalance(contractBuyer);
setBuyerBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractBuyerBalance)); // Should make this part work again.
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // user
const contractUser = await signer.getAddress();
setUser(contractUser);
const contractUserBalance = await provider.getBalance(contractUser);
setUserBalance(ethers.utils.formatEther(contractUserBalance));
if (contractUser === contractSeller) {
setRole("seller");
} else if (contractUser === contractBuyer) {
setRole("buyer");
} else {
setRole("visitor");
}
} catch (error) {
console.log("error");
console.error(error);
}
}
fetchData();
}, []);
// 1. Event functions
async function close() {
if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Sale") {
return;
}
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
// console.log("signer");
// console.log(signer);
const forClose = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await forClose.close();
await transaction.wait();
}
}
// Visitor
async function purchase() {
if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Sale") {
return;
}
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
const forPurchase = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await forPurchase.confirmPurchase({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
await transaction.wait();
}
}
async function receive() {
if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Locked") {
return;
}
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
const contract = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await contract.confirmReceived();
await transaction.wait();
}
}
async function refundBuyer() {
if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Locked") return
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
const forRefund = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await forRefund.refundBuyer();
await transaction.wait();
}
}
async function refundSeller() {
if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Release") return
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
const forRefund = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await forRefund.refundSeller();
await transaction.wait();
// call currentEscrowState here and it will show you inactive at the screen
// fetchGreeting()
}
}
async function restart() {
if (!escrow.state) return
// if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Closed" || escrow.state !== "Complete" ) return
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
const forRestart = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await forRestart.restartContract({ value: ethers.utils.parseEther("2.0") });
await transaction.wait();
}
}
async function end() {
if (!escrow.state) return
// if (!escrow.state || escrow.state !== "Closed" || escrow.state !== "Complete") return
if (typeof window.ethereum !== 'undefined') {
await requestAccount()
const signer = provider.getSigner(); // Your current metamask account;
const forEnd = new ethers.Contract(escrowAddress, Escrow.abi, signer);
const transaction = await forEnd.end();
await transaction.wait();
}
}
// End event
if (!contractEnd) {
return null;
}
if (!escrow.state) {
return null;
}
// const contextRef = createRef();
let balance;
if (role === "seller") {
balance = sellerBalance
} else if (role === "buyer") {
balance = buyerBalance;
} else {
balance = userBalance;
}
return (
<div>
<Sticky >
<Balance
balance={balance}
// setAccountAddress={setAccountAddress}
/>
</Sticky>
<div style={{
// borderTop: "1px solid black",
margin: "0 auto",
display: "flex",
flexFlow: "column",
alignItems: "center",
background: "#efefef",
minHeight: "100vh",
}}>
<ContractDetails
address={contract.address}
sales={escrow.previousBuyers.length}
escrowState={escrow.state}
price={escrow.price}
balance={escrow.balance}
// lastEdited={lastEdited}
/>
<br />
{escrow.previousBuyers.length > 0 && <div style={{
width: "28rem",
marginBottom: "1.5rem",
border: "1px solid black",
borderRadius: "0.5rem",
padding: "0.5rem 1rem 1rem 1rem",
background: "white",
}} ><PreviousBuyers previousBuyers={escrow.previousBuyers} /></div>}
{role && <div style={{
width: "28rem",
marginBottom: "1.5rem",
border: "1px solid black",
borderRadius: "0.5rem",
padding: "0.5rem 1rem 1rem 1rem",
background: "white",
}} >
{role === "seller" && <Seller
address={seller}
buyer={buyer}
escrowState={escrow.state}
close={close}
refundBuyer={refundBuyer}
refundSeller={refundSeller}
restart={restart}
end={end}
/>}
{role === "visitor" && <Visitor
address={user}
seller={seller}
// balance={userBalance}
escrowState={escrow.state}
purchase={purchase}
/>}
{role === "buyer" && <Buyer
address={buyer}
seller={seller}
escrowState={escrow.state}
receive={receive}
/>}
</div>}
</div>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
您可以使用以下方式测试浏览器使用的代码
$yarn start
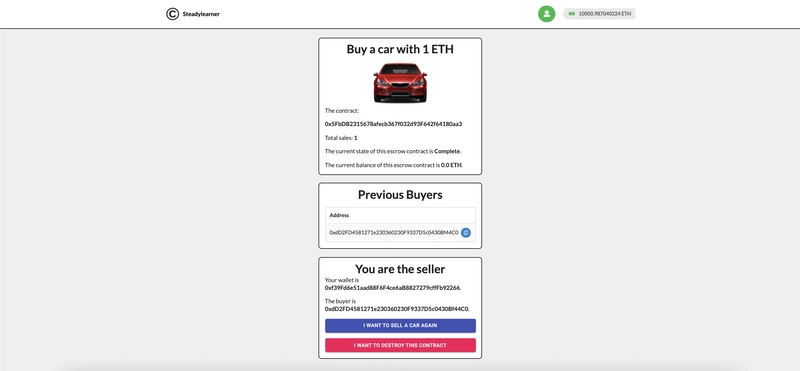
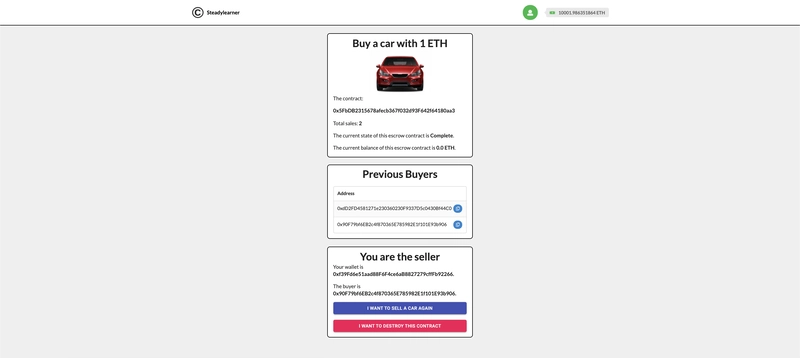
然后,它将显示与您在第一部分看到的图像有些相似的图像。
测试每个按钮和情况,例如卖家、访客、第一个买家、第二个买家等。您将看到页面根据我们之前定义的功能针对区块链的每个请求进行更新。
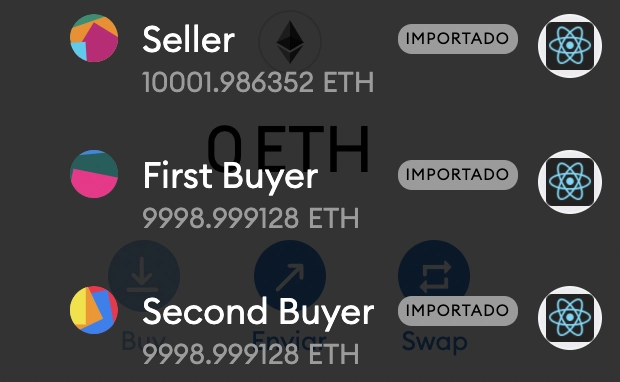
与第一位买家和第二位买家一起测试,您可以看到前一位买家列表出现在您的浏览器中,总销售额变为 2。
希望您能成功,并像上图一样作为卖家赚取 2ETH。
您还可以看到余额也随之修改。
如果您有足够的时间或有付费客户,您可以尝试使用 React Context 或 Redux 或其他任何内容更新前端部分,并使用baseweb提取 CSS 。
4. 结论
在这篇文章中,我们学习了如何使用 React、Hardhat 和 ethers js 编写全栈 dapp。
如果您很好地遵循了这篇文章,那么我在这篇文章开头给您的命令就足以在本地测试您的 dapp。
根据您的兴趣更新智能合约并创建您自己的项目。
准备和撰写这篇博文是一个很好的学习机会。
如果你喜欢这篇文章,请分享给大家。我计划分享更多区块链相关的内容。我对 ETH 和 POLKADOT 很感兴趣。
我可以编写一个全栈应用程序。
谢谢。
鏂囩珷鏉ユ簮锛�https://dev.to/steadylearner/how-to-make-a-fullstack-dapp-with-react-hardhat-and-ether-js-with-examples-4fi2 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com