给 JavaScript 开发者的超级实用技巧
使用切片和 ES8 padStart 方法快速屏蔽数字
const creditCard = "4111111111114321"; // 16 digit credit card number
const lastFourDigits = creditCard.slice(-4); // get last 4 digits
// prepend * to lastFourDigits to make length equal to creditCard number length
const maskedNumber = lastFourDigits.padStart(creditCard.length, '*');
console.log(lastFourDigits); // 4321
console.log(maskedNumber); // ************4321
仅执行一次事件处理程序
通过{ once: true }作为第三个参数传递给addEventListener方法,事件处理程序函数将仅执行一次。
document.getElementById("btn").addEventListener("click",
function () {
console.log("Button clicked!");
},
{ once: true }
);
使用扩展运算符更新对象的属性
const user = {
name: 'David',
age: 30,
city: 'NY'
};
const newAge = 40;
const updatedUser = {
...user,
age: newAge
};
console.log(user); // { name: 'David', age: 30, city: 'NY'}
console.log(updatedUser); // { name: 'David', age: 40, city: 'NY'}
查找对象中的属性数量
const user = {
name: 'David',
age: 30,
city: 'NY'
};
console.log(Object.keys(user).length); // 3
获取数组中的最后一个元素
const numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
const last = numbers.slice(-1);
console.log(last); // [50]
const secondLast = numbers.slice(-2);
console.log(secondLast); // [40, 50]
请注意,slice 方法适用于数组和字符串。
检查提供的数组是否确实是数组的三种方法
在 JavaScript 中,数组也是一个对象,因此,要检查它实际上是一个数组还是对象,可以使用以下 3 种方法。(常见面试问题)
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
- arr.constructor.toString().indexOf("Array") > -1
- 数组实例
- 数组.isArray(arr)
获取当前时间戳
const date = new Date();
console.log(date.getTime()); // 1621708197268
时间戳值有时对于生成唯一值很有用,因为时间戳值每秒总是不同的。
使用 ES6 计算对象属性语法为对象提供动态键
// old way
function getPairs(key, value) {
var object = {};
object[key] = value
return object;
}
console.log(getPairs('name', 'Mike')); // { name: 'Mike'}
console.log(getPairs('age', '40')); // { age: 40}
// new ES6 way
function getPairs(key, value) {
const object = {
[key]: value
};
return object;
}
console.log(getPairs('name', 'Mike')); // { name: 'Mike'}
console.log(getPairs('age', '40')); // { age: 40}
对象解构
const user = {
name: 'David',
age: 30
};
// destructure user properties and use a `status` property with value `Married` If it does not exist
const {name, age, status = 'Married' } = user;
console.log(name, age, status) // David 30 Married
const person = {
age: 30
};
// destructure `person` object and rename `name` to `username` and assign a default value of `Anonymous`, If the property does not exist in the `person` object
const {name: username = 'Anonymous', age } = person;
console.log(username, age); // Anonymous 30
数组解构
const days = ["sunday", "monday", "tuesday", "wednesday", "thursday", "friday", "saturday"];
const [firstDay, secondDay] = days;
console.log(firstDay); // sunday
console.log(secondDay); // monday
使用 ES6 模板文字语法
const user = {
name: 'David',
age: 30,
address: 'NY'
};
// old way: Hi, I'm David with age 30 and living in NY
console.log("Hi, I'm " + user.name + " with age " + user.age + " and living in " + user.address);
// new way: Hi, I'm David with age 30 and living in NY
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${user.name} with age ${user.age} and living in ${user.address}`);
这可以进一步简化,如下所示:
const user = {
name: 'David',
age: 30,
address: 'NY'
};
const { name, age, address } = user;
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${name} with age ${age} and living in ${address}`);
将可变数量的参数传递给函数
ES6 剩余运算符 (...) 将逗号分隔的值转换为数组,因此函数numbers的参数add也变成数组。
function add(...numbers) {
return numbers.reduce((acc, value) => {
return acc + value;
}, 0);
}
const sum = add(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
console.log(sum); // 15
使用扩展运算符创建新数组
const first = ["two", "three", "four"];
const second = [ "six", "seven", "eight"];
const combined = ["one", ...first, "five", ...second]
console.log(combined); // ["one", "two", "three", "four", "five", "six", "seven", "eight"]
用特定值填充数组
const array = Array(5).fill(false); // [false, false, false, false, false]
const array = [...Array(5).keys()] // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
从数组中删除重复项
- 使用 Set
const array = [1, 2, 2, 3, 1, 5];
const unique = [...new Set(array)];
console.log(unique); // [1, 2, 3, 5];
- 使用数组过滤方法
const array = [1, 2, 2, 3, 1, 5];
const unique = array.filter((value, index) => {
return array.indexOf(value) === index;
});
console.log(unique); // [1, 2, 3, 5]
生成特定范围内的随机数
- 0 到 100 之间的随机数:
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)
- 1 到 100 之间的随机数
Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1
- 最小值(含)和最大值(不含)之间的随机数
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min) ) + min;
}
console.log(getRandom(10, 35)); // any random number >= 10 and < 35
- 最小值和最大值之间的随机数(包括最大值和最小值)
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1) ) + min;
}
console.log(getRandom(10, 35)); // any random number >= 10 and <= 35
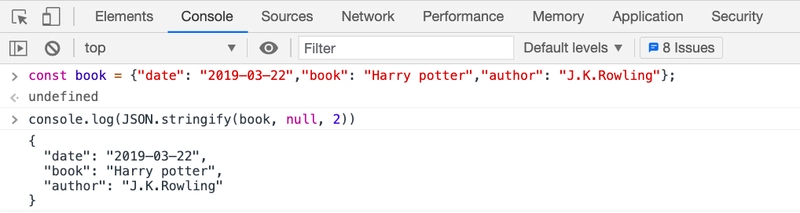
以格式化的方式打印 JSON
const book = {"date": "2019–03–22","book": "Harry potter","author": "J.K.Rowling"};
console.log(JSON.stringify(book, null, 2)) // formatted with 2 spaces
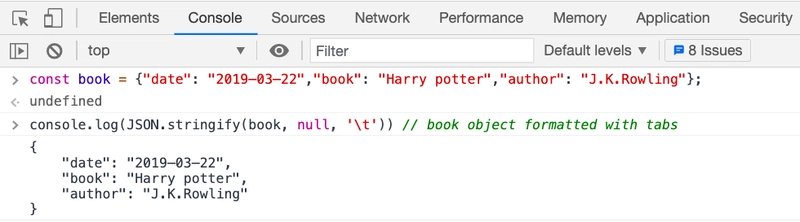
const book = {"date": "2019–03–22","book": "Harry potter","author": "J.K.Rowling"};
console.log(JSON.stringify(book, null, '\t')) // formatted with tabs
实现平滑滚动到页面顶部
window.scrollTo({ top: 0, left: 0, behavior: "smooth" });
将任意值转换为布尔值
let number1;
console.log(!!number1); // false
const number2 = 10;
console.log(!!number2); // true
const name1 = 'Tim';
console.log(!!name1); // true
const name2 = '';
console.log(!!name2); // false
const nullValue = null;
console.log(!!nullValue); // false
如果您想避免将null或undefined作为值发送到后端,这尤其有用。
快速将字符串转换为数字
const number = "20";
const converted = +number;
console.log(converted); // 20
将字符串转换为数组
const name = "Mike johnson";
console.log(name.split("")); // ["M", "i", "k", "e", " ", "j", "o", "h", "n", "s", "o", "n"]
const chars = "a,b,c,d,e,f";
console.log(chars.split(",")); // ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"]
将数字格式化为两位小数
const number = 100.32222;
console.log(number.toFixed(2)); // 100.32
检查数组是否包含特定值
const numbers = [1, 2 ,3, 10, 50];
// old way
console.log(numbers.indexOf(3) > -1); // true as it check if 3 is present in the array
// new way
console.log(numbers.includes(3)); // true
该includes方法在一次比较多个值时也很有用。
const day = "monday";
if(day === "monday" || day === "tuesday" || day === "wednesday" || day === "thursday") {
// do something
}
// The above code is the same as the below code
const day = "monday";
if(["monday", "tuesday", "wednesday", "thursday"].includes(day)) {
// do something
}
使用可选链接运算符
const user = {
name: 'David',
location: {
street: {
number: 20,
name: '11 wall street'
}
}
};
// old way
const streetName = user.location && user.location.street && user.location.street.name;
console.log(streetName); // 11 wall street
// new way
const streetName = user?.location?.street?.name;
console.log(streetName); // 11 wall street
以前,要访问嵌套属性,我们需要检查每个属性是否存在,因为如果或属性不存在,直接访问user.location.street.name将引发错误,我们尝试像这样访问它:locationstreetname
const user = {
name: 'David'
};
const streetName = user.location.street.name; // Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property 'street' of undefined
但是现在有了 ES11 可选链接运算符,只有当前一个引用不存在时,?.才会执行后面的下一个代码,这样我们就不会收到任何错误。undefinednull
const user = {
name: 'David'
};
const streetName = user?.location?.street?.name;
console.log(streetName); // undefined
因此,使用可选链接运算符可以使代码更短且更易于理解。
感谢阅读!
想要详细学习 Redux 并构建一个完整的订餐应用吗?来看看我的“掌握 Redux”课程吧。
以下是我们将在课程中开发的应用程序的预览。这是一个很棒的项目,你可以添加到你的作品集/简历中。
请注意,在此应用程序中,我使用 INR 作为显示价格的货币,但您只需在应用程序中进行一次配置更改即可轻松地将其更改为 USD 或 AUD 或任何其他货币。
想要定期了解有关 JavaScript、React 和 Node.js 的最新内容吗?请在 LinkedIn 上关注我。
文章来源:https://dev.to/myogeshchavan97/super-useful-tips-tricks-for-javascript-developers-702 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com