使用 Node.Js、ExpressJs、MongoDB 和 VueJs 构建 Todo 应用程序 – 第 2 部分
在本教程的第一部分中,我们为一个简单的待办事项应用程序构建了 API,现在我们将学习如何将前端与 VueJS 集成。如果您是 VueJS 新手,也不用担心。我写了《VueJS:4 分钟掌握基础知识》和《在 VueJS 中创建您的第一个组件》,帮助您快速上手 VueJS。
项目目录
在第一部分中,我们创建了backend目录。该backend目录包含我们后端代码的源代码。
我们在这里做类似的事情。让我们创建一个名为 的新目录frontend。这将存放我们的前端代码。
$ mkdir frontend
如果您运行上述命令,您的项目目录现在应该如下所示:
.
├── backend
└── frontend
这篇文章中的所有代码都将进入frontend目录。
Vue CLI
Vue CLI是一个命令行工具,可帮助您快速搭建新项目。要安装 Vue CLI,请在终端运行以下命令:
$ npm install -g @vue/cli
安装 Vue Cli 后,转到frontend目录运行vue create .命令来搭建新项目。
$ vue create .
确保对所有提示都回答“是” 。
Vue CLI v3.5.1
? Generate project in current directory? Yes
? Please pick a preset: default (babel, eslint)
如果一切顺利,您的前端目录将如下所示:
├── README.md
├── babel.config.js
├── node_modules
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico
│ └── index.html
└── src
├── App.vue
├── assets
│ └── logo.png
├── components
│ └── HelloWorld.vue
└── main.js
项目依赖关系
- Bootstrap Vue:兼容 Vue 的 boostrap 框架
- Sass 加载器:将 sass 编译为 css
- Axios:用于对 todo API 进行 REST API 调用
使用以下命令安装 bootstrap-vue 和 axis:
$ npm install vue bootstrap-vue bootstrap axios
使用以下命令安装 sass-loader:
$ npm install sass-loader node-sass --save-dev
在下面的段落中,我们将创建该项目所需的组件。
创建 Vue 组件
基本上,我们需要两个主要的 Vue 组件。第一个组件是CreateTodo,第二个组件是ListTodo
在某些时候,这些组件需要相互通信或共享数据,这时事件总线就发挥作用了。
处理 Vue.Js 中组件间通信的方法之一是使用全局事件总线,这样当一个组件发出一个事件时,事件总线会将该事件传输给其他监听组件。
事件总线
我们创建一个全局事件总线,其名称src/bus.js和代码如下:
//src/bus.js
import Vue from 'vue';
const bus = new Vue();
export default bus;
现在我们已经创建了事件总线,让我们编写添加新待办事项的代码。
用于添加新待办事项的 Vue 组件
创建一个新文件src/components/CreateTodo.vue并更新其内容:
<template>
<div class="col align-self-center">
<h3 class="pb-5 text-left underline">Create todos</h3>
<form class="sign-in" @submit.prevent>
<div class="form-group todo__row">
<input
type="text"
class="form-control"
@keypress="typing=true"
placeholder="What do you want to do?"
v-model="name"
@keyup.enter="addTodo($event)"
/>
<small class="form-text text-muted" v-show="typing">Hit enter to save</small>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
import bus from "./../bus.js";
export default {
data() {
return {
name: "",
typing: false
};
},
methods: {
addTodo(event) {
if (event) event.preventDefault();
let todo = {
name: this.name,
done: false //false by default
};
console.log(todo);
this.$http
.post("/", todo)
.then(response => {
this.clearTodo();
this.refreshTodo();
this.typing = false;
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error);
});
},
clearTodo() {
this.name = "";
},
refreshTodo() {
bus.$emit("refreshTodo");
}
}
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.underline {
text-decoration: underline;
}
</style>
addTodo()enter一旦按下某个键就会执行。它会POST向后端发出一个包含新待办事项的请求。clearTodo()一旦待办事项被保存,就清除输入框。refreshTodo()发出一个事件refreshTodo。这在添加新的待办事项时很有用。重新渲染列表以显示新项目是有意义的。
解释完毕,让我们继续创建ListTodo组件。
用于列出待办事项的组件
src/components/ListTodo.vue使用以下代码创建文件:
<template>
<div v-bind:show="todos.length>0" class="col align-self-center">
<div class="form-row align-items-center" v-for="todo in todos">
<div class="col-auto my-1">
<div class="input-group mb-3 todo__row">
<div class="input-group-prepend">
<span class="input-group-text">
<input
type="checkbox"
v-model="todo.done"
:checked="todo.done"
:value="todo.done"
v-on:change="updateTodo(todo)"
title="Mark as done?"
/>
</span>
</div>
<input
type="text"
class="form-control"
:class="todo.done?'todo__done':''"
v-model="todo.name"
@keypress="todo.editing=true"
@keyup.enter="updateTodo(todo)"
/>
<div class="input-group-append">
<div class="input-group-text">
<span
class="input-group-addon addon-left"
title="Delete todo?"
v-on:click="deleteTodo(todo._id)"
>
X
</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div
class="alert alert-primary todo__row"
v-show="todos.length==0 && doneLoading"
>Hardest worker in the room. No more todos now you can rest. ;)</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
import bus from "./../bus.js";
export default {
data() {
return {
todos: [],
doneLoading: false
};
},
created: function() {
this.fetchTodo();
this.listenToEvents();
},
watch: {
$route: function() {
let self = this;
self.doneLoading = false;
self.fetchData().then(function() {
self.doneLoading = true;
});
}
},
methods: {
fetchTodo() {
this.$http.get("/").then(response => {
this.todos = response.data;
});
},
updateTodo(todo) {
let id = todo._id;
this.$http
.put(`/${id}`, todo)
.then(response => {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error);
});
},
deleteTodo(id) {
this.$http.delete(`/${id}`).then(response => {
this.fetchTodo();
});
},
listenToEvents() {
bus.$on("refreshTodo", $event => {
this.fetchTodo(); //update todo
});
}
}
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.todo__done {
text-decoration: line-through !important;
}
.no_border_left_right {
border-left: 0px;
border-right: 0px;
}
.flat_form {
border-radius: 0px;
}
.mrb-10 {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.addon-left {
background-color: none !important;
border-left: 0px !important;
cursor: pointer !important;
}
.addon-right {
background-color: none !important;
border-right: 0px !important;
}
</style>
让我们花点时间来解释一下代码中发生了什么。
我们在代码片段中创建了 4 个函数。
fetchTodo()调用GET后端并获取所有待办事项。updateTodo(todo)当你修改待办事项并按下回车键时,会被调用。它会将你的更改转发到后端。deleteTodo(id)当你点击垃圾桶按钮时运行。它会DELETE向后端发出请求。listenToEvents():在CreateTodo组件中,当添加新的待办事项时,我们会发出事件,因此列表ListTodo负责渲染待办事项。此方法负责监听refreshTodo事件。
应用程序组件
下面我们将所有组件包装在一个名为 的父组件中。使用以下内容App.vue更新文件:src/App.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row vertical-centre justify-content-center mt-50">
<div class="col-md-6 mx-auto">
<CreateTodo></CreateTodo>
<ListTodo></ListTodo>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CreateTodo from "./components/CreateTodo.vue";
import ListTodo from "./components/ListTodo.vue";
export default {
name: "app",
components: { CreateTodo, ListTodo }
};
</script>
<style lang="scss">
@import "node_modules/bootstrap/scss/bootstrap";
@import "node_modules/bootstrap-vue/src/index.scss";
.vertical-centre {
min-height: 100%;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.todo__row {
width: 400px;
}
</style>
根实例
每个 Vue 应用都必须定义一个根实例。你可以将 Vue 实例或根实例视为构成应用的组件树的根。
让我们修改文件的内容src/main.js:
import Vue from 'vue';
import BootstrapVue from 'bootstrap-vue';
import axios from 'axios';
import App from './App.vue';
const http = axios.create({
baseURL: process.env.BACKEND_URL ? process.env.BACKEND_URL : 'http://localhost/todos',
});
Vue.prototype.$http = http;
Vue.use(BootstrapVue);
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app');
我们导入了 BoostrapVue 和应用程序所需的其他库。
我们还导入了App组件并将其定义为根实例上的组件。
我们导入了axios一个 http 客户端,并配置了后端应用程序的基准 URL。您应该确保它baseUrl与您的后端 URL 匹配。
我们已经走到这一步了,使用以下命令运行该应用程序:
$ npm run serve
构建可能需要一些时间。最后,你应该在控制台中打印出一个 URL:
App running at:
- Local: http://localhost:8080/
- Network: http://192.168.178.20:8080/
Note that the development build is not optimized.
To create a production build, run npm run build.
如果您导航至http://localhost:8080,您会看到类似这样的页面。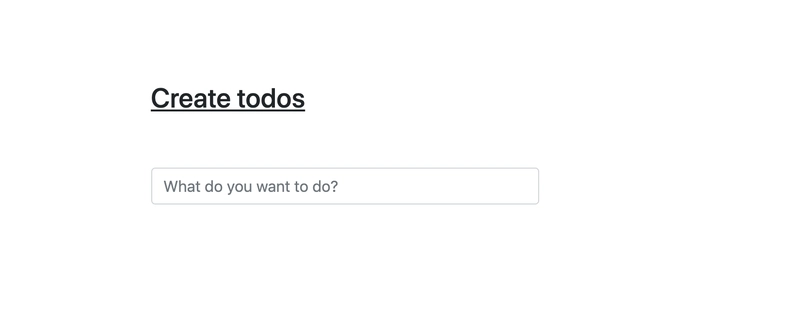
要将前端应用程序与后端连接起来,您还需要启动后端服务器。
导航到backend目录并运行
$ npm start
笔记:
- 您的 MongoDB 连接 URL 必须正确配置,
backend/config/Config.js并且 MongoDB 必须正在运行。 - 您的后端服务器必须正在运行。
- 您的前端服务器必须正在运行。
如果您导航到http://localhost:8080,您将看到如下页面。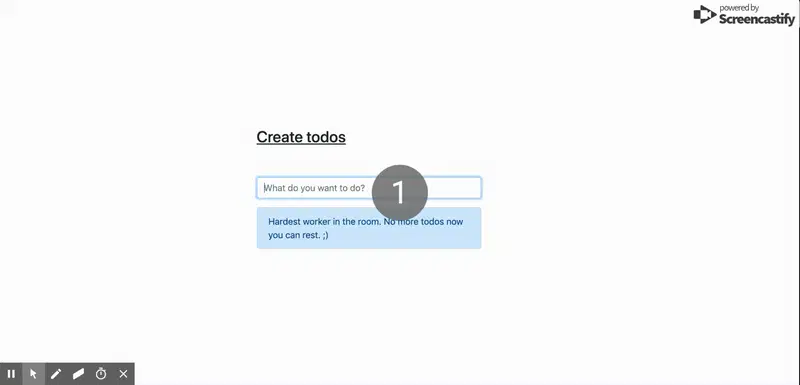
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com