使用 Vue: Electron 构建桌面应用程序
在我之前的文章中,我介绍了如何使用Vuido构建一个基于Vue框架的桌面应用。Vuido 是一个非常棒的库,可以用来创建快速、小巧的桌面应用,并且支持原生平台组件。但它也有一些缺点,例如不支持 CSS 样式或图片。现在,是时候尝试使用Electron来构建一个桌面应用了。
Electron 是由 GitHub 开发的开源库,用于使用 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 构建跨平台桌面应用程序。Electron 通过将Chromium和Node.js整合到一个运行时中来实现这一点,并且可以为 Mac、Windows 和 Linux 打包应用程序。
为了快速入门,我使用了Greg Holguin编写的electron-vue样板。它为开发人员提供了 vue-cli 脚手架、常用的 Vue 插件、打包程序、测试、开发工具和其他功能。
💻我们要构建什么
我们将构建与上一篇文章相同的应用程序:一个基于OpenWeatherMap API构建的用于检查用户所选城市天气的应用程序。
如果您只想检查最终的 Electron 驱动的应用程序代码,请点击此处。
🛠️ 安装
electron-vue 样板文件是作为VueCLI 2.x的模板构建的,其中包含自定义应用程序的选项。因此,你需要全局安装它:
npm install -g vue-cli
如果您更喜欢使用最新版本的 VueCLI,您还需要安装全局桥:
npm install -g @vue/cli @vue/cli-init
然后初始化你的项目:
vue init simulatedgreg/electron-vue weather-app
这将启动一个安装项目,您需要在安装过程中做出一些选择。
很酷的是,如果您需要一些常用的插件和库(例如axios),您可以在安装过程中选择它们。
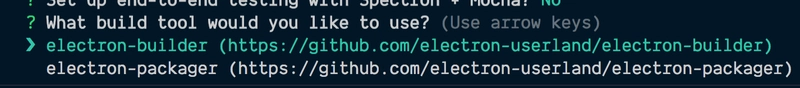
几乎所有选择都很明确,但有一个问题:
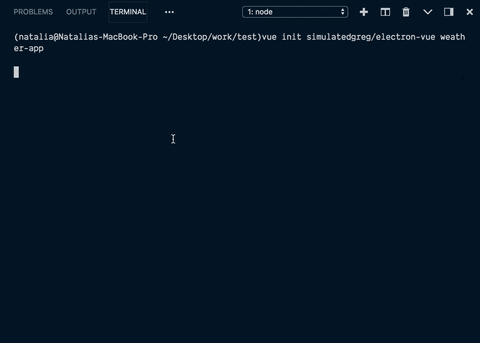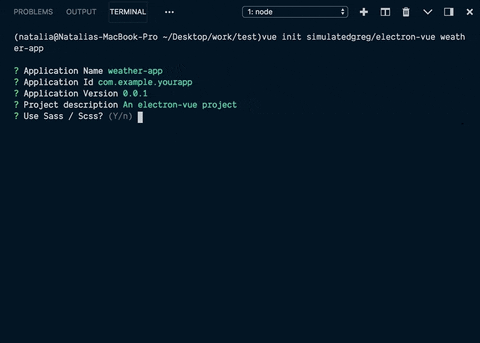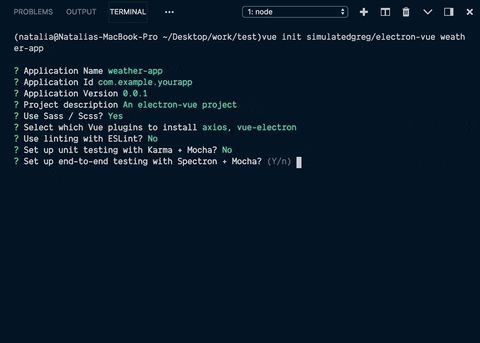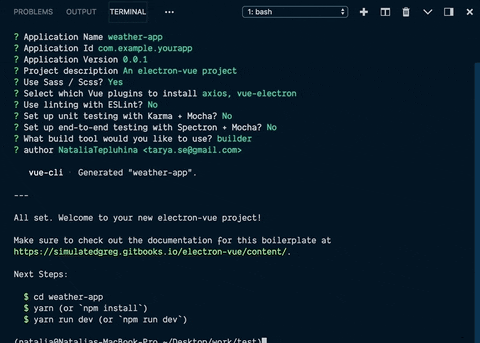
我决定用 Google 一下,然后在 StackOverflow 上找到了这个有用的帖子。根据帖子内容来看,这electron-builder对我来说似乎是个更好的选择,所以我就选择了它。
项目设置完成后,您需要转到应用程序文件夹并运行npm install或,yarn install然后我们就可以开始了。
🔦理解应用程序结构
安装完成后,您可以看到其中有两个文件夹src:main和renderer。第一个文件夹是 Electon 主进程所必需的
根据 electron-vue 文档,在 Electron 中,运行
package.json主脚本的进程称为主进程。在主进程中运行的脚本可以通过创建网页来显示 GUI。
该文件夹中有两个文件main:index.js和index.dev.js。第一个是应用程序的主文件,即应用程序启动时使用的文件electron。它也是 Webpack 在生产环境中的入口文件。所有主要流程工作都应从这里开始。
index.dev.js专门用于开发,因为它会安装electron-debug& vue-devtools。在开发应用程序时无需触碰它。
renderer文件夹是renderer流程所必需的。
由于 Electron 使用 Chromium 来显示网页,因此也使用了 Chromium 的多进程架构。Electron 中的每个网页都在其自己的进程中运行,该进程称为渲染进程。
你可能注意到了,这是一个“普通”的 Vue 应用程序结构,包含文件夹assets和文件。后者的结构如下:componentsmain.jsApp.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<landing-page></landing-page>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import LandingPage from '@/components/LandingPage'
export default {
name: 'weather-app',
components: {
LandingPage
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* CSS */
</style>
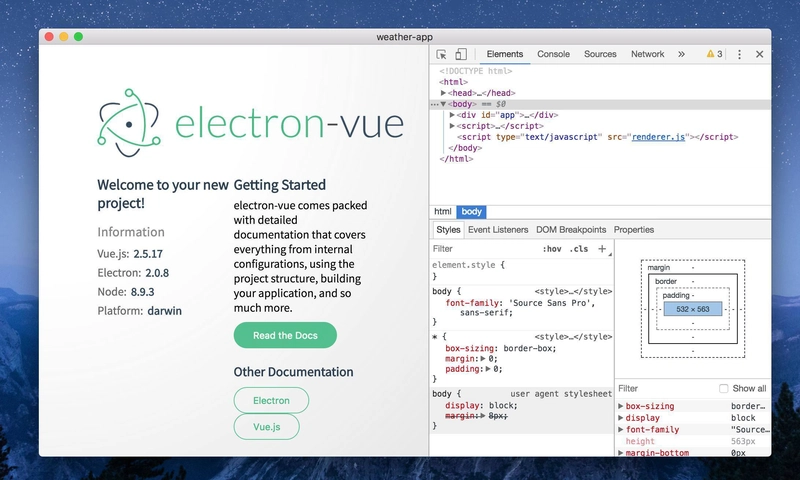
如果你尝试运行dev任务,你将会得到这样的结果:
现在组件已经创建完毕landing-page,开发者工具也已经打开。现在我们可以开始修改它了!
🕹️ 搭建应用程序
与 Vuido 不同,基于 Electron 的应用是用 HTML 标签构建的,而不是原生组件。因此,我们将创建一个类似于普通 Web 应用的结构,并使用 CSS 为其设置样式。
注意:我特意没有安装任何 CSS 框架或组件库:我想在不添加任何依赖项的情况下比较包大小。两个项目中唯一使用的库是axios。
第一步是删除landing-page组件。然后我添加了一个简单的输入字段和一个按钮:
<div id="app">
<p>Enter the city name to check current weather in it</p>
<section class="weather-input">
<input type="text" v-model="query">
<button :disabled="!query.length">Check</button>
</section>
</div>
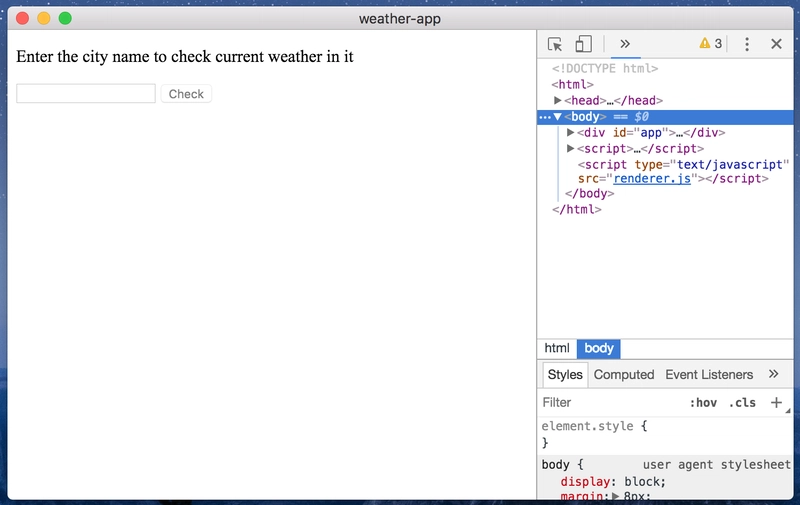
现在我们的应用程序看起来是这样的:
我们在数据中有一个query属性来处理用户输入,我们将以该查询作为参数进行 API 调用。
🔗 进行 API 调用
我使用了OpenWeatherMap 的当前天气 API。它提供了许多不同的信息,您可以在此处查看 JSON 响应的示例。
我们axios在安装过程中已经将其添加到应用程序中。让我们看一下src/renderer/main.js:
import Vue from 'vue';
import axios from 'axios';
import App from './App';
if (!process.env.IS_WEB) Vue.use(require('vue-electron'));
Vue.http = Vue.prototype.$http = axios;
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
所以我们可以像在组件实例中一样使用 axios 方法了this.$http!这里我们唯一需要添加的是 API 调用的基本 URL:
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5';
现在App.vue我们将创建一组数据属性来显示不同的天气数据:
data() {
return {
query: '',
error: false,
city: '',
country: '',
weatherDescription: '',
temp: null,
tempMin: null,
tempMax: null,
humidity: null,
icon: '',
};
},
与 Vuido 版本相比,我添加了一个附加属性,它是一个icon。API 提供了一个天气图标,但我们无法在 Vuido 应用中使用它,因为目前不支持显示图像。
我们还创建一个方法来获取数据:
methods: {
showWeather() {
this.$http
.get(`/weather?q=${this.query}&units=metric&&appid=${API_KEY}`)
.then(response => {
this.city = response.data.name;
this.country = response.data.sys.country;
this.weatherDescription = response.data.weather[0].description;
this.temp = response.data.main.temp;
this.tempMin = response.data.main.temp_min;
this.tempMax = response.data.main.temp_max;
this.humidity = response.data.main.humidity;
this.icon = `http://openweathermap.org/img/w/${
response.data.weather[0].icon
}.png`;
this.error = false;
})
.catch(() => {
this.error = true;
this.city = '';
});
},
},
并将其添加到按钮的点击回调中:
<button :disabled="!query.length" @click="showWeather">Check</button>
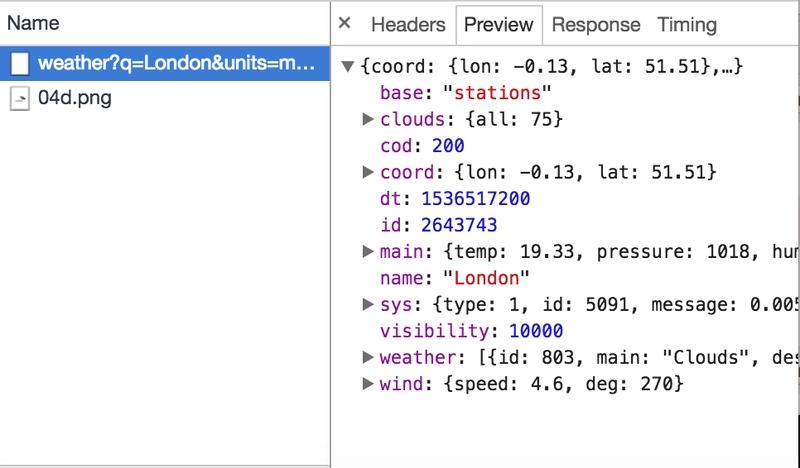
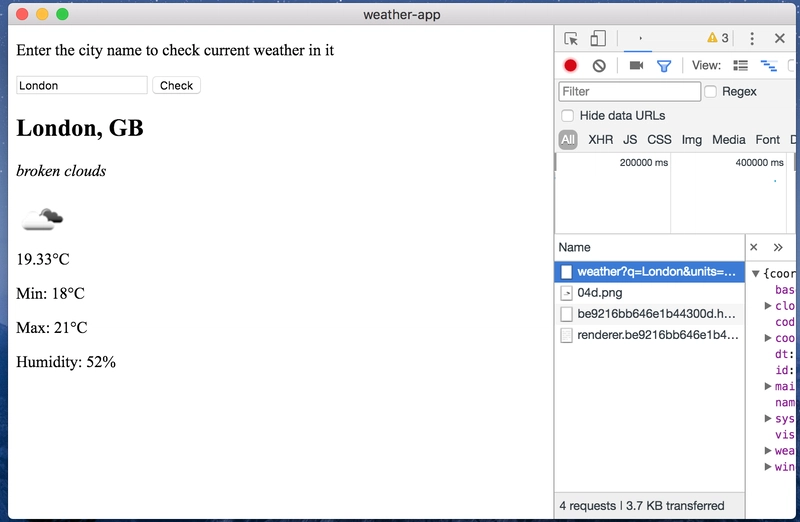
现在,如果您在输入字段中输入文本并单击按钮,您可以在选项Network卡中观察 API 调用:
💅 显示天气数据
让我们将这些数据添加到模板中:
<template>
<main id="app">
<p>Enter the city name to check current weather in it</p>
<section class="weather-input">
<input type="text" v-model="query">
<button :disabled="!query.length" @click="showWeather">Check</button>
</section>
<section v-if="error" class="weather-error">
There is no such city in the database
</section>
<section v-if="city.length" class="weather-result">
<h1>{{city}}, {{country}}</h1>
<p><em>{{weatherDescription}}</em></p>
<div class="weather-result__main">
<img :src="icon" alt="Weather icon">
<div class="weather-result__temp">
{{temp}}°C
</div>
</div>
<div class="weather-result__details">
<p>Min: {{tempMin}}°C</p>
<p>Max: {{tempMax}}°C</p>
<p>Humidity: {{humidity}}%</p>
</div>
</section>
</main>
</template>
我们的应用视图:
太棒了,我们能看到真实的天气了!不过看起来像是 1999 年的……我们来加点 CSS 魔法吧(其实,很多CSS 魔法)!
<style lang="scss">
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html,
body,
#app {
height: 100%;
}
#app {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
font-size: 16px;
padding: 10px;
background: rgb(212, 228, 239);
background: -moz-radial-gradient(
center,
ellipse cover,
rgba(212, 228, 239, 1) 0%,
rgba(134, 174, 204, 1) 100%
);
background: -webkit-radial-gradient(
center,
ellipse cover,
rgba(212, 228, 239, 1) 0%,
rgba(134, 174, 204, 1) 100%
);
background: radial-gradient(
ellipse at center,
rgba(212, 228, 239, 1) 0%,
rgba(134, 174, 204, 1) 100%
);
filter: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient( startColorstr='#d4e4ef', endColorstr='#86aecc',GradientType=1 ); /* IE6-9 fallback on horizontal gradient */
}
.weather-input {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 20px 0;
}
.weather-result {
text-align: center;
&__main {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
padding-top: 5px;
font-size: 1.3rem;
font-weight: bold;
}
&__details {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-around;
color: dimgray;
}
}
.weather-error {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
input {
width: 75%;
outline: none;
height: 20px;
font-size: 0.8rem;
}
button {
display: block;
width: 25%;
height: 25px;
outline: none;
border-radius: 5px;
white-space: nowrap;
margin: 0 10px;
font-size: 0.8rem;
}
</style>
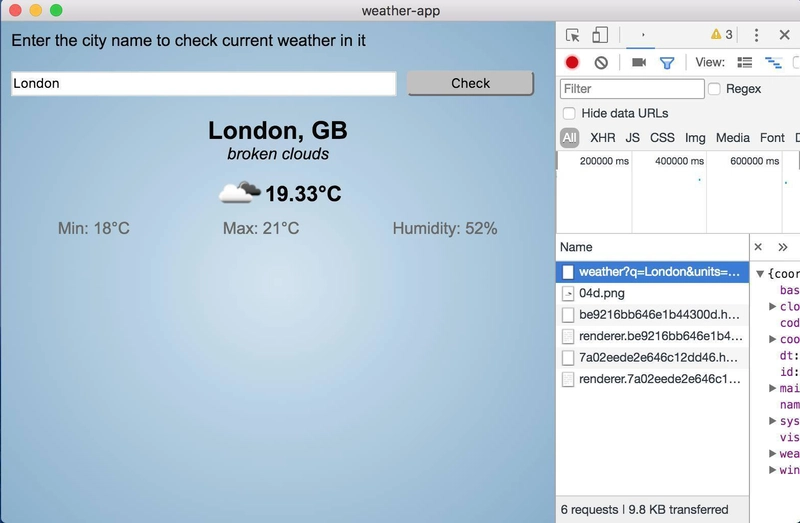
最后,我们得到了功能齐全的应用程序:
打包之前最后一件事是缩小窗口大小。如果我们检查一个src/main/index.js文件,就能找到它的设置:
mainWindow = new BrowserWindow({
height: 563,
useContentSize: true,
width: 1000
})
我们将宽度改为450,高度改为250
📦包装
好消息:你可以将你的应用构建为 Web 应用!运行build:web任务后,你会在一个文件夹中找到一个“构建 Web 应用”文件dist夹。
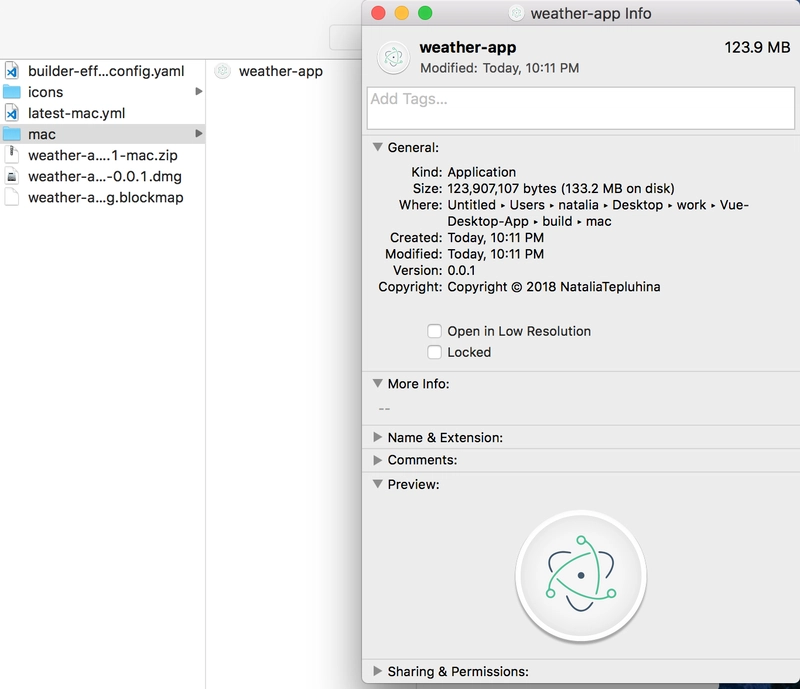
现在让我们回到桌面应用程序并运行build任务。结果,你会在build文件夹内看到一个以你的平台命名的文件夹(对我来说是mac),里面有一个应用程序文件。它的大小……哇,133 MB!
对于这么小的一个应用程序来说,这可真是太多了!另外,如果你尝试运行它,你会发现它的启动速度比 Vuido 驱动的应用程序要慢一些。
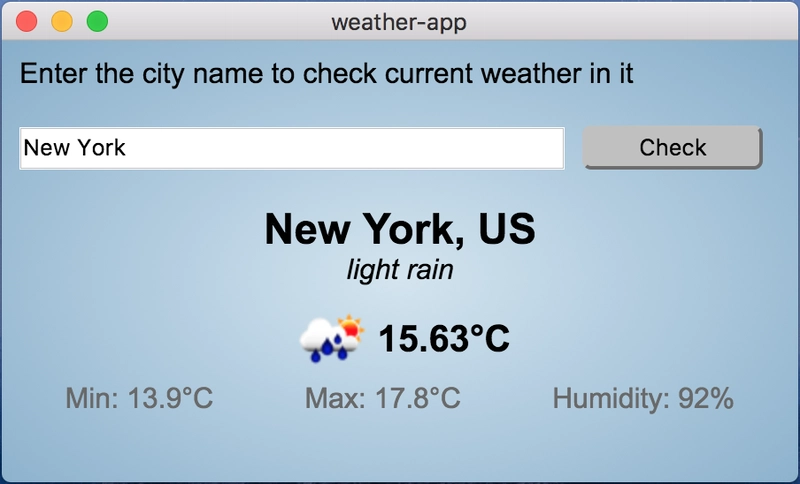
最终外观:
🌟 结论
优点:
- 易于启动
- 好的文档
- 提供 Web 应用程序构建
- 可以通过 CSS 样式进行定制
缺点
- 包装尺寸非常大
- 比使用本机 GUI 组件构建的应用程序慢
如果您的应用程序需要独特的外观并且不太关心包大小和性能,Electron-vue 是一个不错的选择。
更新
如果你的 Web 应用程序是使用 Vue CLI 3 构建的,那么你可以使用Vue CLI 插件 Electron Builder轻松将其转换为桌面应用程序。你只需要在项目根文件夹中运行以下命令:
vue add electron-builder
完成后,您将有两个额外的 npm 任务:serve:electron并build:electron使用桌面应用程序。
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com