PowerShell 速成课程
说实话,cmd.exe糟透了。我对 MS-DOS 6.0/6.22 记忆犹新,但克服了 Linux/Unix 的学习曲线后,就很难再回去了。PowerShell 1.0 发布时,我兴奋不已;终于有了一个“真正的” Windows 命令行界面了。但我又没法真正学习它,所以一直在安装cygwin或msys。
在发现 PowerShell Core支持多平台后,它又回到了我的视野中,因为它有几个用例:
- Windows 自动化
- 持续集成/持续交付
- 我们的JenkinsFile中充斥着内联脚本(有些脚本已迁移至 C#,但这一举措并未成功)
- 一些 AppVeyor可以
pwsh:在 Linux/Windows 上运行
- Windows OEM
- 如果您作为 Windows OEM 许可证持有者、设备 OEM/ODM 或企业 IT 定制/自动化 Windows 操作系统设置,则几乎必须使用 PowerShell
这更像是一份速查表/快速参考/食谱,而不是教程。如果你不习惯学习新的(脚本)语言,这份指南可能没什么帮助。
Shell 键盘快捷键
显示所有快捷方式的列表:
Get-PSReadlineKeyHandler
在 macOS/Linux 上,默认为emacs“编辑模式”。如果您使用过 emacs(或bash 的 emacs 模式),您会感觉很熟悉。在 Windows 上,默认为“编辑模式”,Windows但您可以:
Set-PSReadLineOption -EditMode Emacs
如果您是 PowerShell 新手,我强烈建议您切换到 emacs 模式。如果您只是想熟悉一下 Bash(如果您曾经使用过 Linux 终端的话)。
日常使用的命令:
# Movement
Ctrl+a # Beginning of line
Ctrl+e # End of line
Ctrl+f # Forward one character
Ctrl+b # Back one character
Alt+f # Forward one word
Alt+b # Back one word
# Editing
Alt+. # Insert last argument of previous command
Ctrl+d # Delete character
Alt+d # Delete word
Ctrl+u # Delete to beginning of line
Ctrl+k # Delete to end of line
# Command History
Ctrl+p # Previous command
Ctrl+n # Next command
Ctrl+o # Execute command and advance to next
Ctrl+r <text> # Search command history for <text>
Alt+.这是我在安装 Linux 的第一天就希望学到的。提示:你可以反复按下它来循环查看上次参数的历史记录。
与 相同Ctrl+o。如果您需要重做一系列命令:Ctrl+p回到开始,Ctrl+o Ctrl+o...Ctrl+n如果需要跳过一个命令,等等。
如果你使用的是 macOS/OSX 系统,并且使用默认终端Alt,Esc那么你可以使用Option(推荐)通过终端 > 偏好设置: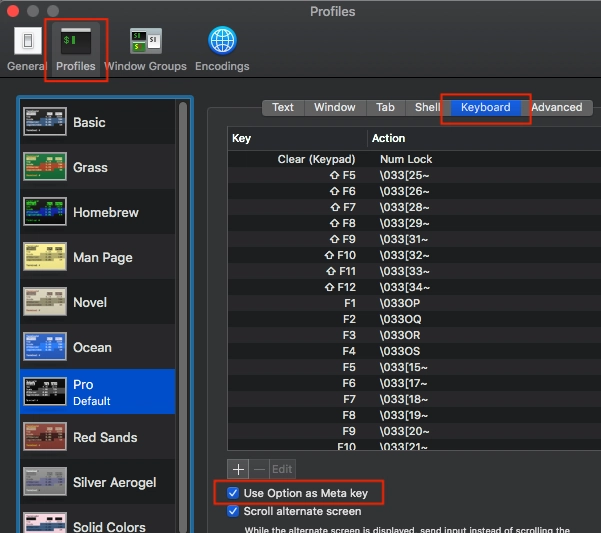
基本语法
文字和变量:
$boolean = $true # or `$false`
$string = "string"
$int = 42
$array = 1, 2, 3
$array2 = @(1, 2, 3)
$array[0] = $null # Remove first item
$hash = @{first = 1
"second" = 2; third = 3
}
# Add to hashtable
$hash += @{4 = "fourth"}
$hash["fifth"] = 5 # Key has to be quoted here
$hash[4] = $null # Remove value (but not key) from hash
# String with `PATH` environment variable
"$env:PATH ${env:PATH}: safer"
# Multi-line "here string"
@"
"Here-string" with value $env:PATH
"@
# Escape character
"literal `$ or `" within double-quotes"
# Evaluate expression
"Hello $(echo world)"
# Casting locks variable type
[int[]]$ints = "1", "2", "3"
$ints = "string" # Throws exception
# Destructuring
$first, $rest = $ints # first = 1; $rest = 2,3
控制流:
$value = 42
if ($value -eq 0) {
# Code
} elseif ($value -gt 1) {
} else {
}
$value = "value"
# Match against each string/int/variable/expression case
switch ($value)
{
"x" { echo "matched string" }
1 { echo "matched int" }
$var { echo "matched variable" }
{ $_ -gt 42 }{ echo "matched expression" }
default { }
}
$collection = 1,2,3,4
# Matched against each element of collection. `$_` is current item. `Break` applies to entire collection
switch ($collection)
{
1 { echo $_ 1 }
{ $_ -gt 1 } { echo "$_ Greater than 1" }
3 { echo $_ 3; break }
}
# Output is (NB: there's no 4):
#1 1
#2 Greater than 1
#3 Greater than 1
#3 3
foreach ($val in $collection) {
}
while ($value -gt 0) {
$value--
}
- 赋值:(
+=-=*=/=++--例如++$int或$int++或$int += 1) - 平等:
-eq-ne-gt-ge-lt-le - 匹配:(
-like-notlike通配符),-match-notmatch(正则表达式;$matches包含匹配的字符串) - 收容措施:
-contains-notcontains-in-notin - 类型:
-is-isnot - 逻辑:
-and-or-xor-not或!(例如$a -and $b或-not $a或!$a) - 替换:(
-replace替换字符串模式) - 除最后一项外,所有退货
$true或$false - 所有字符均不区分大小写。对于区分大小写的前缀,请使用
c(例如-clike) -
如果输入是集合,则输出是匹配的集合
必需品
# List commands containing "Path"
Get-Command -Name *path*
# Get help for `Get-Command`
Get-Help Get-Command
# List properties/methods of object
Get-Command | Get-Member
cd output/Debug
Set-Location output/Debug
# Current file/module's directory
$PSScriptRoot
ls
dir # also works which is freaky/helpful for migration
Get-ChildItem
# Pattern glob
ls *.jpg
Get-ChildItem *.jpg
# Just files
Get-ChildItem -File
# Just directories
Get-ChildItem -Directory
Get-ChildItem | ForEach-Object { $_.Name }
Get-ChildItem | Where-Object {$_.Length -gt 1024}
md tmp/
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Name tmp/ -Force | Out-Null
# Add to PATH
$env:PATH += ";$(env:USERPROFILE)" # `;` for Windows, `:` for *nix
$env:PATH += [IO.Path]::PathSeparator + $(pwd) # Any platform
# Check environment variable `GITHUB_TOKEN` is set
Test-Path Env:\GITHUB_TOKEN
# Test for file/directory
Test-Path subdir/child -PathType Leaf # `Container` for directory
pushd tmp/
popd
Push-Location tmp/
Pop-Location
cd - # Go back to previous directory
# Write to stdout, redirect stderr to stdout, send stdout to /dev/null
Write-Output "echo" 2>&1 > $null
&{
Write-Warning "warning"
Write-Output "stdout"
# Append warnings to tmp.txt, rest to /dev/null
} 3>> ./tmp.txt | Out-Null
# Write to stderr, redirect all, append to file
Write-Warning "oops" *>> ./tmp.txt
# Execute string
$ls = "ls"
& $ls
& $ls -l # with args
# Execute string with args
$ls_l = "ls -l"
Invoke-Expression $ls_l
# Execute file `script.ps1`
& ./script
$file = "./script.ps1"
& $file
# Execute command looking for failure text
$res = Invoke-Expression "& $cmd 2>&1"
if ($LASTEXITCODE -and ($res -match "0x800700C1")) {
# Do something
}
错误处理
Powershell 有终止(即异常)和非终止错误。
# Delete PathToDelete/ folder recursively ignoring all errors
Remove-Item -Force -Recurse -ErrorAction Ignore PathToDelete
# Make terminating error
Write-Error "fail" -ErrorAction Stop
throw "fail"
# Non-terminating errors are terminating
$ErrorActionPreference = "Stop"
# Handle terminating error
try {
throw "fail"
} catch [System.Management.Automation.RuntimeException] {
Write-Output "Throw'd: $_"
] catch [Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.WriteErrorException] {
Write-Output "Write-Error'd"
} catch {
# Any error
} finally {
# Always executes
}
# Handling non-terminating errors
if ($LastExitCode > 0) {
# Exit code of last program >0, which might mean it failed
}
if ($?) {
# Last operation succeeded
} else {
# Last operation failed
}
工作
# Start job in background (sleeps for 200 seconds)
$job = Start-Job { param($secs) Start-Sleep $secs } -ArgumentList 200
# Or
$job = Start-Sleep 200 &
# Wait for it with a timeout
Wait-Job $job -Timeout 4
# Jobs run in their own session, use -ArgumentList
$value = "hi"
Start-Job { Write-Output "value=$value" } | Wait-Job | Receive-Job
# Output: value=
Start-Job { Write-Output "value=$args" } -ArgumentList $value | Wait-Job | Receive-Job
# Output: value=hi
# Start a bunch of work in parallel
Get-Job | Remove-Job # Remove existing jobs
$MaxThreads = 2 # Limit concurrency
foreach ($_ in 0..10) {
# Wait for one of the jobs to finish
while ($(Get-Job -State Running).count -ge $MaxThreads) {
Start-Sleep 1
}
Start-Job -ScriptBlock { Start-Sleep 2 } # Random work
}
# Wait for them all to finish
while ($(Get-Job -State Running)){
Start-Sleep 1
}
- 工作
- 如果使用相对路径,请小心:作业从
$HOMEmacOS/Linux 和Documents/Windows 上启动 - 需要
Receive-Job查看 stdout/stderr - 来自此 SO 的并行工作片段
参数与功能
脚本的命令行参数被视为param()放置在文件顶部。
function Hello { echo Hi }
# Call the function
Hello
# Output: Hi
# Function with two named params. First with type and default (both optional)
function HelloWithParams {
param([string]$name = "<unknown>", $greeting)
echo "hello $name! $greeting"
}
HelloWithParams 1 2
# Output: hello 1! 2
HelloWithParams -greeting 40
# Output: hello <unknown>! 40
# Function with switch and positional parameters
function Greeting {
param([switch]$flag)
echo "hello $flag $args"
}
Greeting more stuff
# Output: hello False more stuff
Greeting -flag more stuff
# Output: hello True more stuff
Greeting -flag:$false more stuff
# Output: hello False more stuff
function PositionalParams {
param(
[parameter(Position=0)]
$greeting,
[string]$name,
[parameter(Position=1)]
$tail
)
echo "$greeting $name$tail"
}
PositionalParams hi "!"
# Output: hi !
PositionalParams hi -name jake "!"
# Output: hi jake!
PositionalParams hi "!" -name jake
# Output: hi jake!
function FormalHello {
param(
# Params default to optional
[parameter(Mandatory=$true, HelpMessage="Initial greeting")]
[string]$greeting,
# If have multiple values have to use @()
[string[]]$name = @("Sir", "<unknown>")
)
echo "$greeting $name $suffix"
}
FormalHello "Greetings"
# Output: Greetings Sir <unknown>
FormalHello -name sir,jake,3rd -greeting welcome
# Output: welcome sir jake 3rd
杂项
Visual Studio 代码:
- 使用扩展名。
- 在 Windows 上,安装 PowerShell Core,然后在 Visual Studio Code 中单击“PowerShell 会话菜单”:
从出现的命令面板中选择切换到 PowerShell Core 6 (x64)。
詹金斯:
- 内联 powershell 或调用脚本:
powershell '''
& ./script.ps1
'''
- 调用脚本并处理退出代码:
def res = powershell returnStatus: true, script: '''
& ./script.ps1
'''
if (res != 0) {
currentBuild.result = 'UNSTABLE'
}
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com