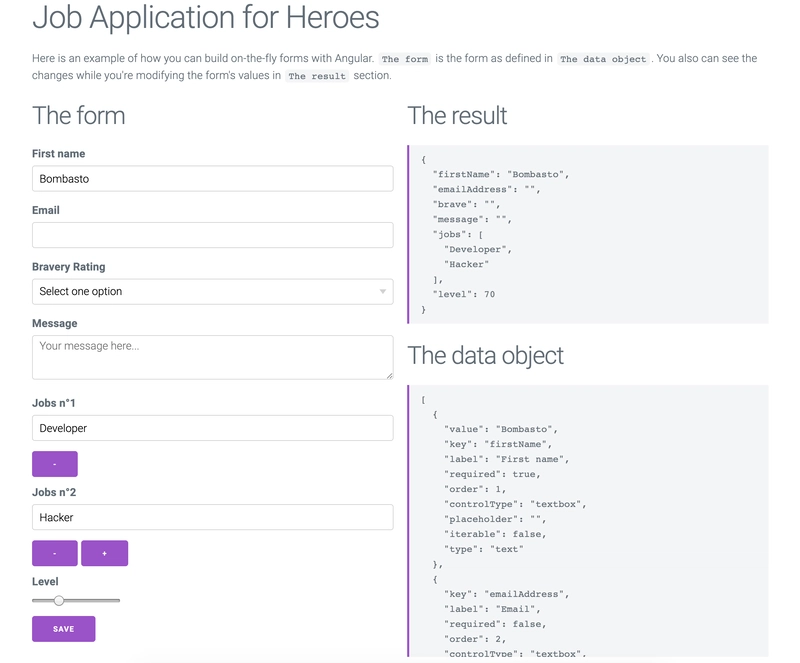
即时构建动态 Angular 表单
元数据
组件
使其可迭代(可重复)
演示和代码
在 Angular 项目中,表单从来都不是一件容易处理的事情:你需要在标记中“恰当地”设计每个表单,同时还要在组件中设计表单,FormControls并确保所有组件都能很好地协同工作。
你还必须记住,表单可能会频繁更改,以满足快速变化的业务和监管要求。
我们将了解如何使用描述业务对象模型的元数据创建动态表单。
元数据
元数据将为我们的系统提供信息,以表明将会发生什么:
- 价值观
- 字段名称
- 字段类型
- 验证条件
- 其他东西,如占位符、模式等等……
它将以 JSON 形式构建,但您显然可以使用您想要的语言:JSON+LD、csv、XML 或任何您喜欢的格式。
数据源也可以是 API、文件或任何其他可用的数据源。
在 JSON 中,它看起来像这样(你显然可以根据自己的需要进行调整):
// question-base.ts
export class QuestionBase<T> {
value: T;
key: string;
label: string;
required: boolean;
order: number;
controlType: string;
placeholder: string;
iterable: boolean;
...
}
这将成为我们创建的所有其他类型元素的骨架,例如:
- 输入
- 文本区域
- 选择
- 任何其他表单字段...
这些表单元素将共享相同的内容Class,并根据各自的需求进行扩展。例如,option仅适用于<select>以下元素:
// question-dropdown.ts
import { QuestionBase } from './question-base';
export class DropdownQuestion extends QuestionBase<string> {
controlType = 'dropdown';
options: { key: string, value: string }[] = [];
constructor(options: {} = {}) {
super(options);
this.options = options['options'] || [];
}
}
组件
为了使代码灵活、可靠、易于测试和维护,它被拆分成两部分。首先,组件 ( app-dynamic-form) 会作为包装器在应用程序的组件中始终被调用:
<!-- app.component.html -->
<app-dynamic-form #dynamicForm
[questions]="questions"></app-dynamic-form>
然后,为了创建每个单独的表单字段,app-question将调用并重复该组件:app-dynamic-form
<!-- dynamic-form.component.html -->
...
<div *ngFor="let question of questions"
class="form-row">
<app-question [question]="question"
[form]="form"></app-question>
</div>
...
使其可迭代(可重复)
正如您在上面看到的,app-question被包装在一个ngFor循环遍历集合的里面questions,而这个集合只不过是一个数组,QuestionBase正如本文开头所演示的那样。
在这个组件内部,有一个ngSwitch。它的作用是根据对象中给定的字段类型显示正确的 HTMLElement:
<!-- dynamic-form-question.component.html -->
<div [ngSwitch]="question.controlType">
<input *ngSwitchCase="'textbox'"
[formControl]="questionControl(index)"
[placeholder]="question.placeholder"
[attr.min]="question['min']"
[attr.max]="question['max']"
[attr.pattern]="question['pattern']"
[id]="questionId(index)"
[type]="question['type']">
<select [id]="question.key"
*ngSwitchCase="'dropdown'"
[formControl]="questionControl(index)">
<option value=""
disabled
*ngIf="!!question.placeholder"
selected>{{ question.placeholder }}</option>
<option *ngFor="let opt of question['options']"
[value]="opt.key">{{ opt.value }}</option>
</select>
...
</div>
您可能已经注意到我们传递属性值的方式,例如向在中分配了属性[attr.min]="question['min']"的元素传递属性值:optionsconstructor
// question-dropdown.ts
import { QuestionBase } from './question-base';
export class TextboxQuestion extends QuestionBase<string> {
type: string;
min: number | string;
...
constructor(options: {} = {}) {
super(options);
this.type = options['type'] || 'text';
this.min = options['min'];
...
}
但不仅有FormControls 可以显示,FormArray' 也很棒!让我们开始进行一些内容投影:
<!-- dynamic-form-question.component.html -->
<div *ngIf="question.iterable; else formTmpl">
<div *ngFor="let field of questionArray.controls;
let i=index; first as isFirst last as isLast">
<ng-container [ngTemplateOutlet]="formTmpl"
[ngTemplateOutletContext]="{index: i}"></ng-container>
<button *ngIf="question.iterable && questionArray.controls.length > 1"
(click)="removeQuestion(i)"
type="button">-</button>
<button *ngIf="question.iterable && isLast"
(click)="addQuestion()"
type="button">+</button>
</div>
</div>
你可以看到,这一行<div *ngIf="question.iterable; else formTmpl">决定显示一个集合FormArray还是一个简单的集合FormControl,所以它被包裹在一个 中ng-template。我将当前索引传递给 ,let-index="index"因为这是知道我们处于哪个迭代步骤的唯一方法:
<!-- dynamic-form-question.component.html -->
..
<ng-template #formTmpl
let-index="index">
<label [attr.for]="questionId(index)">{{ questionLabel(index) }}</label>
<div [ngSwitch]="question.controlType">
...
这里的挑战是保持与正确元素(我们正在迭代的元素)的“链接”,因为在这种配置下, a 中question会有。此时类型和类将保持不变,因为确定 a 是否可迭代的唯一方法是检查的属性。questionsquestionquestioniterablequestion
由于index注入了属性<ng-template #formTmpl let-index="index">,我们可以轻松地通过以下方式检索它ngTemplateOutletContext:
<ng-container [ngTemplateOutlet]="formTmpl"
[ngTemplateOutletContext]="{index: i}"></ng-container>
并在集合的正确迭代中完成工作。
演示和代码
所有源代码均可在 Github 上找到,如果您只是好奇想看看动态表单的精彩之处,我们已经提供了演示!
 maximelafarie /角度动态形式
maximelafarie /角度动态形式
使用 Angular 根据数据即时生成表单
致谢
照片由Patrick Langwallner在Unsplash
上拍摄非常感谢@manekinekko的重读和修改
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com