使用 React Native、Expo 和 AWS Amplify 实现推送通知的指南
结论
如果您开发一款应用,您希望能够吸引客户,让他们尽可能多地使用您的应用,并让应用为他们带来价值。因此,您必须设置推送通知。在本指南中,我将向您展示如何使用一些优秀的工具来实现这一点。我们将构建一个简单的应用来演示推送通知。
有一些强大的工具可以使应用程序开发尽可能简单。
反应原生
React Native 很棒,因为你只需用 JavaScript 编写代码,然后编译到 iOS 和 Android 系统即可。因此成本更低,开发周期更快。
世博会
Expo 之所以表现良好,是因为它包含了许多您需要的功能,并且您无需安装任何其他工具甚至无需 Mac 即可为 IOS 和 Android 进行开发。
AWS Amplify
AWS Amplify 是这些工具与后端之间的粘合剂。在这里,您还可以使用 Javascript 设置 API、存储、身份验证和授权、数据库、数据存储等。
推送通知
当你深入研究这些工具集并设置好你的架构后,你就会开始爱上它们。而当你需要使用推送通知时,你就不得不告别 Expo 了,因为 AWS Amplify 并没有提供开箱即用的解决方案,让你无需弹出即可使用推送通知。幸运的是,AWS 有更多支持无需弹出即可使用推送通知的工具。
建筑学
我们将使用 AWS Amplify、AWS Pinpoint、AWS Lambda、AWS DynamoDB 和 Expo Push Notifications Server 来完成它。
在此示例中,我们将在应用中发送一条消息。我们将通过AWS Lambda Pinpoint创建一个定时 Pinpoint 活动(这也可以是一个即时活动)。一旦活动触发,首先会启动一个钩子。此钩子会将活动数据发送到AWS Lambda 推送通知。我们将准备推送通知消息,并通过 Expo Server SDK 将其发送到 Expo。这会将推送消息发送到客户端,也就是您的应用。同时,活动数据已发送回 AWS Pinpoint,以便进一步发送到其他渠道(如果您需要)。您将设置一个电子邮件渠道,以便了解其工作原理。
入门
我将使用 NPM,但当然您也可以使用 Yarn。
设置 React Native
首先,我们将创建要使用的 React Native 应用程序。
$ npx expo init pushApp
> Choose a template: blank
$ cd pushApp
$ npm install aws-amplify aws-amplify-react-native
设置 AWS Amplify
首先,我们需要安装 AWS Amplify CLI。Amplify CLI 是一个命令行工具,可用于创建和部署各种 AWS 服务。
要安装 CLI,我们将运行以下命令:
$ npm install -g @aws-amplify/cli
接下来,我们将使用来自 AWS 账户的用户配置 CLI:
$ amplify configure
要观看 CLI 配置过程的视频演示,请单击
现在我们可以从 React Native 应用程序的根目录中初始化一个新的 Amplify 项目:
$ amplify init
这里我们将指导您完成一系列步骤:
- 输入项目名称: amplifypushapp (或您喜欢的项目名称)
- 输入环境名称: dev (使用此名称,因为我们将引用它)
- 选择您的默认编辑器: Visual Studio Code (或您的文本编辑器)
- 选择您正在构建的应用程序类型: javascript
- 您正在使用什么 JavaScript 框架: react-native
- 源目录路径: /
- 分发目录路径: build
- 构建命令: npm run-script build
- 启动命令: npm run-script start
- 您想使用 AWS 配置文件吗? 是
- 请选择您要使用的配置文件: YOUR_USER_PROFILE
- 现在,我们的 Amplify 项目已经创建,我们可以继续下一步。
将 Graphql 添加到你的项目中
您的 React Native 应用已启动并运行,AWS Amplify 也已配置完毕。Amplify 提供多种服务,您可以使用它们来丰富您的应用。我们主要关注 API 服务。所以,让我们添加一个 API。
Amplify add api
以下步骤将会发生:
- 选择Graphql
- 输入 API 的名称:pushAPI(您喜欢的 API 名称)
- 为 API 选择授权类型:Amazon Cognito 用户池(因为我们仅对经过身份验证的用户使用此应用程序,但您可以选择其他选项)
- 选择是否使用默认身份验证和安全配置:默认配置
- 您希望用户如何登录?用户名(同时启用 AWS Amplify Auth 模块)
- 您要配置高级设置吗?不,我已经完成了。
- 您有带注释的 GraphQL 架构吗?
- 您想要引导模式创建吗?:n
- 提供自定义类型名称:用户
您的 API 和架构定义现已创建。您可以在项目目录中找到它:
Amplify > backend > api > name of your api
@model 指令将为您创建一个 DynamoDB。还有更多可能的指令,如需完整说明,请参阅AWS Amplify 文档。
配置 AWS 电子邮件服务
登录控制台并访问 SES 服务。然后按照以下说明配置并激活电子邮件地址。您稍后需要使用此电子邮件地址作为发送邮件的地址。
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/ses/latest/DeveloperGuide/setting-up-email.html
向您的项目添加分析
我们将在您的项目中添加分析功能,因为目前这是从您的 pinpoint 函数设置对 pinpoint 的访问权限的最简单方法。您也可以修改 CloudFormation 模板来实现此目的。
Amplify add analytics
使用您的信息完成这些步骤。
向您的项目添加函数
通过添加函数,我们将创建 Lambda。
Amplify add function
请按照以下步骤操作:
- 为您的资源提供一个友好名称,以用作项目中此类别的标签:pushNotification
- 提供 AWS Lambda 函数名称:
- 选择要使用的函数模板:Hello world 函数
- 您想从 Lambda 函数访问此项目中创建的其他资源吗?是
- 选择类别api
- 选择您想要允许 pushAPI读取的操作
- 您要立即编辑本地 lambda 函数吗?N
再次重复此步骤,但调用下一个函数精确定位并使用以下信息回答以下步骤:
- 您想从 Lambda 函数访问此项目中创建的其他资源吗?是
- 选择类别分析
- 选择要允许 Analytics创建、读取、更新、删除的操作
- 您要立即编辑本地 lambda 函数吗?N
您的函数现已创建,您可以在项目目录中找到它:
Amplify > backend > function > name of your function
进入Pinpoint 函数的src 目录并安装此包
$ npm install aws-sdk
打开 index.js 文件并粘贴此代码。请仔细检查代码并替换正确的值。
/* Amplify Params - DO NOT EDIT
You can access the following resource attributes as environment variables from your Lambda function
var environment = process.env.ENV
var region = process.env.REGION
var apiPushAPIGraphQLAPIIdOutput = process.env.API_PUSHAPI_GRAPHQLAPIIDOUTPUT
var apiPushAPIGraphQLAPIEndpointOutput = process.env.API_PUSHAPI_GRAPHQLAPIENDPOINTOUTPUT
var analyticsAmplifypushappId = process.env.ANALYTICS_AMPLIFYPUSHAPP_ID
var analyticsAmplifypushappRegion = process.env.ANALYTICS_AMPLIFYPUSHAPP_REGION
Amplify Params - DO NOT EDIT */
const AWS = require("aws-sdk");
AWS.config.region = "<REGION>"; // fill in your right region ******
const pinpoint = new AWS.Pinpoint();
exports.handler = async (event, context) => {
try {
event = event.arguments.input;
// Create a AWS Pinpoint project
const appID = await createApp();
// Enable the SES email address for the project
enableChannels(appID, event.email);
// Create the endpoints for the Pinpoint project/app
await createEndPoints(
appID,
event.id,
event.email,
event.name,
event.token
);
// Create a segment where you want to filter the endpoint you want to send a message to
const segmentID = await createSegment(appID);
// create starter segment and campaign.
const hookLambda = "pushNotification-dev";
const result = await createCampaign(
appID,
event.message,
hookLambda,
segmentID
);
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.log("Oops! An error happened.");
}
};
async function createApp() {
let params = {
CreateApplicationRequest: {
/* required */
Name: "Push App" /* Campaign name, required */
}
};
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
pinpoint.createApp(params, function(err, data) {
if (err) {
rej(err);
console.log(err, err.stack); // an error occurred
} else {
res(data.ApplicationResponse.Id); //console.log(data);// successful response
}
});
});
}
/*
When you create a new pinpoint app you need to activate an emailaddress where the emails can be send from
*/
function enableChannels(appID, email) {
console.log(appID, email);
var params = {
ApplicationId: appID /* required */,
EmailChannelRequest: {
/* required */
FromAddress:
"<FROM EMAIL ADDRESS>" /* use the emailaddress that you activated in AWS SES, required */,
Identity:
"arn:aws:ses:<REGION>:<ACCOUNTID>:identity/" + email /* required */,
Enabled: true
}
};
pinpoint.updateEmailChannel(params, function(err, data) {
if (err) console.log(err, err.stack);
else console.log(data); // successful response
});
}
/*
An endpoint is an object which contains user data which you can use later in a segment to send messages
*/
async function createEndPoints(appID, id, email, name, token) {
let params = {
ApplicationId: appID /* required */,
EndpointId: id /* required */,
EndpointRequest: {
/* required */
Address: email,
ChannelType: "EMAIL",
EndpointStatus: "ACTIVE",
OptOut: "NONE",
User: {
UserAttributes: {
name: [
name
/* more items */
],
expoToken: [
token
/* more items */
]
}
}
}
};
await pinpoint.updateEndpoint(params, function(err, data) {
if (err) {
console.log(err, err.stack);
// an error occurred
} else {
console.log(data); // successful response
}
});
}
function createSegment(appID) {
let params = {
ApplicationId: appID /* required */,
WriteSegmentRequest: {
/* required */
Dimensions: {
Demographic: {
Channel: {
Values: [
/* required */
"EMAIL"
/* more items */
],
DimensionType: "INCLUSIVE"
}
}
},
Name: "Segment"
}
};
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
pinpoint.createSegment(params, function(err, data) {
if (err) {
rej(err);
console.log(err, err.stack); // an error occurred
} else {
res(data.SegmentResponse.Id); //console.log(data);// successful response
}
});
});
}
/*
With the endpoint(s) created you can create a segment. A segment is a filter which selects the right endpionts to send messages to
*/
async function createCampaign(appID, message, env, segmentID) {
const utcDate = new Date(Date.now());
const params = {
ApplicationId: appID /* required */,
WriteCampaignRequest: {
/* required */
HoldoutPercent: 0,
Hook: {
LambdaFunctionName: env,
Mode: "FILTER"
},
IsPaused: false,
Limits: {},
MessageConfiguration: {
EmailMessage: {
Title: "Test Email Message",
HtmlBody:
`<!DOCTYPE html>\n <html lang="en">\n <head>\n <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />\n</head>\n<body>\n<H2>Hallo {{User.UserAttributes.name}},</H2>\n\n <br />This is a Text Message from PinPoint. \n You have send this text: \n\n` +
message +
`\n</body>\n</html>`,
FromAddress: "<FROM EMAIL ADDRESS>"
},
DefaultMessage: {
// you push message
Body: message
}
},
Name: "push campaign",
Schedule: {
IsLocalTime: false,
QuietTime: {},
StartTime: utcDate.toISOString(),
Frequency: "ONCE"
},
SegmentId: String(segmentID),
SegmentVersion: 1,
tags: {}
}
};
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
pinpoint.createCampaign(params, function(err, data) {
if (err) {
console.log(err, err.stack); // an error occurred
const response = {
statusCode: 500,
body: JSON.stringify(err)
};
rej(response);
} else {
console.log(data);
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify(data)
};
res(response); // successful response
}
});
});
}
快完成了。现在让我们实现下一个函数。转到 Push Notifications 目录,然后转到src目录。安装此 NPM 包
$ npm install expo-server-sdk
打开 index.js 并粘贴此代码
/* Amplify Params - DO NOT EDIT
You can access the following resource attributes as environment variables from your Lambda function
var environment = process.env.ENV
var region = process.env.REGION
var apiPushAPIGraphQLAPIIdOutput = process.env.API_PUSHAPI_GRAPHQLAPIIDOUTPUT
var apiPushAPIGraphQLAPIEndpointOutput = process.env.API_PUSHAPI_GRAPHQLAPIENDPOINTOUTPUT
Amplify Params - DO NOT EDIT */ const {
Expo
} = require("expo-server-sdk");
// Create a new Expo SDK client
let expo = new Expo();
exports.handler = function(event, context, callback) {
try {
let messages = [];
// prettier-ignore
for (var key in event.Endpoints) {
if (event.Endpoints.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
var endpoint = event.Endpoints[key];
messages.push({
to: String(endpoint.User.UserAttributes.expoToken),
sound: "default",
body: event.Message.apnsmessage.body,
data: { "status": "ok" }
});
}
}
// The Expo push notification service accepts batches of notifications so
// that you don't need to send 1000 requests to send 1000 notifications. We
// recommend you batch your notifications to reduce the number of requests
// and to compress them (notifications with similar content will get
// compressed).
let chunks = expo.chunkPushNotifications(messages);
let tickets = [];
(async () => {
// Send the chunks to the Expo push notification service. There are
// different strategies you could use. A simple one is to send one chunk at a
// time, which nicely spreads the load out over time:
for (let chunk of chunks) {
try {
let ticketChunk = await expo.sendPushNotificationsAsync(chunk);
console.log(ticketChunk);
tickets.push(...ticketChunk);
// NOTE: If a ticket contains an error code in ticket.details.error, you
// must handle it appropriately. The error codes are listed in the Expo
// documentation:
// https://docs.expo.io/versions/latest/guides/push-notifications#response-format
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
})();
// Later, after the Expo push notification service has delivered the
// notifications to Apple or Google (usually quickly, but allow the the service
// up to 30 minutes when under load), a "receipt" for each notification is
// created. The receipts will be available for at least a day; stale receipts
// are deleted.
//
// The ID of each receipt is sent back in the response "ticket" for each
// notification. In summary, sending a notification produces a ticket, which
// contains a receipt ID you later use to get the receipt.
//
// The receipts may contain error codes to which you must respond. In
// particular, Apple or Google may block apps that continue to send
// notifications to devices that have blocked notifications or have uninstalled
// your app. Expo does not control this policy and sends back the feedback from
// Apple and Google so you can handle it appropriately.
let receiptIds = [];
for (let ticket of tickets) {
// NOTE: Not all tickets have IDs; for example, tickets for notifications
// that could not be enqueued will have error information and no receipt ID.
if (ticket.id) {
receiptIds.push(ticket.id);
}
}
let receiptIdChunks = expo.chunkPushNotificationReceiptIds(receiptIds);
async () => {
// Like sending notifications, there are different strategies you could use
// to retrieve batches of receipts from the Expo service.
for (let chunk of receiptIdChunks) {
try {
let receipts = await expo.getPushNotificationReceiptsAsync(chunk);
console.log(receipts);
// The receipts specify whether Apple or Google successfully received the
// notification and information about an error, if one occurred.
for (let receipt of receipts) {
if (receipt.status === "ok") {
continue;
} else if (receipt.status === "error") {
console.error(
`There was an error sending a notification: ${receipt.message}`
);
if (receipt.details && receipt.details.error) {
// The error codes are listed in the Expo documentation:
// https://docs.expo.io/versions/latest/guides/push-notifications#response-format
// You must handle the errors appropriately.
console.error(`The error code is ${receipt.details.error}`);
}
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
};
callback(null, event.Endpoints);
} catch (error) {
callback(error);
}
};
现在我们需要先将所有服务推送到云端。转到项目根目录并运行以下命令
amplify push
请按照以下步骤操作:
- 您是否要为新创建的 GraphQL API 生成代码?是的
- 选择代码生成语言目标Javascript
- 输入 graphql 查询、突变和订阅的文件名模式Enter(默认)
- 您是否想要生成/更新所有可能的 GraphQL 操作(查询、变更和订阅)?是
- 输入最大语句深度 [如果架构嵌套较深,则从默认值增加]输入(默认值)
返回pushNotification 函数的src目录。打开此文件:pushNotification-cloudformation-template.json,然后转到“Resources”部分并粘贴以下代码:
"LambdaInvokePermission": {
"Type": "AWS::Lambda::Permission",
"Properties": {
"Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction",
"FunctionName": {
"Fn::If": [
"ShouldNotCreateEnvResources",
"pushNotification",
{
"Fn::Join": [
"",
[
"pushNotification",
"-",
{
"Ref": "env"
}
]
]
}
]
},
"Principal": {
"Fn::Sub": [
"pinpoint.${region}.amazonaws.com",
{
"region": {
"Ref": "AWS::Region"
}
}
]
},
"SourceArn": {
"Fn::Sub": [
"arn:aws:mobiletargeting:${region}:${account}:/apps/*",
{
"region": {
"Ref": "AWS::Region"
},
"account": {
"Ref": "AWS::AccountId"
}
}
]
}
}
},
保存文件。此代码将设置权限,以便 AWS Pinpoint 可以作为钩子调用 Lambda。您必须单独进行推送。如果您尝试与之前的推送同时进行,则在尝试设置权限时,可能会出现并非所有服务都已推送的情况。
amplify push
前往:
Amplify > backend > api > name of your api > open schema.graphql
现在函数已经部署完毕,我们还需要更新架构。将此代码放入 schema.graphql 文件中。它会创建一个额外的变更,以便你在应用中调用这些函数。
type User @model {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
expoToken: String
}
type Mutation {
pinpoint(input: pinpointInput): pinpointResult
@function(name: "pinpoint-${env}")
}
type pinpointResult {
statusCode: Int
body: String
}
input pinpointInput {
token: String!
name: String!
email: String!
message: String!
id: String!
}
再推一下
amplify push
- 您确定要继续吗?Y
转到项目的根目录,然后到 src 目录 > graphql > mutations.js 检查此代码是否存在,如果没有,请添加并保存:
export const pinpoint = /* GraphQL */ `
mutation pinpoint($input: pinpointInput!) {
pinpoint(input: $input) {
statusCode
body
}
}
`;
通过 Cognito 和 AppSync 添加一些数据
进入AWS Cognito控制台,点击“管理用户池”,然后点击“用户池”>“用户和组”>“创建用户”。填写表单,并将所有复选框保留为已选中状态。点击新用户并记下子值(例如 b14cc22-c73f-4775-afd7-b54f222q4758),然后转到菜单中的“应用程序客户端”,记下来自客户端 Web(底部)的应用程序客户端 ID,并在下一步中使用这些值。
让我们添加一些您可以在应用中使用的数据。前往控制台中的 AppSync 服务。
- 通过控制台转到AWS AppSync 。
- 打开你的项目
- 点击查询
- 通过单击“通过 Cognito 用户池登录”按钮,使用 Cognito 用户登录(您可以在控制台中或通过您的应用程序通过 Cognito 创建用户)(使用您写下的数据)
- 添加以下代码并运行代码(使用您的电子邮件地址更新):
mutation PutUser {
createUser( input: {
id: "b14cc22-c73f-4775-afd7-b54f222q4758",
name: "Ramon",
email: "<EMAILADDRESS>"
}
){
id
name
email
}
}
让我们构建 React Native 应用
我做了一个简单(略显丑陋,所有功能都由两个组件组成)的应用。用户需要登录后,我们会获取他的用户资料,检查是否有有效的 ExpoToken,如果没有,我们会请求一个并将其保存在资料中。在应用中,用户可以发送消息,该消息会通过推送通知和电子邮件发送给用户。
转到项目根目录并打开 App.js 并将其替换为以下代码:
import React from "react";
import { withAuthenticator } from "aws-amplify-react-native";
import Amplify, { Analytics } from "aws-amplify";
// Get the aws resources configuration parameters
import awsconfig from "./aws-exports"; // if you are using Amplify CLI
import Main from "./src/Main";
Amplify.configure(awsconfig);
Analytics.disable(); // disabled analytics otherwise you get annoying messages
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return <Main />;
}
}
export default withAuthenticator(App);
这将导入你需要的所有内容,并使用 HOC withAuthenticator 包装你的应用。这将为你的应用创建登录和注册功能。
现在在src 文件夹中创建一个名为Main.js 的文件并粘贴以下代码:
import React from "react";
import { View, TextInput, Button } from "react-native";
import * as queries from "./graphql/queries.js";
import * as mutations from "./graphql/mutations";
import { API, graphqlOperation, Auth } from "aws-amplify";
import { Notifications } from "expo";
import * as Permissions from "expo-permissions";
class Main extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
profile: {},
message: "",
user: ""
};
this.handleSubmit = this.handleSubmit.bind(this);
}
async componentDidMount() {
const user = await Auth.currentSession()
.then(data => {
this.setState({ user: data.idToken.payload.sub });
return data.idToken.payload.sub;
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
const profile = await this.getUserProfile(user);
// There is no expoToken available yet, so we will request that and save it into the profile
if (profile.expoToken === null) {
const { status } = await Permissions.askAsync(Permissions.NOTIFICATIONS);
if (status !== "granted") {
alert("No notification permissions!");
return;
}
let token = await Notifications.getExpoPushTokenAsync();
// Only update the profile with the expoToken if it not exists yet
if (token !== "") {
const inputParams = {
id: user,
expoToken: token
};
await API.graphql(
graphqlOperation(mutations.updateUser, { input: inputParams })
)
.then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
}
}
async getUserProfile(sub) {
const result = await API.graphql(
graphqlOperation(queries.getUser, { id: sub })
)
.then(result => {
this.setState({
profile: result.data.getUser
});
return result.data.getUser;
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
return result;
}
async handleSubmit() {
const inputParams = {
message: this.state.message,
token: this.state.profile.expoToken,
name: this.state.profile.name,
email: this.state.profile.email,
id: this.state.user
};
await API.graphql(
graphqlOperation(mutations.pinpoint, { input: inputParams })
)
.then(result => {
console.log(result);
console.log("success");
this.setState({ message: "" });
})
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
render() {
return (
<View style={{ marginTop: 80, marginLeft: 10, marginRight: 10 }}>
<TextInput
placeholder="Your push message"
value={this.state.message}
onChangeText={input => this.setState({ message: input })}
style={{
paddingLeft: 5,
height: 40,
fontSize: 16,
marginBottom: 6,
marginTop: 2
}}
></TextInput>
<Button title="Submit" onPress={this.handleSubmit} />
</View>
);
}
}
export default Main;
您的应用程序已准备就绪,您可以从根项目启动它:
expo start"
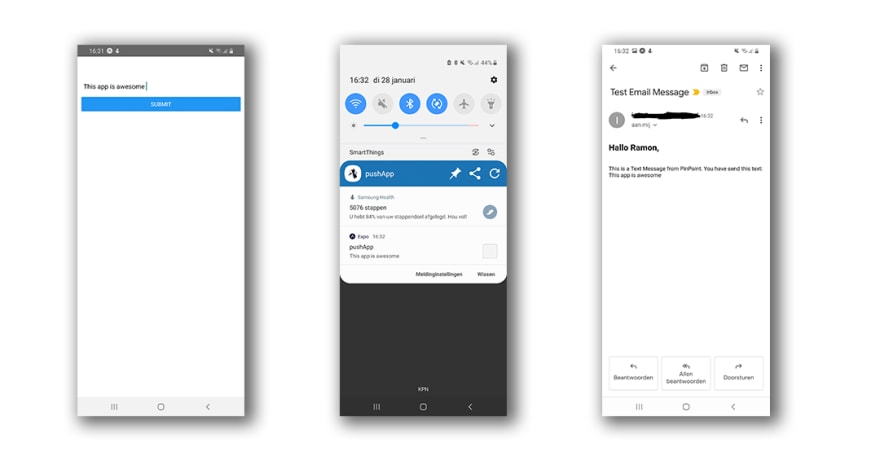
您需要在实体设备上安装 Expo 客户端并启动应用,否则无法测试推送通知。使用您通过 AWS Cognito 创建的用户登录,填写推送消息,等待几秒钟……然后……您就会在应用中收到推送消息,并在您的帐户中收到一封电子邮件。
结论
你能用这些优秀的工具(AWS Amplify、React Native 和 Expo)快速将这些功能交付给客户,真是太棒了。你的应用已经准备好吸引客户了 :)
我一直在努力让推送通知正常运行,同时又要保留所有工具,以便能够从中受益。我必须突破当前的限制,于是就想出了这个架构和实现方案。
希望你喜欢这篇指南,也期待你在评论区留言反馈,或者分享你已实现此设置的项目。祝你编程愉快!
参考链接:https://dev.to/aws-builders/the-guide-to-implement-push-notifications-with-react-native-expo-and-aws-amplify-4imn实际代码请见 github:[ https://github.com/rpostulart/pushapp ]
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com