⚡️Blazing Python🐍 并发脚本⚡️️
为了确保应用程序的高性能,程序员需要编写高效的代码。代码效率与算法效率以及软件运行时执行的速度直接相关。
🐍 Python 语言是一种 🐌 速度较慢的语言 - 与 C 或 FORTRAN 相比,为了解决这个问题,已经开发了各种方法来帮助加快编程语言的速度。
一种方法是CONCURRENCY。
并发
并发是指两个任务可以在重叠的时间段内启动、运行和完成。这并不一定意味着它们会同时运行(也就是Parallelism)。还是一头雾水😕?我们来描绘一个场景:
我们正在为一对新人策划一场梦幻婚礼。我们安排了玛丽、苏珊、马克斯和西蒙四位新人参与。这场梦幻婚礼需要蛋糕、乐队、装饰和请柬。我们安排苏珊负责烘焙蛋糕,西蒙负责聘请乐队,玛丽负责布置装饰,马克斯负责发送请柬。
这四个“朋友”(或称处理器)同时执行各自的任务(或称进程),无需切换或中断,直到任务完成。这, 用外行人的话来说,就是并发。
Python中的并发类型
Python 中的基本并发类型包括:
- 多线程🧵
- 多处理🧩(是的,我知道那是一块拼图😏)
- asyncio ⏰(更多内容请见另一篇教程)
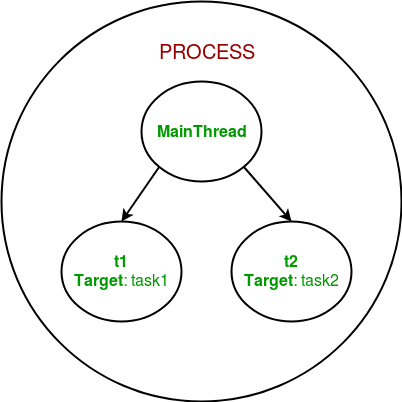
多线程🧵
AThread是操作系统中最小的process执行单元。线程是程序将自身拆分为两个或多个同时运行的任务的一种方式。线程本身并不是一个程序,它只在特定程序或 中运行。
多线程技术正在改变游戏规则,主要用于I/O 密集型操作。它是指中央处理器 (CPU)(或多核处理器中的单个核心)在操作系统的支持下,提供并发执行多个线程的能力。每个线程共享其所在进程提供的相同资源。
我们来举一个多线程操作的例子,首先我们看一下同步的过程。
同步进程
# A simple python script that gets query a list of site
import requests
import time
def get_single_site(url):
with requests.get(url) as response:
print(f"Read {len(response.content)} from {url}")
def get_all_sites(sites):
for url in sites:
get_single_site(url, session)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time()
urls = [
"https://www.google.com",
"https://www.facebook.com",
"https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced"
] * 30
get_all_sites(urls)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} in {end_time} seconds")
这是一个简单的 Python 程序,用于下载指定网站的内容。下载完成后,它会打印出访问的网站数量和所用时间。
该脚本使用了requests库和 Python 内置的标准时间库。
运行代码的输出为:
...
Read 107786 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107786 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608077 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107787 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608077 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107351 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608311 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107507 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107918 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107149 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11365 from https://www.google.com
Read 107445 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608077 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107351 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11369 from https://www.google.com
Read 107482 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Downloaded 90 in 17.5553081035614 seconds
这里,脚本需要 17.5 秒才能完成任务。现在让我们再试一次,看看是否可以使用多线程方法来加快速度。
多线程进程
# A simple python script that gets query a list of site
import requests
import time
import concurrent.futures
def get_single_site(url):
with requests.get(url) as response:
print(f"Read {len(response.content)} from {url}")
def get_all_sites(sites):
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
executor.map(get_single_site, sites)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time() # our scripts start time
sites = [
"https://www.google.com",
"https://www.facebook.com",
"https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced"
] * 30
get_all_sites(sites)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} in {end_time} seconds")
在上面的代码中,我们从 Python 标准库中导入了concurrent.futures模块ThreadPoolExecutor。该模块有一个 Executor 类,子类也由此而来。让我们来分解一下ThreadPoolExecutor。
子ThreadPoolExecutor类所做的只是简单地创建一个Pool线程。Executor 部分控制池中每个线程的运行方式和时间。
上述脚本的输出如下所示:-
...
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11354 from https://www.google.com
Read 107810 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11343 from https://www.google.com
Read 107823 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11326 from https://www.google.com
Read 107388 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 11350 from https://www.google.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 107787 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608311 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 608077 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11299 from https://www.google.com
Read 11367 from https://www.google.com
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 107785 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 11321 from https://www.google.com
Read 107800 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 107350 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608076 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 608312 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 608311 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Downloaded 90 in 6.443061351776123 seconds
这里,脚本完成任务耗时 6.4 秒。相比之下,同步运行代码则耗时 17.5 秒。你可能会心想——这只相差 12 秒,我可以接受。想象一下,如果我们的数据量更大,比如 1000 条,那么两种方法的差异就会非常明显。
多处理🧩
进程只是一个正在运行的程序实例。通俗地说,当我们在文本文件中编写计算机程序/脚本并执行该程序时,它就变成了一个进程,执行程序/脚本中提到的所有任务。进程 A不Process与其他进程共享任何内存空间Threads。
多处理是指在单个计算机系统中使用两个或多个核心。默认情况下,由于 Python 🐍 编程语言不支持多线程GIL or Global Interpreter Lock hindrance。
GIL 障碍
Python 由 Guido van Rossum 于 20 世纪 80 年代开发。当时,计算机仅使用单个 CPU。为了增强内存管理,Guido 实现了 GIL,它只允许一个线程控制 Python 解释器。这意味着,利用多个 CPU 核心或多个独立的 CPU 来并行运行线程是不可能的。
multiprocessing module为了绕过这个问题,引入了。
注意 : GIL 不会阻止创建多个线程。GIL 的作用只是确保同一时间只有一个线程在执行 Python 代码;控制权仍然会在线程之间切换。如果您仍有疑问,请访问
this article will definitely help you out。
让我们说明如何使用上面的同步代码编写多处理操作。
同步进程
# A simple python script that gets query a list of site
import requests
import time
def get_single_site(url):
with requests.get(url) as response:
print(f"Read {len(response.content)} from {url}")
def get_all_sites(sites):
for url in sites:
get_single_site(url, session)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time()
urls = [
"https://www.google.com",
"https://www.facebook.com",
"https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced"
] * 30
get_all_sites(urls)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} in {end_time} seconds")
多处理方法
# A simple python script that gets query a list of site
import requests
import time
import multiprocessing
def get_single_site(url):
with requests.get(url) as response:
print(f"Read {len(response.content)} from {url}")
def get_all_sites(sites):
with multiprocessing.Pool(5) as pool:
pool.map(get_single_site, sites)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = time.time() # our scripts start time
sites = [
"https://www.google.com",
"https://www.facebook.com",
"https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced"
] * 30
get_all_sites(sites)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} in {end_time} seconds")
这里我们从 Python 标准库中导入了 multiprocessing 包。multiprocessing 模块包含几个子类:Process 和 Pool。
这里我们利用了Pool子类。Pool它接收需要生成的工作线程或进程数量作为第一个参数,也就是在线执行的操作with multiprocessing.Pool(5) as pool: 。pool.map(get_single_site, sites)我们使用提供给 Pool 的 map 方法。该方法接收需要调用的函数作为第一个参数,并将可迭代对象(即我们的 URL 列表)作为第二个参数。然后,它将可迭代对象切分成多个块,并将它们作为单独的任务提交给进程池。
此给定操作的输出是:-
...
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 108078 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 11386 from https://www.google.com
Read 11387 from https://www.google.com
Read 11304 from https://www.google.com
Read 11353 from https://www.google.com
Read 108021 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 107985 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 108022 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 108079 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11340 from https://www.google.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11321 from https://www.google.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 107985 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11384 from https://www.google.com
Read 107549 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 11294 from https://www.google.com
Read 608423 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Read 107985 from https://www.facebook.com
Read 11360 from https://www.google.com
Read 609124 from https://www.twitter.com/theghostyced
Downloaded 90 in 6.056399154663086 seconds
在这里,脚本花了 6 秒完成任务,比线程解决方案略快一些。这是合理的,因为执行的操作是 I/O 密集型的。多处理在执行 CPU 密集型操作(例如处理大量数据)时性能更佳。
结论
我知道现在您迫不及待地想亲自尝试一下,所以在您开始之前,请注意何时使用并发。
首先,你需要弄清楚你的程序是CPU 密集型还是 I/O 密集型。记住,I/O 密集型程序是指那些大部分时间都在等待某些事情发生(例如发出外部调用或请求)的程序,而 CPU 密集型程序则主要花时间尽可能快地处理数据或进行数值运算。
因此,对于 I/O 密集型操作,多线程是最好的方法,而对于 CPU 密集型操作,多处理是正确的方法。
👋 👋 👋 👋
我是CED,希望您喜欢有关如何加快 Python 🐍 脚本运行速度的教程。
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com