FullStack - 如何在 2021 年使用纯 HTML、CSS 和 JS 创建可运行的博客网站。
视频教程
代码
您可能觉得有用的文章
大家好,今天我们将学习如何仅使用 HTML、CSS 和 JS 轻松创建一个博客网站,无需其他库。我们还将使用 Firebase Firestore 来存储/检索博客数据。
这是一个非常适合练习全栈开发的项目。我刚开始接触Web开发的时候,总是想着如何搭建自己的博客网站。如今,我很自豪自己尝试做了一个博客网站。我们的网站非常简单,功能如下:
- 动态博客页面。
- 拥有专门的博客编辑器。
- 您可以添加/创建任意数量的博客。
- 您可以向博客文章添加标题、段落和图像。
- 也阅读了更多博客部分。
如果您想观看演示或完整的编码教程视频,可以观看下面的教程。
视频教程
如果您能订阅我的 YouTube 频道来支持我,我将不胜感激。
因此,不要浪费更多时间,让我们看看如何编写代码。
代码
由于这是一个 node.js web 应用,我们需要 NPM 和 Node.js 才能启动,因此请确保您的系统中已安装它们。
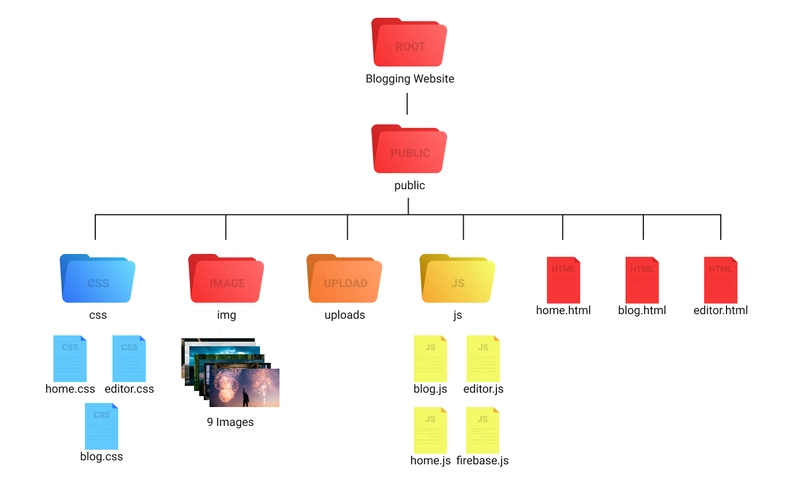
那么让我们从它的文件夹结构开始吧。
文件夹结构。
这是我们的文件夹结构。
那么让我们创建我们的服务器。
服务器
在代码编辑器中打开项目文件(根目录)。打开终端并运行
npm init
这会将 NPM 初始化到我们的项目中。之后,通过这个安装一些包。
npm i express.js express-fileupload nodemon
- express.js- 是创建服务器
- express-fileupload- 是处理上传
- nodemon- 是持续运行服务器
一旦软件包安装完成,你应该会package.json在根目录中看到一个文件。打开它。
并将其更改scripts为
"scripts": {
"start":"nodemon server.js"
}
现在我们可以创建服务器了。在根目录中创建一个新文件,命名为server.js。然后打开它。
首先导入我们需要的所有包。
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const fileupload = require('express-fileupload');
然后将public文件夹路径存储在变量中。
let initial_path = path.join(__dirname, "public");
之后创建expressJS服务器。并将public文件夹路径设置为静态路径。也用于app.use(fileupload())启用文件上传。
const app = express();
app.use(express.static(initial_path));
app.use(fileupload());
之后创建一个主路由并发送home.html文件作为响应。然后在 3000 端口上运行你的服务器。
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(initial_path, "home.html"));
})
app.listen("3000", () => {
console.log('listening......');
})
使用 运行你的服务器npm start。现在我们的服务器就完成了。现在我们来创建主页。
主页
编写基本的 HTML 结构和链接home.css文件。然后开始创建导航栏。
主页.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Blog : Homepage</title>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Poppins:ital,wght@0,400;0,500;0,600;1,600&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/home.css">
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar">
<img src="img/logo.png" class="logo" alt="">
<ul class="links-container">
<li class="link-item"><a href="/" class="link">home</a></li>
<li class="link-item"><a href="/editor" class="link">editor</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</body>
</html>
主页.css
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body{
width: 100%;
position: relative;
font-family: 'poppins', sans-serif;
}
::selection{
background: #1b1b1b;
color: #fff;
}
.navbar{
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
padding: 0 5vw;
background: #fff;
z-index: 9;
}
.links-container{
display: flex;
list-style: none;
}
.link{
padding: 10px;
margin-left: 10px;
text-decoration: none;
text-transform: capitalize;
color: #000;
}
输出
现在创建标题。
<header class="header">
<div class="content">
<h1 class="heading">
<span class="small">welcome in the world of</span>
blog
<span class="no-fill">writing</span>
</h1>
<a href="/editor" class="btn">write a blog</a>
</div>
</header>
.header{
margin-top: 60px;
width: 100%;
height: calc(100vh - 60px);
background: url(../img/header.png);
background-size: cover;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.content{
text-align: center;
}
.heading{
color: #fff;
text-transform: capitalize;
font-size: 80px;
line-height: 60px;
margin-bottom: 80px;
}
.heading .small{
display: block;
font-size: 40px;
}
.heading .no-fill{
font-style: italic;
color: transparent;
-webkit-text-stroke: 2px #fff;
}
.btn{
padding: 10px 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
background: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.7);
color: #000;
text-decoration: none;
text-transform: capitalize;
}
输出
现在我们来制作主页的最后一个元素。创建博客卡片部分并制作一张卡片,因为我们稍后会用 JS 制作这些卡片。
<section class="blogs-section">
<div class="blog-card">
<img src="img/header.png" class="blog-image" alt="">
<h1 class="blog-title">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur.</h1>
<p class="blog-overview">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Sunt incidunt fugiat quos porro repellat harum. Adipisci tempora corporis rem cum.</p>
<a href="/" class="btn dark">read</a>
</div>
</section>
.blogs-section{
width: 100%;
padding: 50px 5vw;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
grid-gap: 80px;
}
.blog-image{
width: 100%;
height: 250px;
object-fit: cover;
border-radius: 10px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.blog-overview{
margin: 10px 0 20px;
line-height: 30px;
}
.btn.dark{
background: #1b1b1b;
color: #fff;
}
输出
现在,你可以注释该blog-card元素了。我们的主页已经完成了。进入服务器并创建/editor路由。
服务器.js
app.get('/editor', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(initial_path, "editor.html"));
})
之后我们来制作我们的编辑器。
编辑。
链接editor.html两个home.css文件editor.css。在 body 标签内,首先创建横幅 div。
<div class="banner">
<input type="file" accept="image/*" id="banner-upload" hidden>
<label for="banner-upload" class="banner-upload-btn"><img src="img/upload.png" alt="upload banner"></label>
</div>
.banner{
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
position: relative;
background: #e7e7e7;
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
}
.banner-upload-btn{
position: absolute;
bottom: 20px;
right: 20px;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
border-radius: 50%;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
cursor: pointer;
}
.banner-upload-btn img{
width: 20px;
}
输出
然后为博客标题、文章创建文本字段。
<div class="blog">
<textarea type="text" class="title" placeholder="Blog title..."></textarea>
<textarea type="text" class="article" placeholder="Start writing here..."></textarea>
</div>
.blog{
width: 70vw;
min-width: 400px;
height: 100px;
display: block;
margin: auto;
padding: 50px 0;
}
textarea::-webkit-scrollbar{
width: 10px;
}
textarea::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb{
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
border-radius: 10px;
}
.title,
.article{
width: 100%;
min-height: 100px;
height: auto;
outline: none;
font-size: 50px;
font-weight: 600;
color: #2d2d2d;
resize: none;
border: none;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
}
.title::placeholder,
.article::placeholder{
color: #2d2d2d;
}
.article{
height: 500px;
font-size: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
line-height: 30px;
font-weight: 500;
padding-bottom: 100px;
white-space: pre-wrap;
}
输出
最后,制作带有上传图像按钮的发布按钮。
<div class="blog-options">
<button class="btn dark publish-btn">publish</button>
<input type="file" accept="image/*" id="image-upload" hidden>
<label for="image-upload" class="btn grey upload-btn">Upload Image</label>
</div>
.blog-options{
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 60px;
background: #fff;
z-index: 9;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.btn{
border: none;
outline: none;
cursor: pointer;
}
.btn.grey{
background: #a5a5a5;
color: #fff;
margin-left: 20px;
font-size: 14px;
}
输出
编辑器的样式已经设计完毕。现在开始实现它的功能。链接editor.js到 HTML 文件,然后打开它。
首先选择我们需要的所有元素。
const blogTitleField = document.querySelector('.title');
const articleFeild = document.querySelector('.article');
// banner
const bannerImage = document.querySelector('#banner-upload');
const banner = document.querySelector(".banner");
let bannerPath;
const publishBtn = document.querySelector('.publish-btn');
const uploadInput = document.querySelector('#image-upload');
选择所有元素后。将change事件添加到我们的上传输入并处理上传。
bannerImage.addEventListener('change', () => {
uploadImage(bannerImage, "banner");
})
uploadInput.addEventListener('change', () => {
uploadImage(uploadInput, "image");
})
现在创建uploadImage函数。
const uploadImage = (uploadFile, uploadType) => {
const [file] = uploadFile.files;
if(file && file.type.includes("image")){
const formdata = new FormData();
formdata.append('image', file);
fetch('/upload', {
method: 'post',
body: formdata
}).then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
if(uploadType == "image"){
addImage(data, file.name);
} else{
bannerPath = `${location.origin}/${data}`;
banner.style.backgroundImage = `url("${bannerPath}")`;
}
})
} else{
alert("upload Image only");
}
}
这就是我们上传文件的方法。但现在还不行,因为我们还没有创建/upload路由。为此,请打开server.js并创建/upload路由。
服务器.js
app.post('/upload', (req, res) => {
let file = req.files.image;
let date = new Date();
// image name
let imagename = date.getDate() + date.getTime() + file.name;
// image upload path
let path = 'public/uploads/' + imagename;
// create upload
file.mv(path, (err, result) => {
if(err){
throw err;
} else{
// our image upload path
res.json(`uploads/${imagename}`)
}
})
})
至此,我们就大功告成了。您可以检查上传是否成功。您可能注意到,我们正在调用,addImage()但还没有执行。那就开始吧。
editor.js
const addImage = (imagepath, alt) => {
let curPos = articleFeild.selectionStart;
let textToInsert = `\r\r`;
articleFeild.value = articleFeild.value.slice(0, curPos) + textToInsert + articleFeild.value.slice(curPos);
}
此功能将允许您插入图像的文本格式,例如,如果我上传,则此功能会在我们的文章字段中1.png插入类似的内容。
到目前为止,我们的上传工作也完成了。现在,前往你的 Firebase 并创建一个博客项目。然后设置你的 Firebase。你可以参考这个视频来了解如何设置。
像这样在上述firebase.js文件中的链接中设置 firebase 变量之后。editor.htmleditor.js
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/8.9.1/firebase-app.js"></script>
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/8.9.1/firebase-firestore.js"></script>
<script src="js/firebase.js"></script>
<script src="js/editor.js"></script>
然后再次进入editor.js。并使发布按钮可用。
let months = ["Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"];
publishBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
if(articleFeild.value.length && blogTitleField.value.length){
// generating id
let letters = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz';
let blogTitle = blogTitleField.value.split(" ").join("-");
let id = '';
for(let i = 0; i < 4; i++){
id += letters[Math.floor(Math.random() * letters.length)];
}
// setting up docName
let docName = `${blogTitle}-${id}`;
let date = new Date(); // for published at info
//access firstore with db variable;
db.collection("blogs").doc(docName).set({
title: blogTitleField.value,
article: articleFeild.value,
bannerImage: bannerPath,
publishedAt: `${date.getDate()} ${months[date.getMonth()]} ${date.getFullYear()}`
})
.then(() => {
location.href = `/${docName}`;
})
.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
})
}
})
这就是我们在 Firebase Firestore 中创建文档的方法。之后我们的编辑器就可以正常工作了。如果你测试一下,你会发现你被重定向到了博客路由。但我们还没有创建那个路由。server.js上次打开过那个路由。创建blog路由,然后404路由。
服务器.js
app.get("/:blog", (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(initial_path, "blog.html"));
})
app.use((req, res) => {
res.json("404");
})
现在你应该能看到blog.html文件了。上次我们先来创建博客页面。这次把所有 3 个 CSS 文件链接到这个页面blog.html,并将导航栏复制home.html到这个页面。
<div class="banner"></div>
<div class="blog">
<h1 class="title"></h1>
<p class="published"><span>published at - </span></p>
<div class="article">
</div>
</div>
.blog, .article{
position: relative;
height: fit-content;
padding-bottom: 0;
}
.article, .title{
min-height: auto;
height: fit-content;
padding: 0 10px;
white-space: normal;
}
.published{
margin: 20px 0 60px;
padding: 0 10px;
text-transform: capitalize;
font-style: italic;
color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
.published span{
font-weight: 700;
font-style: normal;
}
.article *{
margin: 30px 0;
color: #2d2d2d;
}
.article-image{
max-width: 100%;
max-height: 400px;
display: block;
margin: 30px auto;
object-fit: contain;
}
输出
此页面已包含所有元素结构。我们将使用 JS 动态提供其内容。
链接 Firebase 脚本,firebase.js然后blog.js打开blog.js
首先从 URL 中提取博客 ID,然后从 Firestore 获取数据
let blogId = decodeURI(location.pathname.split("/").pop());
let docRef = db.collection("blogs").doc(blogId);
docRef.get().then((doc) => {
if(doc.exists){
setupBlog(doc.data());
} else{
location.replace("/");
}
})
一旦我们获得了博客数据。制作setupBlog()。
const setupBlog = (data) => {
const banner = document.querySelector('.banner');
const blogTitle = document.querySelector('.title');
const titleTag = document.querySelector('title');
const publish = document.querySelector('.published');
banner.style.backgroundImage = `url(${data.bannerImage})`;
titleTag.innerHTML += blogTitle.innerHTML = data.title;
publish.innerHTML += data.publishedAt;
const article = document.querySelector('.article');
addArticle(article, data.article);
}
在上面的函数中,我们选择了所有需要的元素并设置了它们的内容。
最后,我们调用addArticle这个函数是因为我们需要格式化文章。
addArticle对从 firstore 获取的文章文本进行功能化和格式化。
const addArticle = (ele, data) => {
data = data.split("\n").filter(item => item.length);
// console.log(data);
data.forEach(item => {
// check for heading
if(item[0] == '#'){
let hCount = 0;
let i = 0;
while(item[i] == '#'){
hCount++;
i++;
}
let tag = `h${hCount}`;
ele.innerHTML += `<${tag}>${item.slice(hCount, item.length)}</${tag}>`
}
//checking for image format
else if(item[0] == "!" && item[1] == "["){
let seperator;
for(let i = 0; i <= item.length; i++){
if(item[i] == "]" && item[i + 1] == "(" && item[item.length - 1] == ")"){
seperator = i;
}
}
let alt = item.slice(2, seperator);
let src = item.slice(seperator + 2, item.length - 1);
ele.innerHTML += `
<img src="${src}" alt="${alt}" class="article-image">
`;
}
else{
ele.innerHTML += `<p>${item}</p>`;
}
})
}
之后,让我们比较一下我们在编辑器中输入的内容和我们在博客中看到的内容。
编辑
博客
我们的博客也完成了。现在我们想在博客页面中添加推荐或阅读更多元素。
因此打开blog.html并制作一个。
<h1 class="sub-heading">Read more</h1>
.sub-heading{
padding: 0 5vw;
color: #2d2d2d;
font-weight: 500;
font-size: 40px;
margin-top: 80px;
}
此后,将blog-section元素从home.html复制到blog.html
<section class="blogs-section">
<!-- <div class="blog-card">
<img src="img/header.png" class="blog-image" alt="">
<h1 class="blog-title">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur.</h1>
<p class="blog-overview">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Sunt incidunt fugiat quos porro repellat harum. Adipisci tempora corporis rem cum.</p>
<a href="/" class="btn dark">read</a>
</div> -->
</section>
正如您所见,我们在“阅读更多”和“博客”中使用了相同的元素。因此,我们将使用相同的 JavaScript 函数来创建这两个元素。因此,对于上面的链接home.js文件,请参考。blog.htmlblog.js
然后最后打开home.js并编码。
const blogSection = document.querySelector('.blogs-section');
db.collection("blogs").get().then((blogs) => {
blogs.forEach(blog => {
if(blog.id != decodeURI(location.pathname.split("/").pop())){
createBlog(blog);
}
})
})
const createBlog = (blog) => {
let data = blog.data();
blogSection.innerHTML += `
<div class="blog-card">
<img src="${data.bannerImage}" class="blog-image" alt="">
<h1 class="blog-title">${data.title.substring(0, 100) + '...'}</h1>
<p class="blog-overview">${data.article.substring(0, 200) + '...'}</p>
<a href="/${blog.id}" class="btn dark">read</a>
</div>
`;
}
这就是我们制作博客卡片的方法。完成了。
输出 - Home.html
输出 - Blog.html
好了,就是这样。希望你理解了所有内容。如果你有疑问或者我遗漏了什么,请在评论区告诉我。
您可能觉得有用的文章
如果您能订阅我的YouTube频道,我将不胜感激。我创作了非常棒的网络内容。
感谢您的阅读。
文章来源:https://dev.to/themodernweb/fullstack-how-to-create-a-working-blogging-website-with-pure-html-css-and-js-in-2021-9di 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com