使用 React Hooks 制作一个包含 15 个谜题的游戏
我们正在做什么!
在本文中,我们将使用 React Hooks 制作一个简单的 15-Puzzle,但首先什么是 15-Puzzle 呢?
正如维基百科所定义的那样,
15 拼图(也称为宝石拼图、Boss 拼图、十五游戏、神秘广场等等)是一种滑动拼图,由一框按随机顺序排列的编号方形瓷砖组成,其中缺少一块瓷砖。
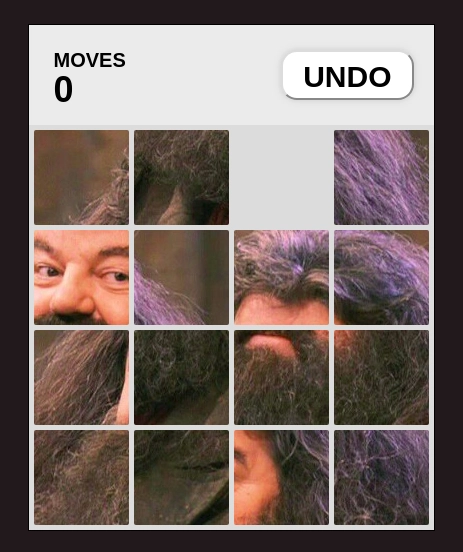
然而,数字版的拼图或多或少是数学版的。玩具店里出售的通常是游戏的图像版。在这个版本中,每个方块都是图像的一个小方块,当这些方块按正确的顺序排列时,完整的图像就形成了。就像下图(这里的拼图处于乱序状态)一样,
在本文中,我们将构建这个特定版本的谜题。当谜题的图块按正确顺序排列后,我们将得到一幅鲁伯·海格的图像,他是霍格沃茨的猎场看守人兼钥匙和场地保管人。
一些观察
在我们开始编写这个谜题的代码之前,让我们先注意一下关于这个谜题的一些事情;
- 只能移动与网格中的空白方块相邻(即共享边)的方块。
- 它们只能移动到空方块的位置。
- 如果我们将空方块视为空瓷砖,那么将相邻瓷砖移动到空方块就可以建模为将瓷砖的位置与空瓷砖交换。
- 当瓷砖的顺序正确时,
i-th瓷砖占据网格中第Math.floor(i / 4)行第 列的方格。i % 4 - 在任何时间点,最多只能在任意一个方向上移动一块瓷砖。
考虑到这些观察结果,让我们开始构建谜题。
脚手架和常量
首先,我们来写一个简单的网页,用于渲染我们的 React 应用。为了简单起见,我们用 Pug 来写。
html
head
title 15 Puzzle (Using React Hooks)
meta(name='viewport', content='initial-scale=1.0')
link(rel='stylesheet', href='/style.css')
body
#root
script(type='text/javascript', src='https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/react/16.8.6/umd/react.production.min.js')
script(type='text/javascript', src='https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/react-dom/16.8.6/umd/react-dom.production.min.js')
script(type='text/javascript', src='/index.js')
有了这个网页结构,让我们在中定义一些常量和实用程序index.js。
const NUM_ROWS = 4;
const NUM_COLS = 4;
const NUM_TILES = NUM_ROWS * NUM_COLS;
const EMPTY_INDEX = NUM_TILES - 1;
const SHUFFLE_MOVES_RANGE = [60, 80];
const MOVE_DIRECTIONS = ['up', 'down', 'left', 'right'];
function rand (min, max) {
return min + Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1));
}
这里,rand函数生成一个介于min和max(含)之间的随机整数。常量SHUFFLE_MOVES_RANGE定义了为了打乱拼图板,我们想要执行的最小和最大随机移动次数。EMPTY_INDEX是空图块的索引。当所有图块都按正确顺序排列时,右下角的方格,即第 16 个方格(数组索引 15)将成为空方格。
定义GameState
现在让我们编写谜题的逻辑,并将其封装在一个名为 的类中GameState。这个GameState类应该是单例的,因为在任何时间点,应用中都应该只有一个游戏在运行。所以,我们先来编写这段逻辑。
为了使类成为单例,我们将定义一个名为的静态属性,instance它将保存对类的当前实例的引用,以及一个静态方法getInstance,如果存在则返回当前实例,否则它将创建一个新实例并将其返回给我们。
class GameState {
static instance = null;
static getInstance () {
if (!GameState.instance) GameState.instance = new GameState();
return GameState.instance;
}
}
在内部,GameState我们希望跟踪棋盘的当前状态、用户已玩过的移动次数以及之前的棋盘状态堆栈,以便用户可以撤消他/她当前的移动并回到之前的状态。
这里我们存储的最重要的信息是拼图板的状态。我们先来对它进行建模。
拼图板由 16 块方块组成(包括空方块)。在任何时间点,每块方块都位于网格中的特定位置。方块的位置可以用两个整数表示row index和column index。我们可以将其建模为一个整数对数组,如下所示(以下是方块按正确顺序排列的棋盘表示):
[
[0, 0], // 1st tile is at 1st row, 1st column
[0, 1], // 2nd tile is at 1st row, 2nd column
[0, 2],
[0, 3], // 4th tile is at 1st row, 4th column
[1, 0], // 5th tile is at 2nd row, 1st column
[1, 1],
...
[3, 2],
[3, 3], // 16th tile is at 4th row, 4th column (this is the empty tile)
]
让我们编写一个静态方法来生成一个棋盘状态,其中的瓷砖按正确的顺序排列,记住,当瓷砖按正确的顺序排列时,i-th瓷砖位于Math.floor(i / 4) th行和i % 4列。
另外,当谜题解决后,方块的顺序是正确的。因此,我们定义一个名为 的静态属性solvedBoard,用于存储棋盘的解决状态。
class GameState {
// ...
static getNewBoard () {
return Array(NUM_TILES).fill(0).map((x, index) => [
Math.floor(index / NUM_ROWS),
index % NUM_COLS
]);
}
static solvedBoard = GameState.getNewBoard();
}
当游戏开始时,
- 移动计数器设置为 0,
- 先前状态的堆栈为空,并且
- 棋盘处于有序状态。
然后,从这个状态开始,我们在将棋盘呈现给用户进行解题之前,对其进行打乱/打乱。我们先写一下这个方法。现在,我们将跳过打乱/打乱棋盘的方法的编写。我们暂时只编写一个存根来代替它。
class GameState {
// ...
constructor () {
this.startNewGame();
}
startNewGame () {
this.moves = 0;
this.board = GameState.getNewBoard();
this.stack = [];
this.shuffle(); // we are still to define this method,
// let's put a stub in its place for now
}
shuffle () {
// set a flag that we are to shuffle the board
this.shuffling = true;
// Do some shuffling here ...
// unset the flag after we are done
this.shuffling = false;
}
}
现在,让我们定义移动图块的方法。首先,我们需要确定某个图块是否可以移动。假设该图块现在i-th位于位置。然后,只有当空图块(即该图块当前位于其相邻位置)时,该图块才可以移动。要相邻,两个图块必须位于同一行或同一列;如果它们位于同一行,则它们的列索引之差必须等于 1;如果它们位于同一列,则它们的行索引之差必须等于 1。(r, c)i-th16th
class GameState {
// ...
canMoveTile (index) {
// if the tile index is invalid, we can't move it
if (index < 0 || index >= NUM_TILES) return false;
// get the current position of the tile and the empty tile
const tilePos = this.board[index];
const emptyPos = this.board[EMPTY_INDEX];
// if they are in the same row, then difference in their
// column indices must be 1
if (tilePos[0] === emptyPos[0])
return Math.abs(tilePos[1] - emptyPos[1]) === 1;
// if they are in the same column, then difference in their
// row indices must be 1
else if (tilePos[1] === emptyPos[1])
return Math.abs(tilePos[0] - emptyPos[0]) === 1;
// otherwise they are not adjacent
else return false;
}
}
实际上,将棋子移动到空格要容易得多,我们只需要交换棋子和空格的位置即可。此外,我们还需要做一些记录工作,即增加移动次数计数器,并将移动前的棋盘状态压入堆栈。(如果处于洗牌阶段,我们不需要计数移动次数或将状态压入堆栈)。
如果棋盘已解,我们希望冻结棋盘并禁止棋子进一步移动。但目前,我们不会实现检查棋盘是否已解的方法。我们将编写一个存根来代替实际的方法。
class GameState {
// ...
moveTile (index) {
// if we are not shuffling, and the board is already solved,
// then we don't need to move anything
// Note that, the isSolved method is not defined yet
// let's stub that to return false always, for now
if (!this.shuffling && this.isSolved()) return false;
// if the tile can not be moved in the first place ...
if (!this.canMoveTile(index)) return false;
// Get the positions of the tile and the empty tile
const emptyPosition = [...this.board[EMPTY_INDEX]];
const tilePosition = [...this.board[index]];
// copy the current board and swap the positions
let boardAfterMove = [...this.board];
boardAfterMove[EMPTY_INDEX] = tilePosition;
boardAfterMove[index] = emptyPosition;
// update the board, moves counter and the stack
if (!this.shuffling) this.stack.push(this.board);
this.board = boardAfterMove;
if (!this.shuffling) this.moves += 1;
return true;
}
isSolved () {
return false; // stub
}
}
通过观察,我们知道,在任意时间点,最多只能在任意方向上移动一个方块。因此,如果已知移动方向,我们就可以确定移动哪个方块。例如,如果已知移动方向向上,那么只能移动空方块正下方的方块。同样,如果已知移动方向向左,那么只能移动空方块正右侧的方块。让我们编写一个方法,根据给定的移动方向推断出要移动哪个方块,然后移动它。
class GameState {
// ...
moveInDirection (dir) {
// get the position of the empty square
const epos = this.board[EMPTY_INDEX];
// deduce the position of the tile, from the direction
// if the direction is 'up', we want to move the tile
// immediately below empty, if direction is 'down', then
// the tile immediately above empty and so on
const posToMove = dir === 'up' ? [epos[0]+1, epos[1]]
: dir === 'down' ? [epos[0]-1, epos[1]]
: dir === 'left' ? [epos[0], epos[1]+1]
: dir === 'right' ? [epos[0], epos[1]-1]
: epos;
// find the index of the tile currently in posToMove
let tileToMove = EMPTY_INDEX;
for (let i=0; i<NUM_TILES; i++) {
if (this.board[i][0] === posToMove[0] && this.board[i][1] === posToMove[1]) {
tileToMove = i;
break;
}
}
// move the tile
this.moveTile(tileToMove);
}
}
现在我们已经完成了图块移动的逻辑,接下来我们来编写撤销上一次移动的方法。这很简单,我们只需要从堆栈中弹出之前的状态并恢复即可。此外,我们还需要减少移动计数器。
class GameState {
// ...
undo () {
if (this.stack.length === 0) return false;
this.board = this.stack.pop();
this.moves -= 1;
}
}
至此,我们已经完成了大部分游戏逻辑,除了shuffle和isSloved方法,它们目前还是存根。现在让我们来编写这些方法。为了简单起见,我们将在棋盘上执行一些随机移动来打乱棋盘。为了检查棋盘是否已解决,我们只需将棋盘的当前状态与solvedBoard我们之前定义的静态属性进行比较即可。
class GameState {
// ...
shuffle () {
this.shuffling = true;
let shuffleMoves = rand(...SHUFFLE_MOVES_RANGE);
while (shuffleMoves --> 0) {
this.moveInDirection (MOVE_DIRECTIONS[rand(0,3)]);
}
this.shuffling = false;
}
isSolved () {
for (let i=0; i<NUM_TILES; i++) {
if (this.board[i][0] !== GameState.solvedBoard[i][0]
|| this.board[i][1] !== GameState.solvedBoard[i][1])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
现在,为了方便起见,让我们编写一种方法,将游戏的当前状态作为一个简单的对象提供给我们。
class GameState {
// ...
getState () {
// inside the object literal, `this` will refer to
// the object we are making, not to the current GameState instance.
// So, we will store the context of `this` in a constant called `self`
// and use it.
// Another way to do it is to use GameState.instance instead of self.
// that will work, because GameState is a singleton class.
const self = this;
return {
board: self.board,
moves: self.moves,
solved: self.isSolved(),
};
}
}
至此,我们GameState类的实现就完成了。我们将在自定义 React Hook 中使用它来驱动游戏的 React 应用。
自useGameState定义钩子
现在,让我们将 GameState 功能包装到一个自定义的 React Hook 中,以便在我们的 React 应用程序中使用它。在这个 Hook 中,我们需要注册按键事件处理函数,以便用户可以使用键盘的方向键来玩拼图;生成点击处理函数,以便用户可以点击方块来移动它们;此外,我们还希望创建辅助函数来撤消移动并开始新游戏。
我们将把 keyup 事件处理程序附加到 document 对象。此操作只需在应用挂载时执行一次,并在应用卸载时移除事件处理程序。
此 Hook 的主要目的是将 GameState 实例包装为 React 状态,以便 React 组件可以使用和更新该状态。当然,我们不会将原始的 setState 方法暴露给组件。相反,我们会将诸如newGame、undo和 之类的函数暴露move给组件,以便它们在用户想要开始新游戏、撤消移动或移动特定图块时触发状态更新。我们只会暴露使用 Hook 的组件绝对需要的那部分状态和更新逻辑。(键盘事件将由附加到 document 对象的监听器处理。组件无需访问这些事件处理程序。)
function useGameState () {
// get the current GameState instance
const gameState = GameState.getInstance();
// create a react state from the GameState instance
const [state, setState] = React.useState(gameState.getState());
// start a new game and update the react state
function newGame () {
gameState.startNewGame();
setState(gameState.getState());
}
// undo the latest move and update the react state
function undo () {
gameState.undo();
setState(gameState.getState());
}
// return a function that will move the i-th tile
// and update the react state
function move (i) {
return function () {
gameState.moveTile(i);
setState(gameState.getState());
}
}
React.useEffect(() => {
// attach the keyboard event listeners to document
document.addEventListener('keyup', function listeners (event) {
if (event.keyCode === 37) gameState.moveInDirection('left');
else if (event.keyCode === 38) gameState.moveInDirection('up');
else if (event.keyCode === 39) gameState.moveInDirection('right');
else if (event.keyCode === 40) gameState.moveInDirection('down');
setState(gameState.getState());
});
// remove the evant listeners when the app unmounts
return (() => window.removeEventListener(listeners));
}, [gameState]);
// this effect hook will run only when the GameState instance changes.
// That is, only when the app is mounted and the GameState instance
// is created
// expose the state and the update functions for the components
return [state.board, state.moves, state.solved, newGame, undo, move];
}
Puzzle 的 React 组件
现在我们已经有了谜题的概念模型,以及在用户交互事件发生时更新该模型的函数,接下来让我们编写一些组件来在屏幕上显示游戏。这里的游戏显示非常简单,它有一个标题部分,显示用户已进行的移动次数和撤消按钮。标题下方是包含图块的谜题板。谜题板还会PLAY AGAIN在谜题解决后显示一个按钮。
在拼图板中,我们不需要渲染第 16 个图块,因为它代表空图块。在显示中,它将保持为空。在每个显示的图块上,我们将添加一个onClick事件处理程序,以便当用户点击一个图块时,如果它可以移动,它就会移动。
拼图板的尺寸应与拼图板的尺寸相符400px * 400px,瓷砖的放置位置也应与拼图板的尺寸相符。每块瓷砖的尺寸应95px * 95px与5px瓷砖之间留有间距。
以下函数实现了该App组件。这是应用程序的基本布局。
function App () {
const [board, moves, solved, newGame, undo, move] = useGameState();
return (
<div className='game-container'>
<div className='game-header'>
<div className='moves'>
{moves}
</div>
<button className='big-button' onClick={undo}> UNDO </button>
</div>
<div className='board'>
{
board.slice(0,-1).map((pos, index) => (
<Tile index={index} pos={pos} onClick={move(index)} />
))
}
{ solved &&
<div className='overlay'>
<button className='big-button' onClick={newGame}>
PLAY AGAIN
</button>
</div>
}
</div>
</div>
);
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
现在,让我们实现一个Tile组件,它将显示并定位棋盘上每个单独的图块。如前所述,图块将相对于棋盘进行绝对定位。给定图块的row index和column index,我们可以找到它在棋盘上的位置。我们知道网格上每个方格的尺寸是图块之间100px * 100px留有5px间距。因此,我们只需将图块的row index和column index乘以 100 再加 5,即可得到图块的顶部和左侧位置。
类似地,我们可以通过确定每个图块按正确顺序排列时显示的背景图像的哪个部分来推导其背景图像的 backgroundPosition。为此,首先需要计算图块按正确顺序排列时的位置。我们知道图块按正确的顺序i-th位于Math.floor(i / 4)第 行i % 4第 列。由此,我们可以通过将行和列索引乘以 100,然后加 5,以距离顶部和左侧像素为单位计算出其位置。背景位置将是这些值的负数。
function Tile ({index, pos, onClick}) {
const top = pos[0]*100 + 5;
const left = pos[1]*100 + 5;
const bgLeft = (index%4)*100 + 5;
const bgTop = Math.floor(index/4)*100 + 5;
return <div
className='tile'
onClick={onClick}
style={{top, left, backgroundPosition: `-${bgLeft}px -${bgTop}px`}}
/>;
}
拼图造型
在设计拼图样式之前,我们需要找到一张合适的400px * 400px图片作为图块的背景图。或者,我们也可以使用数字作为拼图的样式(就像维基百科中提到的 15-Puzzle 那样)。无论如何,让我们来看看设计这个应用样式的一些重要步骤。
定位棋盘和棋子
棋盘的实际宽度和高度为400px + 5px,因为 4 列或 4 行需要 5 个边距。然而,这并不影响图块的尺寸,因为我们可以放心地认为第 5 个边距位于棋盘之外。棋盘需要将位置声明为 ,relative以便图块可以相对于棋盘进行绝对定位。
对于图块,其尺寸将为 ,95px * 95px以容纳5px间距。background-size然而,它们的 应该是400px * 400px,因为每个图块仅显示完整尺寸图像中的特定方块400px * 400px。背景位置将由 React 组件设置为内联样式。
为了让图块的移动看起来流畅自然,我们可以使用 CSS 过渡效果。这里我们在图块上使用了 0.1 秒的缓入缓出过渡效果。
.board {
width: 405px;
height: 405px;
position: relative;
background: #ddd;
}
.tile {
width: 95px;
height: 95px;
position: absolute;
background: white;
transition: all 0.1s ease-in-out;
border-radius: 2px;
background-image: url('@{bg-img}');
background-size: 400px 400px;
}
定位覆盖层
覆盖层是棋盘的另一个直接子元素。游戏结束时,它需要覆盖棋盘。因此,我们将赋予它与棋盘相同的尺寸,并将其绝对放置在 的位置(0, 0)。它需要位于棋盘上方,因此我们将高度设置为z-index。我们还将赋予它一个半透明的深色背景色。它将包含PLAY AGAIN位于中心的按钮,因此我们将它设置为一个弹性容器,并将align-items和justify-content设置为center。
.overlay {
width: 405px;
height: 405px;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
z-index: 10;
background: #0004;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
这是包含本文所述所有内容的笔。
(请原谅我在 less 文件的开头嵌入了 base64 编码形式的图像。在 codepen 上添加资产文件是 PRO 独有的功能,而我很遗憾,我是免费用户。)
希望你喜欢阅读这个小项目并从中有所收获。你可以在gnsp.in
上找到更多关于我的信息。
谢谢阅读!
鏂囩珷鏉ユ簮锛�https://dev.to/gnsp/making-a-15-puzzle-game-using-react-hooks-3110 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com