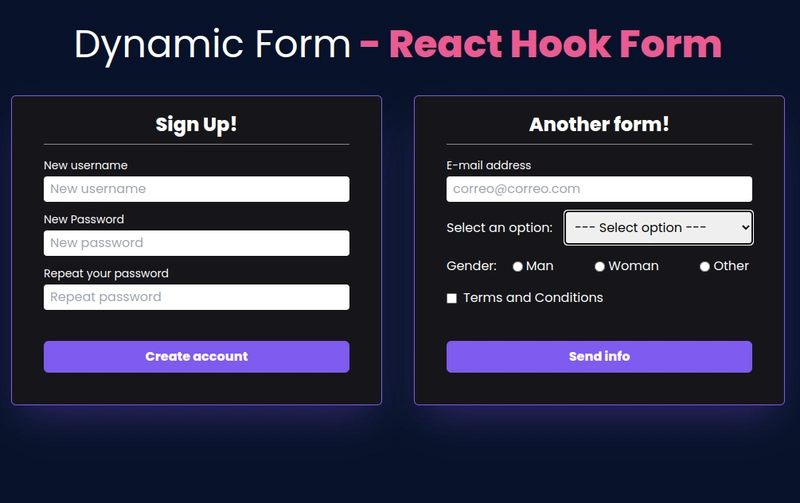
使用 React Hook Form 实现动态表单。📝
这次,我们将再次创建动态表单,但现在借助react-hook-form库。
注意📣:您需要具备 Typescript 知识才能学习本教程,以及 React JS 知识。
你可能会对这篇文章感兴趣,我们在这篇文章中也做了同样的事情,但使用了Formik库。😉
目录。
📌需要用到的技术。📌 创建项目。📌
第一步。📌 创建表单对象。📌为我们的表单创建验证模式。📌生成输入的函数。📌 创建
表单组件。📌 创建每个输入的组件。📌 使用我们的表单组件。📌 总结。
💊 要使用的技术。
- React JS 18.2.0
- TypeScript 4.9.3
- React Hook Form 7.43.0
- Vite JS 4.1.0
- Tailwind CSS 3.2.4(不显示安装和配置过程)。
💊 创建项目。
我们将为该项目命名:(dynamic-forms-rhf可选,您可以随意命名)。
npm create vite@latest
我们使用 Vite JS 创建项目,并选择 React with TypeScript。
然后运行以下命令导航到刚刚创建的目录。
cd dynamic-forms-rhf
然后我们安装依赖项。
npm install
然后我们在代码编辑器中打开项目(在我的情况下是 VS 代码)。
code .
💊 第一步。
在src/App.tsx文件中,我们删除所有内容并创建一个显示 的组件hello world。
const App = () => {
return (
<div>Hello world</div>
)
}
export default App
🚨 注意:每次创建新文件夹时,我们都会创建一个index.ts文件,将同一文件夹内其他文件的所有函数和组件进行分组导出,这样这些函数就可以通过单一引用导入,这称为barrel 文件。
让我们创建一个布局,创建一个文件夹src/components并在里面创建一个文件Layout.tsx。
export const Layout = ({ children }: { children: JSX.Element | JSX.Element[] }) => {
return (
<>
<h1 className='text-center my-10 text-5xl'>
<span>Dynamic Form</span>
<span className='font-bold bg-clip-text text-transparent text-[#EC5990]'>
{' - '}
React Hook Form
</span>
</h1>
<main className='grid sm:grid-cols-2 grid-cols-1 sm:mb-0 mb-10 gap-10 place-items-start justify-items-center px-5'>
{children}
</main>
</>
)
}
现在,在src/App.tsx文件中,我们添加布局。
import { Layout } from './components'
const App = () => {
return (
<Layout>
<span>Form</span>
</Layout>
)
}
export default App
然后我们将安装必要的软件包。
- react-hook-form,以更简单的方式处理表单。
- 是的,处理表单验证。
- @hookform/resolvers,将 yup 与 react-hook-form 集成。
npm install -E react-hook-form @hookform/resolvers yup
之前我已经做过同样的动态表单练习,但使用的是 Formik 库,事实与我们要做的非常相似,唯一需要改变的是表单和输入等组件。
💊 创建表单对象。
💊 为输入创建类型。
首先,让我们创建类型。我们创建一个新文件夹src/types并创建 index.ts 文件。
现在我们首先为输入创建接口,它可以有更多的属性,但这些足以构成这个例子。
重点是InputProps接口的最后三个属性:
- typeValue:必要的,因为我们需要告诉 Yup 输入接受什么类型的值。
- 验证:根据输入设置为 Yup 的验证;我只设置了基本验证,但如果您查看 Yup 文档,则可以集成更多验证。
- 如果您没有使用过 Yup,那么对您来说可能更复杂的验证可能是oneOf。此验证需要另一个输入框的引用或名称,以验证两个输入框是否包含相同的内容。此验证的一个例子是,在一个输入框中创建密码,而在另一个输入框中需要重复输入密码,并且两个值必须匹配。
- 选项:仅当输入是选择或一组单选类型输入时,此属性才是必需的。
export interface InputProps {
type: 'text' | 'radio' | 'email' | 'password' | 'select' | 'checkbox'
name: string
value: string | number | boolean
placeholder?: string
label?: string
typeValue?: 'boolean' | 'number'
validations?: Validation[]
options?: Opt[]
}
export interface Opt {
value: string | number
desc: string
}
export interface Validation {
type: 'required' | 'isEmail' | 'minLength' | 'isTrue' | 'oneOf'
value?: string | number | boolean
message: string
ref?: string
}
我们同时为即将开发的表单类型创建了此类型。
在本例中,我们只需创建两个表单。
export type FormSection = 'register' | 'another'
💊 现在我们借助类型来创建表单对象。
感谢 Typescript,我们可以在这个对象中创建表单。
我们创建一个新文件夹src/lib,并在其中创建文件form.ts并添加以下内容:
import { FormSection, InputProps } from '../types';
export const forms: { [K in FormSection]: InputProps[] } =
{
register: [
{
label: "New username",
type: "text",
name: "username",
placeholder: "New username",
value: "",
validations: [
{
type: "minLength",
value: 3,
message: "Min. 3 characters",
},
{
type: "required",
message: "Username is required"
},
],
},
{
label: "New Password",
type: "password",
name: "password",
placeholder: "New password",
value: "",
validations: [
{
type: "required",
message: "Password is required"
},
{
type: "minLength",
value: 5,
message: "Min. 5 characters",
}
],
},
{
label: 'Repeat your password',
type: "password",
name: "repeat_password",
placeholder: "Repeat password",
value: "",
validations: [
{
type: "required",
message: "Repeat password is required"
},
{
type: "minLength",
value: 5,
message: "Min. 5 characters",
},
{
type: 'oneOf',
message: 'Passwords must match',
ref: 'password'
}
],
},
],
another: [
{
label: "E-mail address",
type: "email",
name: "email",
placeholder: "correo@correo.com",
value: "",
validations: [
{
type: "required",
message: "Email is required"
},
{
type: "isEmail",
message: "Email no valid"
}
],
},
{
type: "select",
name: "rol",
label: "Select an option: ",
value: "",
options: [
{
value: "admin",
desc: "Admin",
},
{
value: "user",
desc: "User"
},
{
value: "super-admin",
desc: "Super Admin"
}
],
validations: [
{
type: "required",
message: "Rol is required"
}
]
},
{
type: "radio",
name: "gender",
label: "Gender: ",
value: "",
options: [
{
value: 'man',
desc: "Man"
},
{
value: "woman",
desc: "Woman"
},
{
value: "other",
desc: "Other"
},
],
validations: [
{
type: "required",
message: "Gender is required"
}
]
},
{
type: "checkbox",
name: "terms",
typeValue: "boolean",
label: "Terms and Conditions",
value: false,
validations: [
{
type: "isTrue",
message: "Accept the terms!"
}
]
},
]
}
💊 为我们的表单创建验证模式。
让我们在 src/lib 中创建一个新文件,并将其命名为getInputs.ts。
我们创建一个新函数来生成每个输入的验证。
此函数接收字段,每个字段的类型均为 InputProps 。我们还将仅创建两种类型,以便 Typescript 稍后不会打扰我们。
请注意,我们创建了 YupBoolean 和 YupString 类型。如果您需要,可以添加其他类型来处理其他数据类型,例如数字或数组。例如:
type YupNumber = Yup.NumberSchema<boolean | undefined, AnyObject, number | undefined>我没有添加它,因为在我的界面中我没有处理任何类型数字或数组的验证。
import * as Yup from "yup";
import { AnyObject } from "yup/lib/types";
import { FormSection, InputProps } from '../types';
import { forms } from '../lib';
type YupBoolean = Yup.BooleanSchema<boolean | undefined, AnyObject, boolean | undefined>
type YupString = Yup.StringSchema<string | undefined, AnyObject, string | undefined>
const generateValidations = (field: InputProps) => {}
首先,我们创建一个变量,并用处理输入的数据类型进行初始化。数据类型由typeValue属性获取,如果未定义,则默认数据类型为string。然后,我们执行函数:
let schema = Yup[field.typeValue || 'string']()
然后我们将对该字段进行验证,因为它是一个数组。
在循环中,我们将使用 switch case,评估字段具有什么类型的规则。
const generateValidations = (field: InputProps) => {
let schema = Yup[field.typeValue || 'string']()
for (const rule of field.validations) {
switch (rule.type) { }
}
}
在每次切换时,我们都会覆盖 schema 变量。方法如下:
如果它有“isTrue”验证,则表示输入处理布尔值,因此我们希望我们的模式表现为 YupBoolean,否则 Typescript 会报错。然后我们执行与每个案例相关的函数。
例如,在“isTrue”的情况下,我们执行具有完全相同名称的函数,并在其中传递消息
case 'isTrue' : schema = (schema as YupBoolean).isTrue(rule.message); break;
如果验证是 oneOf,我们需要将其作为第一个参数发送一个数组,并将消息作为第二个参数发送。
如果是数组,它必须是你想要匹配的值,但在本例中,我们想要匹配另一个字段的值,因此我们使用Yup.ref ,它需要一个指向输入框name属性的字符串。
这样,验证完成后,它会检查两个字段是否包含相同的值。
case 'oneOf' : schema = (schema as YupString)
.oneOf(
[ Yup.ref(rule.ref as string) ],
rule.message
);
break;
这就是我们的第一个函数。最后,我们返回变量schema。
注意,在函数的开头,我们设置了一个条件:如果字段没有验证,则返回 null 并避免执行循环。
import * as Yup from "yup";
import { AnyObject } from "yup/lib/types";
import { FormSection, InputProps } from '../types';
import { forms } from '../lib';
type YupBoolean = Yup.BooleanSchema<boolean | undefined, AnyObject, boolean | undefined>
type YupString = Yup.StringSchema<string | undefined, AnyObject, string | undefined>
const generateValidations = (field: InputProps) => {
if (!field.validations) return null
let schema = Yup[field.typeValue || 'string']()
for (const rule of field.validations) {
switch (rule.type) {
case 'isTrue' : schema = (schema as YupBoolean).isTrue(rule.message); break;
case 'isEmail' : schema = (schema as YupString).email(rule.message); break;
case 'minLength': schema = (schema as YupString).min(rule?.value as number, rule.message); break;
case 'oneOf' : schema = (schema as YupString).oneOf([Yup.ref((rule as any).ref)], rule.message); break;
default : schema = schema.required(rule.message); break;
}
}
return schema
}
💊 生成输入的函数。
首先,我们要创建一个函数,并将其命名为 getInputs,它是通用类型,并接收部分作为参数(也就是说,您想要获取其字段的表单,在这种情况下它可以是 signUp 或其他表单)。
我们将创建两个变量,并将它们初始化为空对象,最后必须包含新属性。
export const getInputs = <T>(section: FormSection) => {
let initialValues: { [key: string]: any } = {};
let validationsFields: { [key: string]: any } = {};
};
在函数内部,我们将创建一个 for 循环。在其中,我们将遍历特定表单的字段。
-
在循环内部,我们将计算 initialValues 变量中的值,并使用字段的 name 属性来计算值。
-
我们验证该字段是否有验证。
- 如果没有验证,则继续下一个字段。
- 如果有验证,我们将执行在generateValidations之前创建的函数并将字段作为参数发送。
-
然后对于 validationsFields 变量,我们还使用字段的名称属性计算值,并分配已生成的验证模式。
for (const field of forms[section]) {
initialValues[field.name] = field.value;
if (!field.validations) continue;
const schema = generateValidations(field)
validationsFields[field.name] = schema;
}
一旦循环完成,我们必须返回 3 个属性。
- Yup.object中的验证模式,扩展了validationsFields属性。```tsx
验证模式:Yup.object({...validationsFields}),
- The initial values, and we will make them behave as generic so that we can use them afterwards
```tsx
initialValues: initialValues as T,
- 我们想要在表单中显示的字段。```tsx
输入:forms[section]
This is what our function will look like at the end
```tsx
export const getInputs = <T>(section: FormSection) => {
let initialValues: { [key: string]: any } = {};
let validationsFields: { [key: string]: any } = {};
for (const field of forms[section]) {
initialValues[field.name] = field.value;
if (!field.validations) continue;
const schema = generateValidations(field)
validationsFields[field.name] = schema;
}
return {
validationSchema: Yup.object({ ...validationsFields }),
initialValues: initialValues as T,
inputs: forms[section],
};
};
💊 创建表单组件。
首先,我们要为我们的 Form 组件将要接收的 props 准备接口。
- onSubmit,执行表单的函数。
- labelButtonSubmit,显示按钮的文本。
- titleForm,显示表单的文本。
最后 3 个属性返回我们用来生成输入及其验证的函数。
interface Props {
onSubmit: (data: unknown) => void
labelButtonSubmit?: string
titleForm?: string
initialValues: unknown
validationSchema: SchemaForm
inputs: InputProps[]
}
validationSchema 属性属于SchemaForm类型。
// src/types/index.ts
export type SchemaForm = OptionalObjectSchema<{
[x: string]: any;
}, AnyObject, TypeOfShape<{
[x: string]: any;
}>>
现在我们创建组件,并在其中解构组件接收的 props。
然后我们使用 useForm 的钩子,我们将建立一个对象作为参数,我们访问该属性:
- resolver,设置验证方案,为此我们使用函数yupResolver,并将props 提供的validationSchema作为参数传递。
- defaultValues ,用于建立默认值,我们将分配initialValues的 props 。
请注意,我们不会解构useForm钩子的任何内容。
import { yupResolver } from '@hookform/resolvers/yup'
import { useForm } from 'react-hook-form'
export const Form = ({ ...props }: Props) => {
const {
initialValues,
inputs,
onSubmit,
validationSchema,
titleForm,
labelButtonSubmit = 'Submit'
} = props
const formMethods = useForm({
resolver: yupResolver(validationSchema),
defaultValues: { ...(initialValues as any) }
})
return (
<></>
)
}
接下来,我们将使用一个为我们提供 react-hook-form 的组件,它是FormProvider,我们将传播useForm钩子的formMethods。
FormProvider将帮助我们与嵌套在 FormProvider 内部的组件(输入框)沟通表单的状态。这样做的目的是分离组件,避免将所有内容放在同一个文件中。
在 FormProvider 内部,我们将放置一个表单,并在表单标签的 onSubmit 方法中执行 formMethods 的一个属性,即handleSubmit,并将通过 props 接收组件 Form 的 onSubmit 作为参数传递。
此handleSubmit仅当每个输入都没有错误时才会执行,并且执行时它将返回每个输入的值。
import { FormProvider, useForm } from 'react-hook-form'
// interface
export const Form = ({ ...props }: Props) => {
// props
const formMethods = useForm({
resolver: yupResolver(validationSchema),
defaultValues: { ...(initialValues as any) }
})
return (
<FormProvider {...formMethods}>
<form
onSubmit={formMethods.handleSubmit(onSubmit)}
className='bg-secondary rounded-md p-10 pt-5 shadow-2xl shadow-primary/30 flex flex-col gap-2 border border-primary w-full min-h-[390px]'
>
<section className='flex-1 flex flex-col gap-3'>
{/* inputs here */}
</section>
</form>
</FormProvider>
)
}
现在我们要创建一个函数,用于返回不同类型的输入。
我们使用从 Form 组件接收的 props 中解构出来的input 属性。
根据输入的类型,我们将呈现一个或另一个输入。
请注意,我们正在使用尚未创建的组件。另请注意,我们将从每个输入的属性中排除验证 typeValue 和 value,因为它们是我们的输入不需要直接使用的值。
关于这个函数,有一点需要改进,那就是你可以创建一个单独的组件,并创建一个包含组件和输入类型的字典。
在本例中,我没有这样做,以免进一步扩展。
const createInputs = () =>
inputs.map(({ validations, typeValue, value, ...inputProps }) => {
switch (inputProps.type) {
case 'select':
return <CustomSelect {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
case 'checkbox':
return <CustomCheckbox {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
case 'radio':
return <CustomRadio {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
default:
return <CustomInput {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
}
})
最后,我们在 section 标签内执行createInputs函数。然后我们就可以立即创建自定义输入了。
// imports
// interface
export const Form = ({ ...props }: Props) => {
// props
const formMethods = useForm({
resolver: yupResolver(validationSchema),
defaultValues: { ...(initialValues as any) }
})
const createInputs = () =>
inputs.map(({ validations, typeValue, value, ...inputProps }) => {
switch (inputProps.type) {
case 'select':
return <CustomSelect {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
case 'checkbox':
return <CustomCheckbox {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
case 'radio':
return <CustomRadio {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
default:
return <CustomInput {...inputProps} key={inputProps.name} />
}
})
return (
<FormProvider {...formMethods}>
<form
onSubmit={formMethods.handleSubmit(onSubmit)}
className='bg-secondary rounded-md p-10 pt-5 shadow-2xl shadow-primary/30 flex flex-col gap-2 border border-primary w-full min-h-[390px]'
>
<section className='flex-1 flex flex-col gap-3'>
{ createInputs() }
</section>
</form>
</FormProvider>
)
}
💊 创建每个输入的组件。
首先,我们将创建一个错误消息,该消息将在每次输入验证失败时显示。
在src/components中我们创建ErrorMessage.tsx。
interface Props { error?: string }
export const ErrorMessage = ({ error }: Props) => {
if (!error) return null
return (
<div className='w-full grid place-content-end'>
<p className='text-red-400 text-sm'>{error}</p>
</div>
)
}
现在,我们将创建一个新文件夹src/components/inputs,并在其中创建 4 个文件。
我们将要创建的这四个组件接收CustomInputProps类型的 props 。你可以将其放在 src/types/index.ts 文件中。
export type CustomInputProps = Omit<InputProps, 'validations' | 'typeValue' | 'value'>
而且由于我们创建的每个输入都位于FormProvider中,我们可以使用 react-hook-form 的另一个自定义钩子,即useFormContext,这个钩子将帮助我们将表单的状态与输入连接起来。
- 自定义通用输入.tsx
从useFormContext中,我们获取了 register 属性,以及 formState 中的 error 属性。
const {
register,
formState: { errors }
} = useFormContext()
我们创建错误,使用组件接收的 prop 名称计算错误对象并获取消息。
const error = errors[name]?.message as string | undefined
在构造输入时,我们需要扩展register函数的属性,并传入 prop名称,以便 react-hook-form 识别此输入应包含的错误和验证。然后,如果输入包含其他属性(例如placeholder
) ,则需要扩展其他属性。
<input
className='py-1 px-2 rounded w-full text-black'
{...register(name)}
{...props}
id={id}
/>
这个组件最终将会是这个样子。
import { useFormContext } from 'react-hook-form'
import { ErrorMessage } from '../../components'
import { CustomInputProps } from '../../types'
export const CustomInput = ({ name, label, ...props }: CustomInputProps) => {
const {
register,
formState: { errors }
} = useFormContext()
const error = errors[name]?.message as string | undefined
const id = `${name}-${props.type}-${label}`
return (
<div className='w-full flex gap-1 flex-col'>
{label && (
<label className='text-white text-sm' htmlFor={id}>
{label}
</label>
)}
<input
className='py-1 px-2 rounded w-full text-black'
{...register(name)}
{...props}
id={id}
/>
<ErrorMessage error={error} />
</div>
)
}
- 自定义复选框.tsx
import { useFormContext } from 'react-hook-form'
import { ErrorMessage } from '../../components'
import { CustomInputProps } from '../../types'
export const CustomCheckbox = ({ name, label, ...props }: CustomInputProps) => {
const {
register,
formState: { errors }
} = useFormContext()
const error = errors[name]?.message as string | undefined
return (
<div>
<label className='flex gap-2 items-center cursor-pointer w-fit'>
<input {...props} {...register(name)} />
{label}
</label>
<ErrorMessage error={error} />
</div>
)
}
- 自定义选择.tsx
此输入几乎与所有其他输入相同,只有在这里我们有 prop 选项,其中可以选择的选择的值将会出现。
import { useFormContext } from 'react-hook-form'
import { ErrorMessage } from '../../components'
import { CustomInputProps } from '../../types'
export const CustomSelect = ({ name, label, options, ...props }: CustomInputProps) => {
const {
register,
formState: { errors }
} = useFormContext()
const error = errors[name]?.message as string | undefined
const id = `${name}-${props.type}-${label}`
return (
<div className='flex flex-col gap-2'>
<div className='flex items-center gap-4'>
<label htmlFor={id}>{label}</label>
<select {...register(name)} {...props} id={id} className='p-2 rounded flex-1 text-black'>
<option value=''>--- Select option ---</option>
{options &&
options.map(({ desc, value }) => (
<option key={value} value={value}>
{desc}
</option>
))}
</select>
</div>
<ErrorMessage error={error} />
</div>
)
}
- 自定义RadioGroup
与 CustomSelect.tsx 非常相似。只是这里我们渲染了一个 radio 类型的输入。
import { useFormContext } from 'react-hook-form'
import { ErrorMessage } from '../../components'
import { CustomInputProps } from '../../types'
export const CustomRadio = ({ name, label, options, ...props }: CustomInputProps) => {
const {
register,
formState: { errors }
} = useFormContext()
const error = errors[name]?.message as string | undefined
return (
<div className='flex flex-col'>
<div className='flex items-center gap-4'>
<label>{label}</label>
<section className='flex justify-between flex-1'>
{options &&
options.map(({ desc, value }) => (
<label
key={value}
className='flex items-center gap-1 cursor-pointer hover:underline rounded p-1'
>
<input {...register(name)} {...props} value={value} type='radio' />
{desc}
</label>
))}
</section>
</div>
<ErrorMessage error={error} />
</div>
)
}
💊 使用我们的表单组件。
现在我们转到src/App.tsx文件。
使用表单组件。
我们必须执行getInputs函数并获取验证、初始值和输入。我们将在组件外部执行此操作。我们还创建一个接口,以便初始值的行为与该接口类似。
interface SignUpFormType {
username: string
password: string
repeat_password: string
}
const signUpForm = getInputs<SignUpFormType>('register')
然后我们导入 Form 组件,并传播getInput返回的属性。同时,我们也传递了其他 props。
import { Layout, Form } from './components'
import { getInputs } from './lib'
interface SignUpFormType {
username: string
password: string
repeat_password: string
}
const signUpForm = getInputs<SignUpFormType>('register')
const App = () => {
const onSubmitSignUp = (data: unknown) => console.log({ singUp: data })
return (
<Layout>
<Form
{...signUpForm}
onSubmit={onSubmitSignUp}
titleForm='Sign Up!'
labelButtonSubmit='Create account'
/>
</Layout>
)
}
export default App
如果您想覆盖初始值,只需通过扩展初始值并覆盖所需的值来创建一个新的常量。然后将新值传递给initialValues属性。
const App = () => {
const onSubmitSignUp = (data: unknown) => console.log({ singUp: data })
const initialValuesSignUp: SignUpFormType = {
...signUpForm.initialValues,
username: '@franklin361'
}
return (
<Layout>
<Form
{...signUpForm}
initialValues={initialValuesSignUp}
onSubmit={onSubmitSignUp}
titleForm='Sign Up!'
labelButtonSubmit='Create account'
/>
</Layout>
)
}
export default App
您还可以动态地包含多个表单。
import { Layout, Form } from './components'
import { getInputs } from './lib'
interface SignUpFormType {
username: string
password: string
repeat_password: string
}
interface AnotherFormType {}
const signUpForm = getInputs<SignUpFormType>('register')
const anotherForm = getInputs<AnotherFormType>('another')
const App = () => {
const onSubmitSignUp = (data: unknown) => console.log({ singUp: data })
const onSubmitAnotherForm = (data: unknown) => console.log({ another: data })
const initialValuesSignUp: SignUpFormType = {
...signUpForm.initialValues,
username: '@franklin361'
}
return (
<Layout>
<Form
{...signUpForm}
initialValues={initialValuesSignUp}
titleForm='Sign Up!'
onSubmit={onSubmitSignUp}
labelButtonSubmit='Create account'
/>
<Form
{...anotherForm}
titleForm='Another form!'
onSubmit={onSubmitAnotherForm}
labelButtonSubmit='Send info'
/>
</Layout>
)
}
export default App
💊 结论。
React Hook Form 是我最喜欢的库之一,因为它比其他流行的库(例如 Formik)具有某些优势;例如,捆绑包大小更小、依赖项更少、重新渲染次数更少等。😉。
但这两个仍然是非常常用的库。
我希望你喜欢这篇文章,也希望我能帮助你了解如何使用 React Hook Form 制作动态表单🙌。
如果您知道任何其他不同或更好的方法来制作此应用程序,请随时发表评论。
如果您有兴趣就某个项目与我联系,我邀请您查看我的投资组合。!富兰克林·马丁内斯·卢卡斯
🔵 别忘了在推特上关注我:@Frankomtz361
💊 演示。
https://dynamic-form-rhf.netlify.app/
💊 源代码。
https://github.com/Franklin361/dynamic-form-rhf/
文章来源:https://dev.to/franklin030601/dynamic-forms-with-react-hook-form-2ml8 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com