面向初学者的 Sass(SCSS)
什么是 Sass(SCSS)?
Sass 和 SCSS
环境
分离文件并撰写注释
嵌套属性
&(与号)
@at-root
多变的
关于 List 和 Map 的更多信息
范围
操作员
什么是 Sass(SCSS)?
Sass 是一种预处理脚本语言,它可以被解释或编译为层叠样式表 (CSS)。
浏览器本身不会加载 Sass,但会先用 Sass 编写代码,然后再导出为 CSS。(这是因为浏览器无法读取 Sass,所以需要进行编译)
Sass 和 SCSS
Sass 有两种可用的语法。
SCSS 示例
它与 CSS 更相似,因为它使用类似 CSS 的括号。使用此语法的文件具有.scss扩展名。
//SCSS
$font-stack: Helvetica, sans-serif;
$primary-color : #333;
body {
font: 100% $font-stack;
color: $primary-color;
}
Sass 示例
Sass使用缩进(而非括号)来表示选择器的嵌套,并使用换行符(而非分号)来分隔属性。使用此语法的文件的.sass扩展名为。
//Sass
$font-stack: Helvetica, sans-serif
$primary-color : #333
body
font: 100% $font-stack
color: $primary-color
环境
我以前自己用过 Sass (SCSS),使用方式是通过 node-sass。我是通过 npm 安装的,但在课堂上我们学习了 ruby-sass,并使用了名为Live Sass Compiler 的VSC 扩展 。安装它,然后重启 VS Code。(如果你要使用 node-sass,应该先安装 node-sass)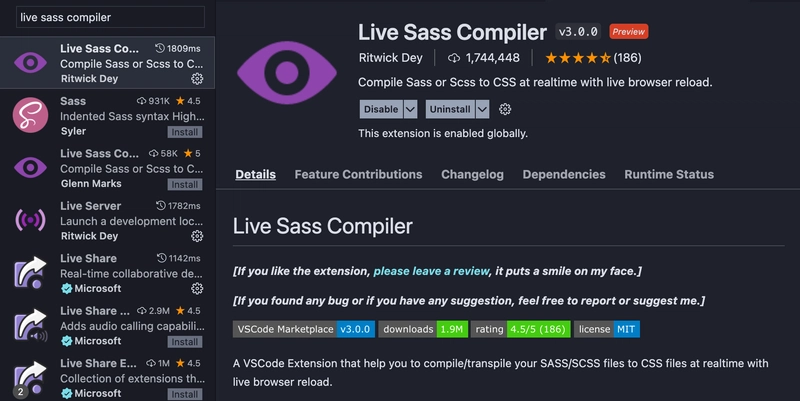
分离文件并撰写注释
您可以为每个部分创建单独的文件,例如_header.scss,_home.scss或_variable.scss,_mixin.scss。这完全取决于您,但您应该将这些分离的 scss 文件导入到一个文件中,style.scss
如果您按功能或布局分离文件,则可以轻松维护和重用代码。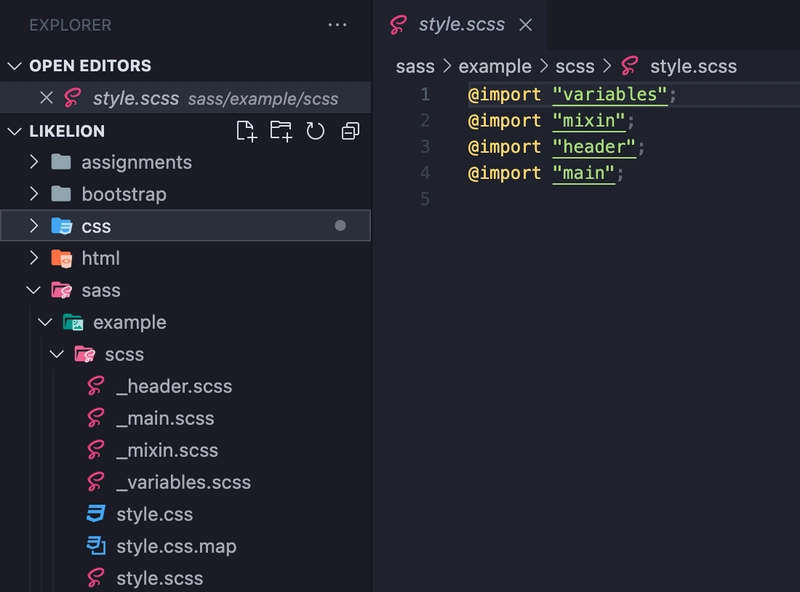
原因是文件名前面有下划线_。
如果文件名前不加下划线,每个单独的 scss 文件都会被编译,并因此保存在单独的 css 文件中。
但是,如果在文件名前加下划线,可以让 sass 知道它是主文件的一部分,主文件不会被编译,你可以使用以下命令导入该文件:@import
评论
/* This comment will be visible in CSS even after compiling. */
// This won't be compiled, only visible in Scss
嵌套
我个人认为这是 SCSS 的优点之一。
通过嵌套这些代码,你可以像查看 HTML 一样查看 CSS 代码的结构。这使得代码更具可读性。
nav {
background : #C39BD3;
padding : 10px;
height: 50px;
ul {
display: flex;
list-style : none;
justify-content: flex-end;
li {
color: white;
margin-right: 10px;
}
}
}
为什么要使用嵌套?
使用 CSS,如果你想给继承自父元素的元素赋予样式,则每次都需要选择父元素。CSS
示例
.info-list div {
display: flex;
font-size: 14px;
color: #4f4f4f;
}
.info-list div dt {
font-weight: 700;
margin-right: 7px;
}
但是你可以在 SCSS 中像下面这样执行此操作
.info-list {
div {
display: flex;
font-size: 14px;
color: #4f4f4f;
dt {
font-weight: 700;
margin-right: 7px;
}
}
}
**注意!避免嵌套过多。(尽量不要超过 3 层。如果超过 3 层,可读性会下降,而且编译成 CSS 时会使用不必要的选择器。)
嵌套属性
除了选择器之外,您还可以嵌套属性。
它用于为类添加背景样式。您可以嵌套名称为、、 等的 属性。 此外,您必须使用冒号 (:)来嵌套属性。.add-iconbackgroundbackground-imagebackground-position
add-icon {
background : {
image: url("./assets/arrow-right-solid.svg");
position: center center;
repeat: no-repeat;
size: 14px 14px;
}
}
然后上面的代码将被编译为如下所示的 CSS。
.add-icon {
background-image: url("./assets/arrow-right-solid.svg");
background-position: center center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: 14px 14px;
}
&(与号)
& 指的是外部选择器。您还可以添加伪元素,例如 after、hover、伪元素,或者在父元素之前添加选择器
。SCSS
.box {
// pseudo classes
&:focus{}
&:hover{}
&:active{}
&:first-child{}
&:nth-child(2){}
// pseudo elements
&::after{}
&::before{}
}
CSS
.box:focus{}
.box:hover{}
.box:active{}
.box:frist-child{}
.box:nth-child(2){}
.box::after{}
.box::before{}
示例- 赋予li其伪元素和伪类的样式。
ul {
li {
//pseudo element
&:hover {
background: white;
cursor: pointer;
}
//pseudo class
&:last-child {
border-bottom: 2px solid black;
}
}
}
此外,如果类以相同的单词开头,例如 box-yellow 或 box-red,则可以嵌套类。 “ box”是常用词,因此您可以这样做。SCSS
.box {
&-yellow {
background: #ff6347;
}
&-red {
background: #ffd700;
}
&-green {
background: #9acd32;
}
}
CSS
.box-yellow {
background: #ff6347;
}
.box-red {
background: #ffd700;
}
.box-green {
background: #9acd32;
}
@at-root
您可以使用其中的所有内容从文档的根目录发出,而不是使用常规嵌套来摆脱嵌套代码。SCSS@at-root
.article {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
margin-top: 10px;
.article-content {
font-size: 14px;
opacity: 0.7;
@at-root i {
opacity: 0.5;
}
}
}
CSS
.article {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.article .article-content {
font-size: 14px;
opacity: 0.7;
}
/* You can see this isn't nested. It's separated from the nested code. */
i {
opacity: 0.5;
}
多变的
能够赋值意味着您无需逐个更改变量的值。这使得代码维护更加容易。
** 注意!请注意,如果随意声明变量,可能会导致程序崩溃。仅在有充分理由的情况下才声明变量。如果您在团队中,则需要在声明变量之前充分讨论这些理由。
何时使用变量?
- 如果该值将被重复使用。(您可以不记住该值,而只需使用变量即可设置元素样式。)
- 如果您需要将现有值更改为其他值。(它用于许多没有变量的不同元素/属性中,您必须逐个更改,这很耗时,但如果将值设置为变量,则只需要更改变量的值,这需要更短的时间。)
在 Sass 中声明变量
/* bg */
$bgColor : #FFF
如果有重复使用的值,您可以使用变量轻松地对其进行样式设置。
// colour
$red: #ee4444;
$black: #222;
$bg-color: #3e5e9e;
$link-color: red;
$p-color: #282A36;
// font-size
$font-p: 13px;
$font-h1: 28px;
// font
$base-font: 'Noto Sans KR', sans-serif;
body {
background-color : $bg-color;
font-size : $font-p;
font-family : $base-font;
}
h1 {
font-size: $font-h1;
color: $black;
}
p {
font-size: $font-p;
color: $black;
}
a {
color: $link-color;
}
变量类型
- 数字(例如 1、.82、20px、2em 等)
- 字符串(例如“/img/cutedog.png”,粗体,左,大写,...)
- 颜色(例如绿色,#fff,rgba(255,0,0,.5),...)
- 布尔值(真,假)
- 无效的
- 列表
$font-size : 10px 12px 16px; // list of font-size
$image-file : photo_01, photo_02, photo_03 // list of image-file
// can also use this way - ruby sass
// it iterates from index 1 in sass(*** not 0)
nth(10px 12px 16px, 2); // 2nd value of $font-size is 12px
nth([line1, line2, line3], -1); // if it's negative, it iterates from right to left. Therefore, -1 of $image-file is line3
- 地图
$font-weights: ("regular": 400, "medium": 500, "bold": 700); // map of font-weights. (key-value pair)
// use this way - ruby sass
map-get($font-weights, "medium"); // 500
map-get($font-weights, "extra-bold"); // null
关于 List 和 Map 的更多信息
列表
// You can declare value of list using , or whitespace
$sizes: 40px, 50px, 80px;
// above code works the same with $sizes: 40px 50px 80px;
$valid-sides: top, bottom, left, right;
*** 列表索引从 1 开始
内置列表功能
append(list,value,[s]):向列表添加值的函数。index(list, value):返回列表值索引的函数。nth(list, n):返回列表索引值的函数。示例
// Scss
$valid-sides: left, center, right;
.screen-box {
text-align : nth($valid-sides, 1);
}
/* CSS */
.screen-box {
text-align: left;
}
地图
Map 将值保存为括号 () 内的键:值对。键必须是唯一的!
内置地图功能
map-get(map, key):返回其键的值的函数。map-get(map):返回 map 键的函数map-values(map):返回 map 值的函数示例
// Scss
$font-sizes: ("h1": 45px, "h2": 19px, "p": 16px);
section {
h2 {
font-size : map-get($font-sizes, "h2");// 19px
}
}
map-get($font-size, "h3");// null
/* CSS */
section h2 {
font-size : 19px;
}
- 字符串和数字也具有函数。了解更多关于Sass 中的字符串函数的信息
范围
有局部变量和全局变量。
局部变数
.info{
// local variable
$line-normal : 1.34;
font-size : 15px;
line-height : $line-normal;
text-align : right;
span{
line-height : $line-normal;
}
}
全局变量
//Scss
// global variable
$font-p : 15px;
.main-box{
p {
font-size : $font-p;
}
a {
font-size : $font-p;
color : blue;
text-decoration : none;
}
}
.main-box p {
font-size: 15px;
}
.main-box a {
font-size: 15px;
color: blue;
text-decoration: none;
}
您还可以使用 !global 将局部变量变为全局变量。
$mycolor: #ffffff !global;
有关Sass 中的变量的更多信息
操作员
a < b:检查 a 是否小于 ba <= b:检查 a 是否与 b 相同或小于 ba > b:检查 a 是否大于 bea >= b:检查 a 是否大于 be 或与 b 相同
@debug 100 > 50; // true
@debug 10px < 17px; // true
@debug 96px >= 1in; // true
@debug 1000ms <= 1s; // true
错误:
如果它们都有单位,并且单位不同,则会导致错误。
但是!如果用数字比较,再用带单位的数字比较,则没问题。
示例
@debug 100px > 10s;
// Error: Incompatible units px and s
@debug 100 > 50px; // true
@debug 10px < 17; // true
// Not Error
a == b:检查 a 和 b 是否相同。a !== b:检查 a 和 be 是否不同。
例子
// number
@debug 1px == 1px; // true
@debug 1px != 1em; // true
@debug 1 != 1px; // true
@debug 96px == 1in; // true
// string
@debug "Poppins" == Poppins; // true
@debug "Open Sans" != "Roboto"; // true
// colour
@debug rgba(53, 187, 169, 1) == #35bba9; // true
@debug rgba(179, 115, 153, 0.5) != rgba(179, 115, 153, 0.8); // true
// list
@debug (5px 7px 10px) != (5px, 7px, 10px); // true
@debug (5px 7px 10px) != [5px 7px 10px]; // true
@debug (5px 7px 10px) == (5px 7px 10px); // true
a + ba - ba * ba / ba % b:a/b 的余数
@debug 10s + 15s; // 25s
@debug 1in - 10px; // 0.8958333333in
@debug 5px * 3px; // 15px*px
@debug 1in % 9px; // 0.0625in (1in == 96px)
错误
@debug 100px + 10s;
// Error: Incompatible units px and s.
@debug 100px / 2;
// 50px (Not Error)
字符串 a + b
如果有 + 运算符,且 a、b 均为字符串,则将 a、b 合并并返回合并后的字符串。
即使其中一个不是字符串,也会将它们全部转换为字符串并合并。
@debug "Helvetica" + " Neue"; // "Helvetica Neue"
@debug sans- + serif; // sans-serif
@debug sans - serif; // sans-serif
@debug "Elapsed time: " + 10s; // "Elapsed time: 10s";
@debug true + " is a boolean value"; // "true is a boolean value";
布尔值
not:如果为 true,则返回 false。如果为 false,则返回 true。and:当两者均为真时,返回 true。如果其中一个为假,则返回 false。or:如果两个都为 false,则返回 false。如果其中一个为 true,则返回 true。
@debug not true; // false
@debug not false; // true
@debug true and true; // true
@debug true and false; // false
@debug true or false; // true
@debug false or false; // false
 后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com
后端开发教程 - Java、Spring Boot 实战 - msg200.com